BMM BibleMapper.com Maps:
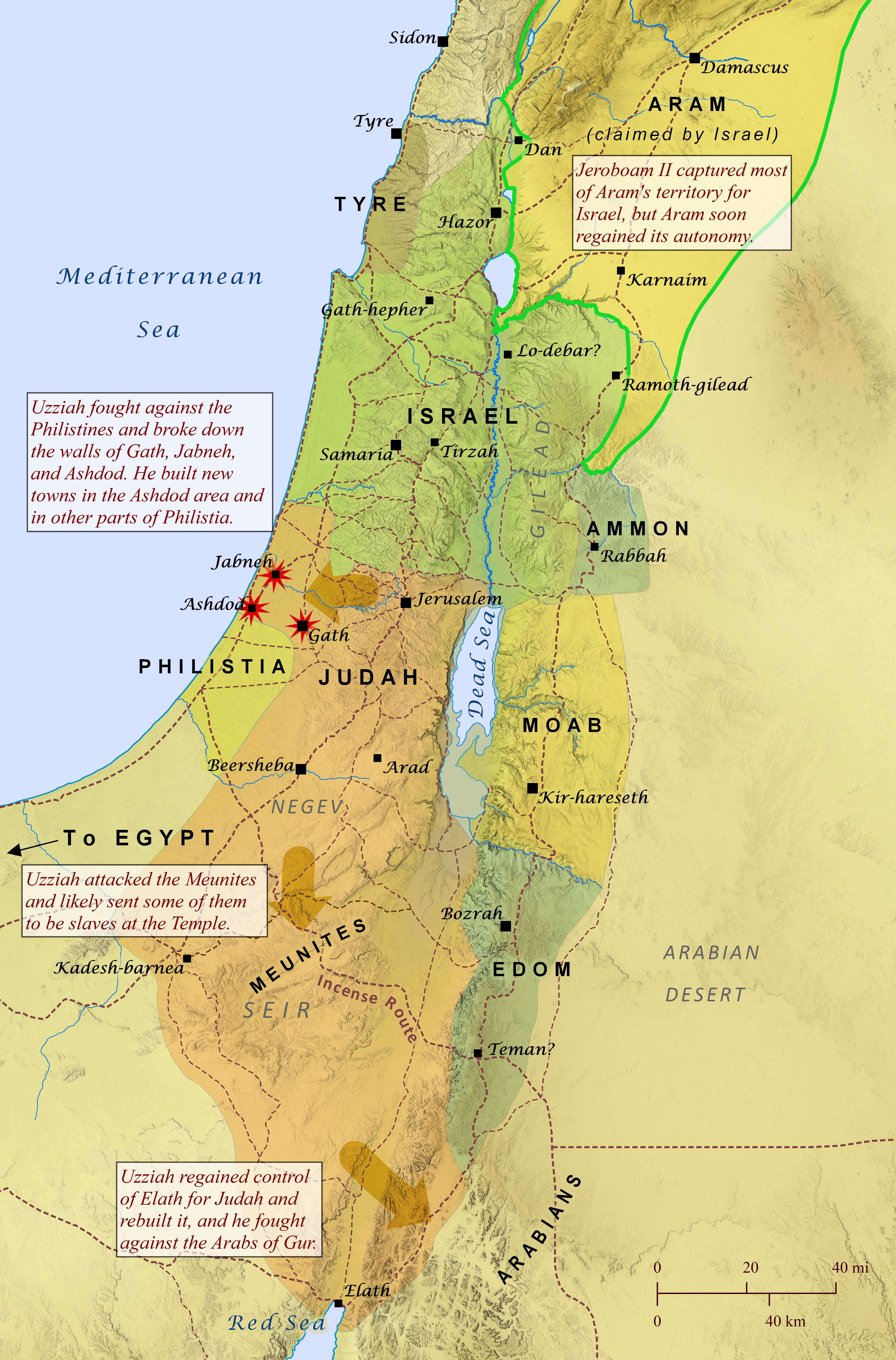
2 Kings 14:23-29; 15:1-7; 2 Chronicles 26
The long, concurrent reigns of Jeroboam II of Israel and Uzziah (also called Azariah) of Judah marked a period of resurgence after their nations had suffered nearly sixty years of decline and unrest. By the time both kings ascended to the throne in 793 B.C. and 792 B.C., Moab had revolted from Israel and seized land belonging to the tribe of Reuben (2 Kings 1:1; see “The Nation of Moab and the Tribe of Reuben”), and Edom and Libnah had revolted from Judah (2 Kings 8:16-24; 2 Chronicles 21:1-11; see “Edom and Libnah Revolt”). Jehu then brutally overthrew Ahab’s dynasty, but he later suffered the loss of all Gilead to the rising power of Aram (2 Kings 1:1; 3:1-27; 8:12; 10:32-33; 2 Chronicles 21:8-10; see “Aram Captures Gilead”). Soon after this, however, the Assyrian king Adad-nirari III (who may be the “savior” of 2 Kings 13:5) attacked Aram, but then he withdrew, thus creating a power vacuum to the north. Jeroboam of Israel took advantage of this opportunity and captured much of Aram, though it is unclear how firmly he held Aram or for how long. During this same time, king Uzziah of Judah captured the Red Sea port city of Elath in the far south, which belonged to Edom, and he also attacked the Arabs of Gur, who were likely located nearby. He also attacked the Meunites who lived in Seir, the formerly Edomite region south of the Judean Negev, though the Meunites themselves do not appear to have been Edomites. The Meunites are probably the same as the “Maonites” mentioned in Judges 10:12, and they also joined the Moabite alliance that attacked king Jehoshaphat of Judah (2 Chronicles 20). About a century after Uzziah’s time, during the reign of Hezekiah, some Simeonites attacked some Meunites in the Negev and seized their land (1 Chronicles 4:41-43). According to the Septuagint, the