Open Bible Data Home About News OET Key
OET OET-RV OET-LV ULT UST BSB MSB BLB AICNT OEB WEBBE WMBB NET LSV FBV TCNT T4T LEB BBE Moff JPS Wymth ASV DRA YLT Drby RV SLT Wbstr KJB-1769 KJB-1611 Bshps Gnva Cvdl TNT Wycl SR-GNT UHB BrLXX BrTr Related Topics Parallel Interlinear Reference Dictionary Search
ParallelVerse GEN EXO LEV NUM DEU JOB JOS JDG RUTH 1 SAM 2 SAM PSA AMOS HOS 1 KI 2 KI 1 CHR 2 CHR PROV ECC SNG JOEL MIC ISA ZEP HAB JER LAM YNA (JNA) NAH OBA DAN EZE EZRA EST NEH HAG ZEC MAL LAO GES LES ESG DNG 2 PS TOB JDT WIS SIR BAR LJE PAZ SUS BEL MAN 1 MAC 2 MAC 3 MAC 4 MAC YHN (JHN) MARK MAT LUKE ACTs YAC (JAM) GAL 1 TH 2 TH 1 COR 2 COR ROM COL PHM EPH PHP 1 TIM TIT 1 PET 2 PET 2 TIM HEB YUD (JUD) 1 YHN (1 JHN) 2 YHN (2 JHN) 3 YHN (3 JHN) REV
Hab 1 V2 V3 V4 V5 V6 V7 V8 V9 V10 V11 V12 V13 V14 V15 V16 V17
Note: This view shows ‘verses’ which are not natural language units and hence sometimes only part of a sentence will be visible—click on any Bible version abbreviation down the left-hand side to see the verse in more of its context. Normally the OET discourages the reading of individual ‘verses’, but this view is only designed as a tool for doing comparisons of different translations—the older translations are further down the page (so you can read up from the bottom to trace the English translation history). The OET segments on this page are still very early looks into the unfinished texts of the Open English Translation of the Bible—please double-check these texts in advance before using in public.
Text critical issues=minor/spelling Clarity of original=clear Importance to us=normal (All still tentative.)
OET (OET-RV) Here is the message that the prophet Havakkuk (Habakkuk) saw:![]()
OET-LV The_oracle[fn][fn][fn][fn] which he_saw Ḩₐⱱaqqūq the_prophet.
1:1 OSHB note: We read one or more accents in L differently from BHQ.
1:1 OSHB note: Marks a place where we agree with BHQ against BHS in reading L.
1:1 OSHB note: Marks an anomalous form.
1:1 OSHB note: We read punctuation in L differently from BHS.![]()
UHB הַמַּשָׂא֙ אֲשֶׁ֣ר חָזָ֔ה חֲבַקּ֖וּק הַנָּבִֽיא׃ ‡
(hammasāʼ ʼₐsher ḩāzāh ḩₐⱱaqqūq hannāⱱiyʼ.)
Key: khaki:verbs.
Note: Automatic aligning of the OET-RV to the LV is done by some temporary software, hence the OET-RV alignments are incomplete (and may occasionally be wrong).
BrLXX ΤΟ λῆμμα ὃ εἶδεν Ἀμβακοὺμ ὁ προφήτης.
(TO laʸmma ho eiden Ambakoum ho profaʸtaʸs. )
BrTr The burden which the prophet Ambacum saw.
ULT The message that Habakkuk the prophet received,
UST This is the conversation between Habakkuk the prophet and Yahweh.
BSB [This is] the burden that Habakkuk the prophet received in a vision:
MSB (Same as BSB above)
OEB The message seen by the prophet Habakkuk.
WEBBE The revelation which Habakkuk the prophet saw.
WMBB (Same as above)
NET The following is the message which God revealed to Habakkuk the prophet:
LSV The burden that Habakkuk the prophet has seen:
FBV This is the message that Habakkuk saw in vision.
T4T I am Habakkuk, a prophet. This is the message that Yahweh gave to me in a vision.
LEB No LEB HAB 1:1 verse available
BBE The word which Habakkuk the prophet saw.
Moff The oracle, the vision of the prophet Habakkuk.
¶
JPS THE BURDEN which Habakkuk the prophet did see.
ASV The burden which Habakkuk the prophet did see.
DRA The burden that Habacuc the prophet saw.
