Readers’ Version
Literal Version
16 In the fifth year of the reign of Ahab’s son Yoram as king of Yisrael, Yehoshafat’s son Yehoram became king of Yehudah. 17 He was thirty-two when he became king and he reigned from Yerushalem for eight years. 18 He followed in the evil ways of the kings of the northern kingdom of Yisrael, just as Ahab’s descendants had done, because he’d married one of Ahab’s daughters. He did what Yahweh had said was evil, 19 but Yahweh wasn’t willing to destroy Yehudah, for the sake of his servant David—he’d promised David that his descendants would always rule Yehudah.
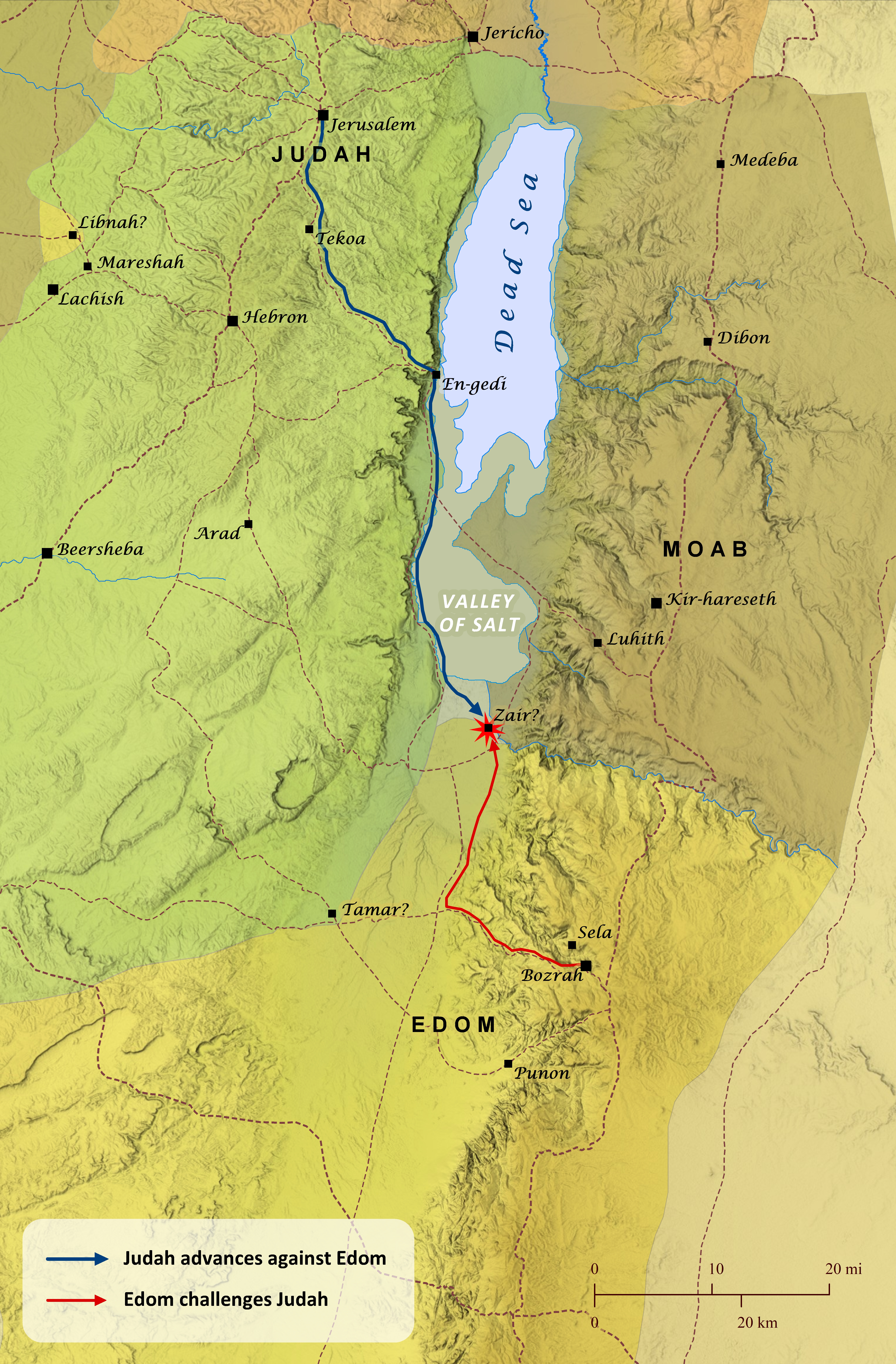
20 It was during King Yehoram’s time that Edom rebelled from Yehudah’s control, and they appointed their own king. 21 So Yehoram took his army and chariots and crossed the valley towards Zair in Edom. They attacked at night, but as the Edomite army and chariots started to surround them, they had to retreat back to their tents. 22 So Edom has been out from under the control of Yehudah to this day. Then Livnah revolted at the same time.
23 Everything else that Yehoram said and did is written in the book of the events of the kings of Yehudah. 24 Then Yehoram died and was buried with his ancestors in the city of David, and his son Ahazyah replaced him as king.
17 A_son_of thirty and_two year[s] he_was in/on/at/with_became_king_he and_eight years[fn] he_reigned in/on/at/with_Yərūshālam/(Jerusalem).
18 And_he/it_went in/on/at/with_way_of the_kings_of Yisrāʼēl/(Israel) just_as they_had_done the_house_of ʼAḩʼāⱱ if/because the_daughter_of ʼAḩʼāⱱ she_had_become for_him/it to/for_(a)_woman and_he/it_made the_evil in/on_both_eyes_of YHWH.
19 And_not YHWH he_was_willing to_destroy DOM Yəhūdāh for_the_sake_of Dāvid servant_of_his just_as he_had_said to_him/it to_give to_him/it a_lamp to_sons_of_his all_of the_days.
20 In/on/at/with_days_of_his ʼEdōm it_rebelled from_under the_hand_of Yəhūdāh and_they_set_king over_their_own a_king.
21 And_he/it_passed_through Yəhōrām Zair_to and_all the_chariots with_him/it and_he/it_was he he_arose night and_attacked DOM ʼEdōm the_surrounded to_him/it and_DOM the_commanders_of the_chariot and_fled the_army to_tents_of_his/its.
22 And_ ʼEdōm _revolted from_under the_hand_of Yəhūdāh until the_day the_this then Liⱱnāh it_rebelled in/on/at/with_time the_same.
23 And_rest_of the_matters_of Yəhōrām/(Joram) and_all that he_did am_not are_they written on the_scroll_of the_matters_of the_days of_kings_of of_Yəhūdāh/(Judah).
24 And_ Yəhōrām _slept with fathers_of_his and_buried with fathers_of_his in/on/at/with_city_of Dāvid and_ ʼAḩazyāh _became_king son_of_his in_place_him.
8:17 OSHB variant note: שנה: (x-qere) ’שָׁנִ֔ים’: lemma_8141 n_0.1 morph_HNcfpa id_12jxp שָׁנִ֔ים