Meunites also paid Uzziah tribute (2 Chronicles 26:7-8), and Uzziah likely captured some of the Meunites and gave them as servants for the Temple of the Lord, which appears to have been a common practice in Israel since the time of Moses and Joshua (see Numbers 31:30; Joshua 9:27; Ezra 8:20). Their descendants are listed among the “Nethinim,” who served at the Temple during time of Ezra and Nehemiah (Ezra 2:50; Nehemiah 7:52). Uzziah also attacked the Philistine cities of Gath, Ashdod, and Jabneh and established other cities throughout Philistia. He built towers in Jerusalem at the Corner Gate, the Valley Gate, and the Angle as well as towers in the wilderness. He also dug many cisterns to store water for his large herds, both in the Shephelah (the foothills near Gath) and in the plain. He also had large farms and vineyards and strengthened Judah’s army. As far as moral leadership, the writer of Kings deems Jeroboam as a bad king for allowing idolatry to continue in Israel, but Uzziah is deemed as good, though he later sinned and was afflicted with leprosy for making an offering on the altar of incense.
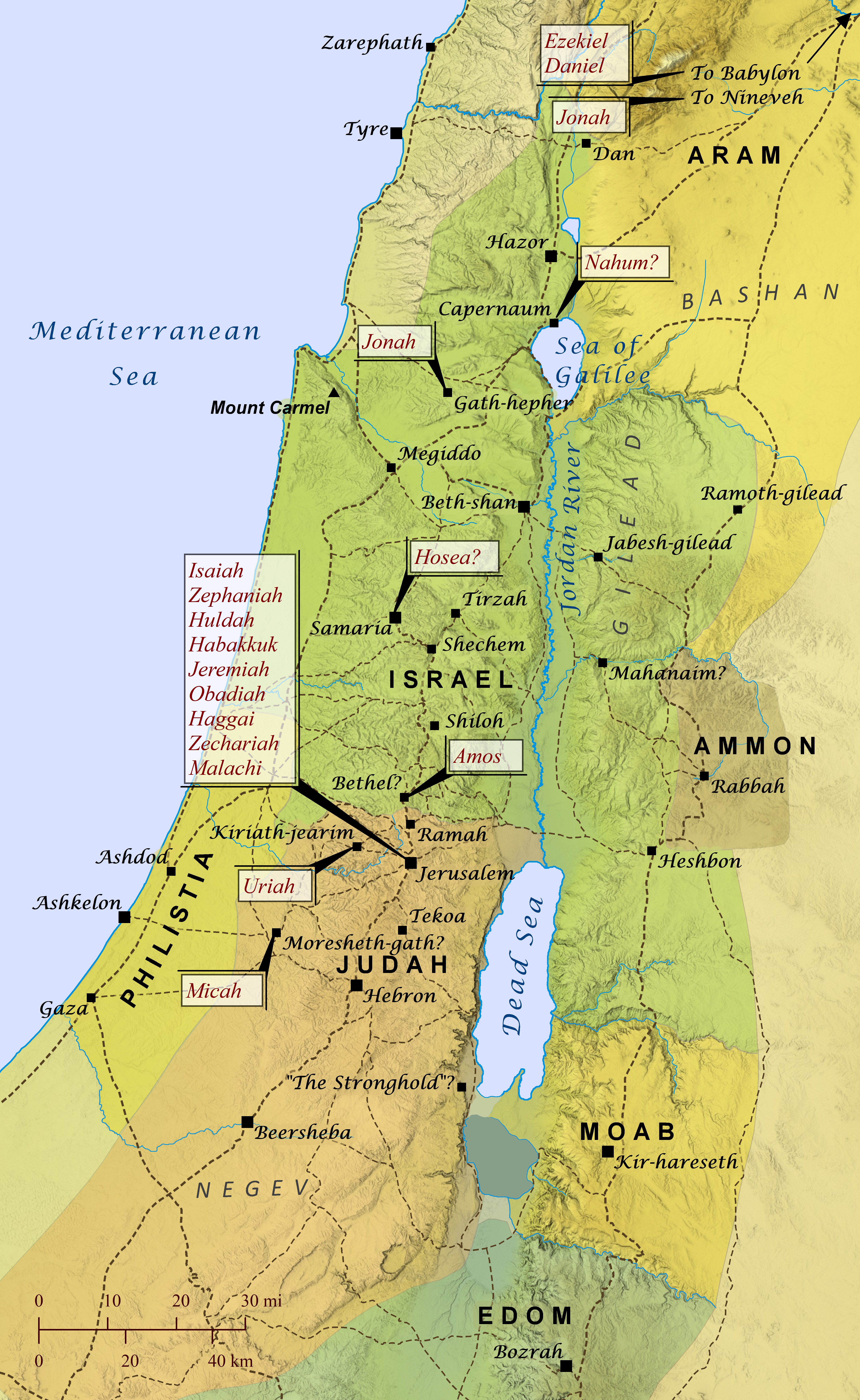
Prophets of the Old Testament after 800 B.C.
If you ask someone today what biblical prophets did, they will likely tell you that they divinely foretold of future events. While this was often the case, most prophets in the Bible focused as much on “forthtelling” God’s messages as they did on “foretelling” the future. That is, their primary role was to simply “forthtell” divinely acquired messages to leaders and groups of people, and at times that included foretelling of coming judgment, blessing, rescue, etc. Also, though plenty of prophets (sometimes called “seers” in Scripture) often spoke in confrontational or eccentric language that put them at odds with kings and religious leaders, the biblical writers also applied the term prophet to people who