Readers’ Version
Literal Version
11:1 Shelomoh turns from God
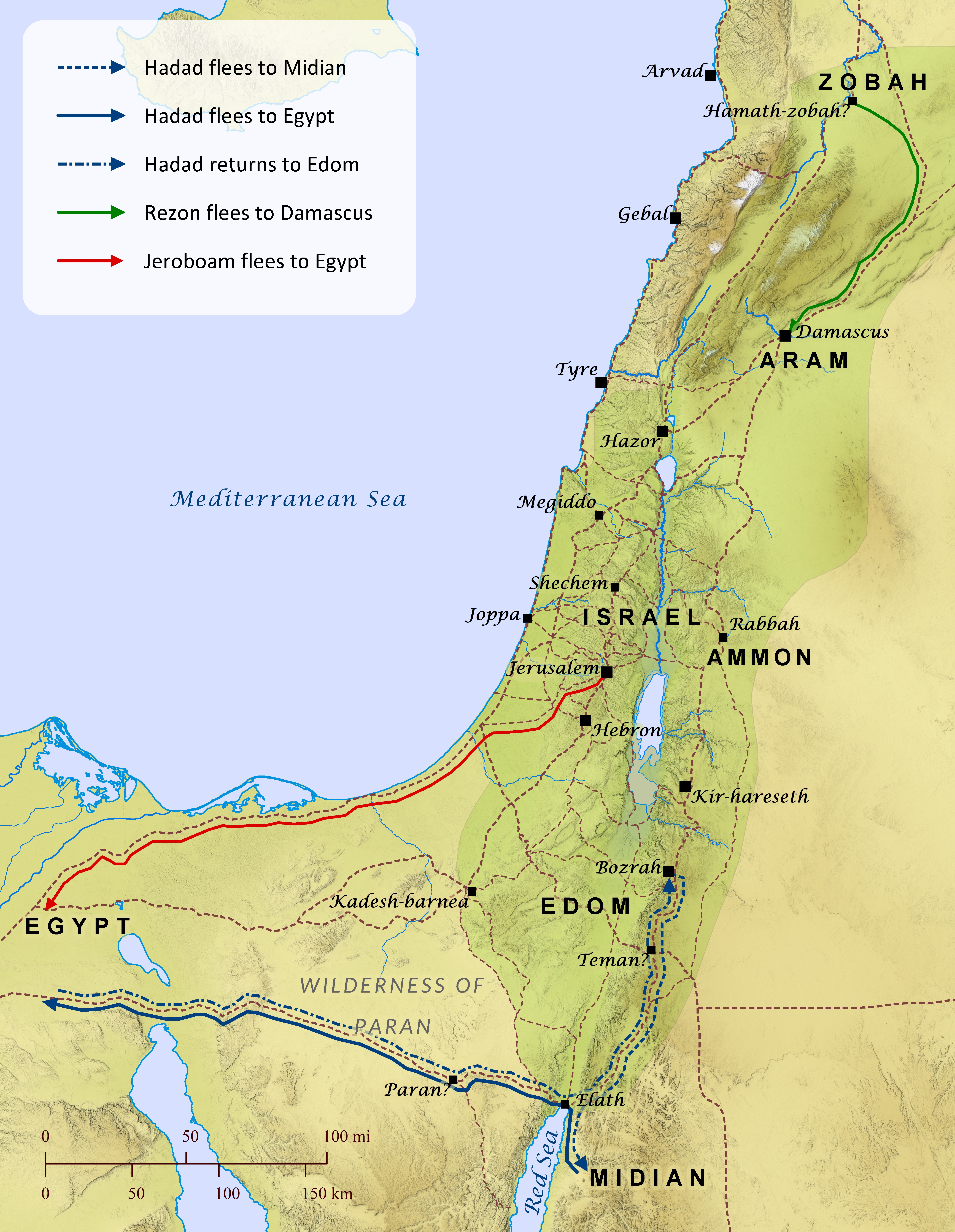
11 Now King Shelomoh loved many foreign women—besides Far-oh’s daughter there were Moabite women, Ammonite women, Edomite women, Sidonian women, and Hittite women.[ref] 2 They were from the nations that Yahweh had told Yisrael about, “You must not mix with people from those nations, and they must not join together with you. They will certainly entice you to worship their gods.” However, Shelomoh clung to them for love.[ref] 3 He had seven hundred wives who were kings’ daughters, as well as three hundred slave-wives, and his wives were instrumental in his turning away from Yahweh. 4 By the time of his old age, Shelomoh’s wives had persuaded him to worship the gods from their countries—his heart wasn’t totally dedicated to Yahweh like his father David had been. 5 So Shelomoh started to worship the Tsidonians’ God Ashtoret and the Ammonites’ detestable God Milkom, 6 so he did many things that Yahweh had said were evil—he didn’t remain fully committed to Yahweh like his father David had been. 7 Then Shelomoh built a place to worship Kemosh, the Moabites detestable God, on a hill facing Yerushalem, and also for Molek, the Ammonites’ detestable God. 8 He did those things for his foreign wives who were burning incense and sacrificing to their gods.