YLT The burden that Habakkuk the prophet hath seen:
Drby The burden which Habakkuk the prophet did see.
RV The burden which Habakkuk the prophet did see.
SLT The lifting up which Habbakuk the prophet saw.
Wbstr The burden which Habakkuk the prophet saw.
KJB-1769 The burden which Habakkuk the prophet did see.
KJB-1611 ¶ The burden which Habakkuk ye Prophet did see.
(Modernised spelling is same as from KJB-1769 above, apart from capitalisation and punctuation)
Bshps The burde which Habacuc the prophete dyd see.
(The burde which Habacuc the prophet did see.)
Gnva The burden, which Habakkuk the Prophet did see.
Cvdl This is the heuy burthe, which the prophet Abacuc dyd se.
(This is the heavy burden, which the prophet Abacuc did see.)
Wycl The birthun that Abacuk, the profete, sai.
(The burden that Abacuk, the prophet, sai.)
Luth Dies ist die Last, welche der Prophet Habakuk gesehen hat.
(This/These is the Last, which the/of_the Prophet Habakuk seen has.)
ClVg Onus quod vidit Habacuc propheta.
(Burden that he_saw Habacuc a_prophet. )
1:1 The word message (or oracle) identifies the book as God’s revelation through his prophet (cp. Nah 1:1; Mal 1:1).
Note 1 topic: figures-of-speech / explicit
(Occurrence 0) The message that Habakkuk the prophet received,
(Some words not found in UHB: the,oracle which/who saw Ḩₐⱱaqqūq the,prophet )
These words introduce the first two chapters of the book. It is implicit that Habakkuk received this message from Yahweh. This can be stated as a complete sentence. Alternate translation: “This is the message that Habakkuk the prophet received from Yahweh.”
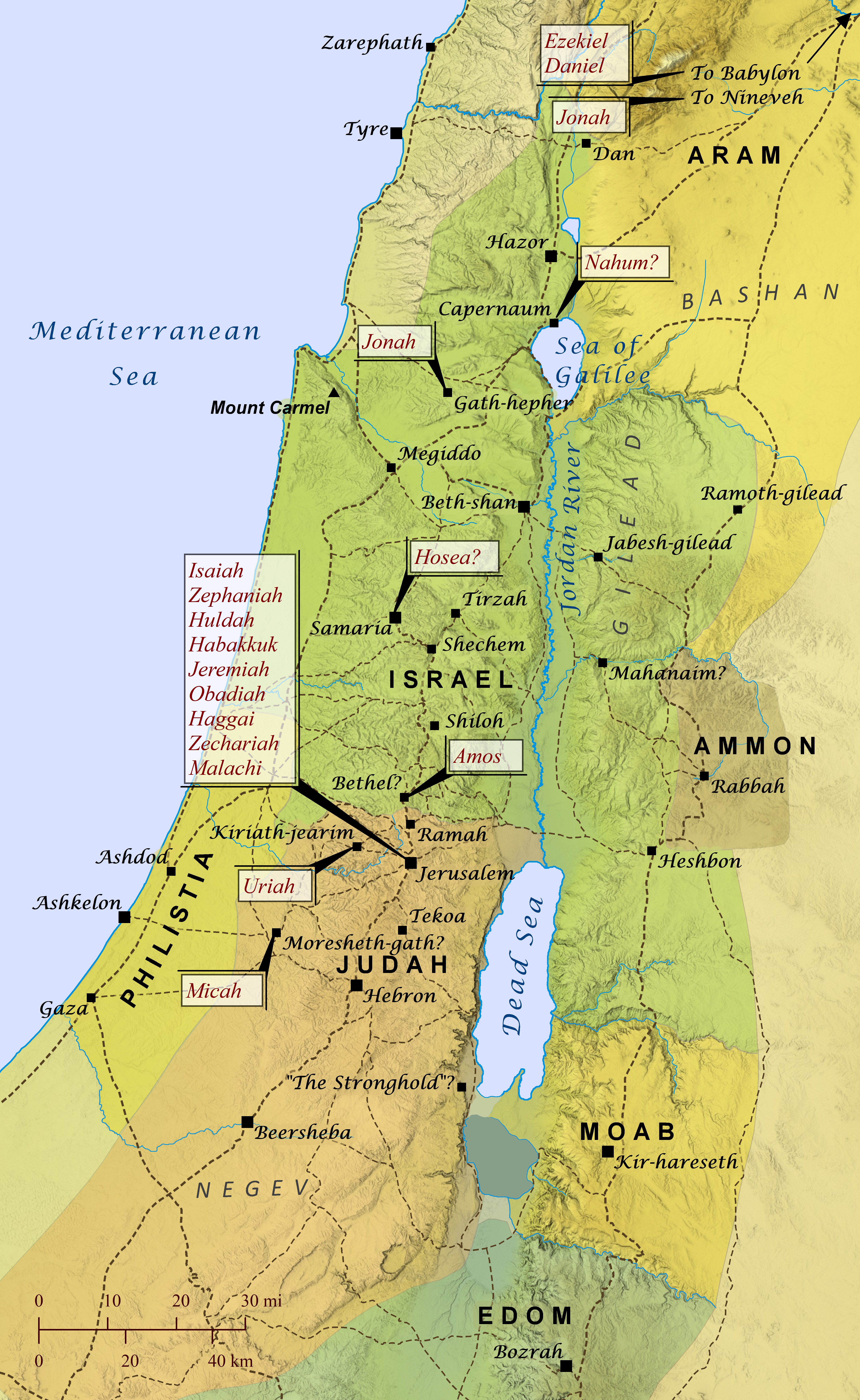
If you ask someone today what biblical prophets did, they will likely tell you that they divinely foretold of future events. While this was often the case, most prophets in the Bible focused as much on “forthtelling” God’s messages as they did on “foretelling” the future. That is, their primary role was to simply “forthtell” divinely acquired messages to leaders and groups of people, and at times that included foretelling of coming judgment, blessing, rescue, etc. Also, though plenty of