BMM BibleMapper.com Maps:
Isaiah 36-37; 2 Kings 18-19; 2 Chronicles 32
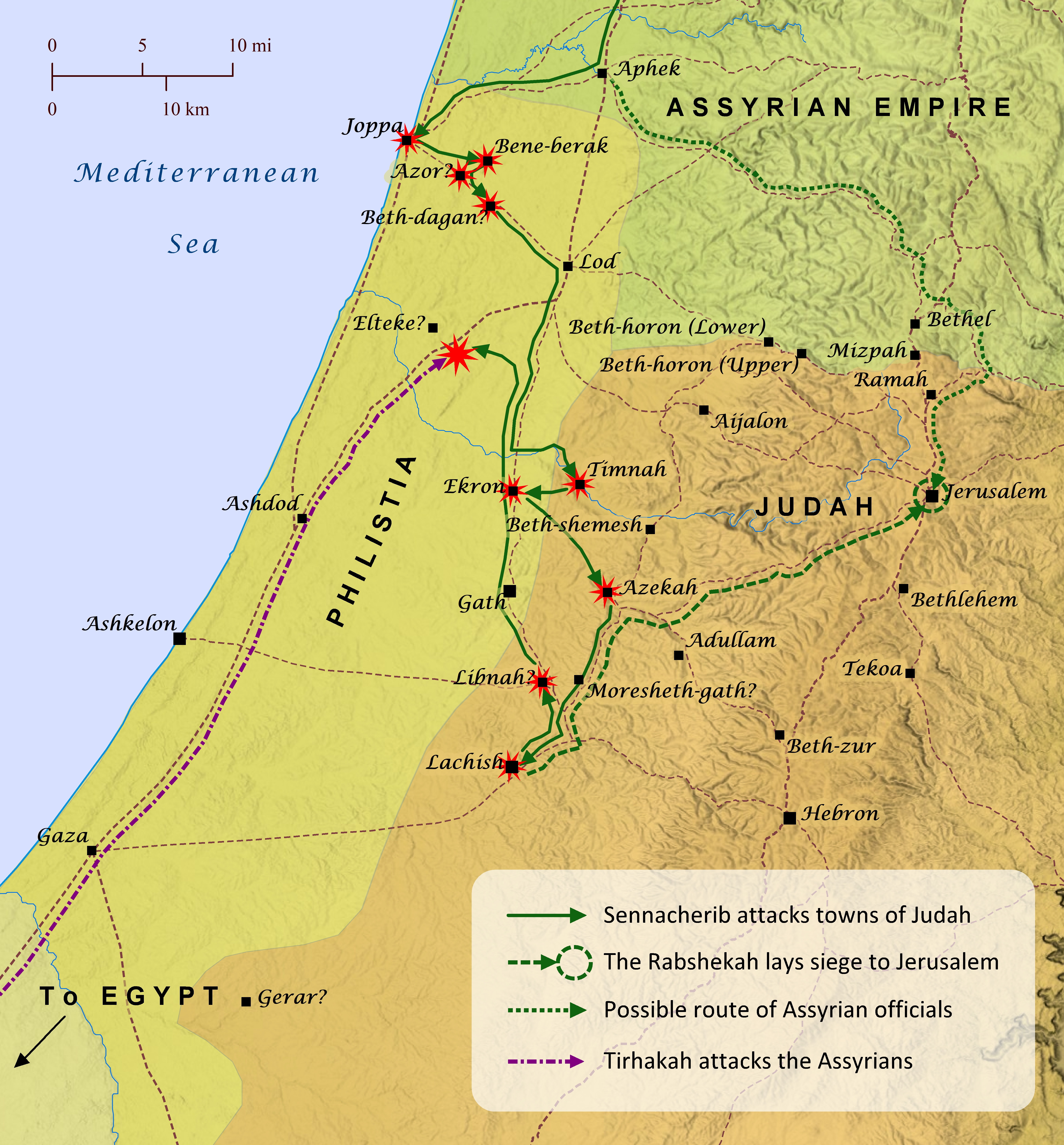
The harrowing experience of the attack on Judah by King Sennacherib of Assyria during Hezekiah’s reign is recorded by three different writers of Scripture and even by Sennacherib himself. Many scholars also suspect that this event formed the basis for Herodotus’s story regarding an army of mice eating the bow strings of the Assyrian army during their campaign against the Egyptians (Histories, 2.141). The origins of this event stretch back into the reign of Hezekiah’s father Ahaz, who enticed the Assyrians to attack Israel and Aram in exchange for making Judah a vassal of Assyria (2 Kings 16-17; 2 Chronicles 28; Isaiah 7-8; also see “The Final Days of the Northern Kingdom of Israel” map). Judah continued to be a vassal of Assyria through the early part of Hezekiah’s reign, but Hezekiah also quietly made extensive preparations to throw off the yoke of Assyria one day (2 Kings 18:1-12; 1 Chronicles 4:39-43; 2 Chronicles 29-31; also see “Hezekiah Strengthens Judah” map). Hezekiah also appears to have been hoping for support from Babylon and Egypt regarding his efforts to revolt against Assyria’s rule, but the prophet Isaiah warned Judah against placing their hopes in these foreign powers (Isaiah 30:1-5; 31:1-3; 39:1-8; 40:10-15; 2 Kings 20:12-19). After a few years spent quashing rebellion among the Babylonians, the Kassites, and the Medes in the east, Sennacherib turned his sights westward and began a campaign to subdue the various vassal nations that were refusing to submit to Assyria’s rule any longer. He first reconquered the Phoenician cities of Sidon and Tyre and then moved south to Philistia. He subdued Joppa, Beth-dagon, Bene-berak, and Azor and then moved to capture the cities of the Shephelah, which guarded the entrances to the valleys leading into the central hill country of Judah. While Sennacherib was attacking Lachish he sent his officers to demand Hezekiah’s surrender. This may be the Assyrian advance upon Jerusalem from the north described in Isaiah 10:28-32, but this is not certain (see “Assyria Advances on Jerusalem” map). Hezekiah sent officers back to Sennacherib with gold and silver taken from Temple and the royal treasury, but he would not surrender. The officers then traveled to Libnah to meet with Sennacherib, for he gone to fight there by that time. In the meantime King Tirhakah of Cush, who was ruling over Egypt at this time, came to attack Sennacherib, so Sennacherib sent his officials back to Hezekiah with a message that Jerusalem would be taken if he resisted. Hezekiah laid the letter from the officials before the Lord and prayed, and the Lord sent word through the prophet Isaiah that Jerusalem would not be taken. Then that very night the angel of the Lord killed 185,000 Assyrian soldiers (probably those with Sennacherib fighting the Egyptians), and Sennacherib went back to Assyria. There while he was worshiping in the temple of Nisroch, Sennacherib’s sons killed him and fled to Ararat (see “Ararat” map).