9 Although Yisrael’s god Yahweh had appeared twice to Shelomoh, he now turned his devotion away from Yahweh, who then became angry with him. 10 Yahweh had warned Shelomoh not to follow after other gods, but he didn’t obey Yahweh’s instructions, 11 and Yahweh told him, “You have this against you: you haven’t kept my agreement and you’ve disobeyed my statutes that I gave you. So I’ll definitely tear the kingdom away from you and give it to your servant, 12 except that for the sake of your father David I won’t do it in your lifetime, rather, I’ll tear the kingdom away from your son. 13 What’s more, I won’t tear the whole kingdom away—I’ll leave one tribe for your son to rule for my servant David’s sake, and for the sake of my chosen city Yerushalem.”
2 From the_nations which he_had_said YHWH to the_people_of Yisrāʼēl/(Israel) not you(pl)_must_go in/among_them and_they not they_will_go in/on/at/with_you(pl) truly they_will_turn_aside DOM heart_of_your(pl) after gods_of_their (is)_in_them Shəlomoh he_cleaved in_love.
3 And_he/it_was to_him/it wives noble_ladies seven hundred(s) and_concubines three hundred(s) wives_of_his and_turned_away DOM his/its_heart.
4 And_he/it_was at_time_of the_old_age_of Shəlomoh wives_of_his they_turned_aside DOM heart_of_his after gods other and_not it_was heart_of_his complete with YHWH his/its_god as_heart_of Dāvid his/its_father.
5 And_ Shəlomoh/(Solomon) _he/it_went after Astarte the_god_of the_Tsīdonī/(Sidonians) and_after Malkām the_detestable_thing_of the_ˊAmmōnī.
6 And_ Shəlomoh _he/it_made the_evil in/on_both_eyes_of YHWH and_not he_filled after YHWH as_Dāvid his/its_father.
7 then Shəlomoh he_built a_high_place for_Kəmōsh/(Chemosh) the_detestable_thing_of Mōʼāⱱ in/on/at/with_mountain which is_on the_face_of Yərūshālam/(Jerusalem) and_for_Molek the_detestable_thing_of the_people_of ˊAmmōn.
8 And_thus/so/as_follows he_did to/from_all/each/any/every wives_of_his the_foreign who_made_smoke and_sacrificed to_gods_of_their.
9 And_ YHWH _angry in/on/at/with_Shəlomoh if/because heart_of_his it_had_turned_aside from_with YHWH the_god_of Yisrāʼēl/(Israel) the_appeared to_him/it two_times.
10 And_commanded to_him/it on the_matter the_this to_not to_walk after gods other and_not he_observed DOM that_which he_had_commanded YHWH.
11 and_ YHWH _he/it_said to_Shəlomoh because that it_has_been this with_you and_not you_have_observed covenant_of_my and_regulations_of_my which I_commanded to_you certainly_(tear) I_will_tear_away DOM the_kingdom from_on_you and_give_it to_servant_of_your.
12 Only in/on/at/with_lifetime_of_your not do_it for_the_sake_of Dāvid I_will_show_you(ms) out_of_hand_of son_of_your tear_it.
13 Only DOM all_of the_kingdom not I_will_tear_away a_tribe one I_will_give to_son_of_your for_the_sake_of Dāvid servant_of_my and_for_the_sake_of Yərūshālam/(Jerusalem) which I_have_chosen.