communicated God’s messages in ways that many readers today might not think of as prophecy, such as worship leaders appointed by David to “prophesy with lyres, harps, and cymbals” (1 Chronicles 25:1). Similarly, the books of Joshua, Judges, 1 & 2 Samuel, and 1 & 2 Kings are typically categorized as history by Christians, but in the Hebrew canon they belong to the category of Former Prophets. The Lord raised up prophets throughout all of biblical history, from the giving of the law under Moses to the revelation of the last days by the apostle John, and the kings of Israel and Judah often recognized and supported specific people as official prophets of the royal court and consulted them to find out God’s perspective about official matters. Following is a list of nearly everyone designated as prophet or seer in the Old Testament and the primary area of their ministry.
• Zechariah (796 B.C.) [2 Chronicles 24:20] => Jerusalem
• Jonah (780 B.C.) [2 Kings 14:25; Jonah 1:1] => Gath-hepher, Nineveh
• Hosea (770 B.C.) [Hosea 1:1] => Samaria?
• Amos (760 B.C.) [Amos 1:1] => Bethel
• Isaiah (730 B.C.) [2 Kings 19:2; 20:1; 2 Chronicles 26:22; 32:20, 32; Isaiah 1:1] => Jerusalem
• Micah (730 B.C.) [Jeremiah 26:18; Micah 1:1] => Moresheth
• Nahum (650 B.C.) [Nahum 1:1] => Elkosh (Capernaum?)
• Zephaniah (630 B.C.) [Zephaniah 1:1] => Jerusalem?
• Huldah (630 B.C.) [2 Kings 22:14] => Jerusalem
• Habakkuk (600 B.C.) [Habakkuk 1:1; 3:1] => Jerusalem?
• Ezekiel (592 B.C.) [Ezekiel 1:3] => Babylonia/Chebar River
• Uriah (600 B.C.) [Jeremiah 26:20] => Kiriath-jearim
• Jeremiah (587 B.C.) [2 Chronicles 36:12; Jeremiah 1:1; 19:14] => Jerusalem
• Obadiah (586 B.C.) [Obadiah 1:1] => Jerusalem
• Daniel (560 B.C.) [Daniel 7:1; Matthew 24:15] => Babylon
• Haggai (520 B.C.) [Ezra 5:1; Haggai 1:1] => Jerusalem
• Zechariah (520 B.C.) [Ezra 5:1; Zechariah 1:1] => Jerusalem
• Malachi (432 B.C.) [Malachi 1:1] => Jerusalem?