prophets (sometimes called “seers” in Scripture) often spoke in confrontational or eccentric language that put them at odds with kings and religious leaders, the biblical writers also applied the term prophet to people who communicated God’s messages in ways that many readers today might not think of as prophecy, such as worship leaders appointed by David to “prophesy with lyres, harps, and cymbals” (1 Chronicles 25:1). Similarly, the books of Joshua, Judges, 1 & 2 Samuel, and 1 & 2 Kings are typically categorized as history by Christians, but in the Hebrew canon they belong to the category of Former Prophets. The Lord raised up prophets throughout all of biblical history, from the giving of the law under Moses to the revelation of the last days by the apostle John, and the kings of Israel and Judah often recognized and supported specific people as official prophets of the royal court and consulted them to find out God’s perspective about official matters. Following is a list of nearly everyone designated as prophet or seer in the Old Testament and the primary area of their ministry.
• Zechariah (796 B.C.) [2 Chronicles 24:20] => Jerusalem
• Jonah (780 B.C.) [2 Kings 14:25; Jonah 1:1] => Gath-hepher, Nineveh
• Hosea (770 B.C.) [Hosea 1:1] => Samaria?
• Amos (760 B.C.) [Amos 1:1] => Bethel
• Isaiah (730 B.C.) [2 Kings 19:2; 20:1; 2 Chronicles 26:22; 32:20, 32; Isaiah 1:1] => Jerusalem
• Micah (730 B.C.) [Jeremiah 26:18; Micah 1:1] => Moresheth
• Nahum (650 B.C.) [Nahum 1:1] => Elkosh (Capernaum?)
• Zephaniah (630 B.C.) [Zephaniah 1:1] => Jerusalem?
• Huldah (630 B.C.) [2 Kings 22:14] => Jerusalem
• Habakkuk (600 B.C.) [Habakkuk 1:1; 3:1] => Jerusalem?
• Ezekiel (592 B.C.) [Ezekiel 1:3] => Babylonia/Chebar River
• Uriah (600 B.C.) [Jeremiah 26:20] => Kiriath-jearim
• Jeremiah (587 B.C.) [2 Chronicles 36:12; Jeremiah 1:1; 19:14] => Jerusalem
• Obadiah (586 B.C.) [Obadiah 1:1] => Jerusalem
• Daniel (560 B.C.) [Daniel 7:1; Matthew 24:15] => Babylon
• Haggai (520 B.C.) [Ezra 5:1; Haggai 1:1] => Jerusalem
• Zechariah (520 B.C.) [Ezra 5:1; Zechariah 1:1] => Jerusalem
• Malachi (432 B.C.) [Malachi 1:1] => Jerusalem?