Open Bible Data Home About News OET Key
OET OET-RV OET-LV ULT UST BSB MSB BLB AICNT OEB WEBBE WMBB NET LSV FBV TCNT T4T LEB BBE Moff JPS Wymth ASV DRA YLT Drby RV SLT Wbstr KJB-1769 KJB-1611 Bshps Gnva Cvdl TNT Wycl SR-GNT UHB BrLXX BrTr Related Topics Parallel Interlinear Reference Dictionary Search
ParallelVerse GEN EXO LEV NUM DEU JOB JOS JDG RUTH 1 SAM 2 SAM PSA AMOS HOS 1 KI 2 KI 1 CHR 2 CHR PROV ECC SNG JOEL MIC ISA ZEP HAB JER LAM YNA (JNA) NAH OBA DAN EZE EZRA EST NEH HAG ZEC MAL LAO GES LES ESG DNG 2 PS TOB JDT WIS SIR BAR LJE PAZ SUS BEL MAN 1 MAC 2 MAC 3 MAC 4 MAC YHN (JHN) MARK MAT LUKE ACTs YAC (JAM) GAL 1 TH 2 TH 1 COR 2 COR ROM COL PHM EPH PHP 1 TIM TIT 1 PET 2 PET 2 TIM HEB YUD (JUD) 1 YHN (1 JHN) 2 YHN (2 JHN) 3 YHN (3 JHN) REV
Ezra Intro C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 C9 C10
Ezra 2 V1 V4 V7 V10 V13 V16 V19 V22 V25 V28 V31 V34 V37 V40 V43 V46 V49 V55 V58 V61 V64 V67 V70
Note: This view shows ‘verses’ which are not natural language units and hence sometimes only part of a sentence will be visible—click on any Bible version abbreviation down the left-hand side to see the verse in more of its context. Normally the OET discourages the reading of individual ‘verses’, but this view is only designed as a tool for doing comparisons of different translations—the older translations are further down the page (so you can read up from the bottom to trace the English translation history). The OET segments on this page are still very early looks into the unfinished texts of the Open English Translation of the Bible—please double-check these texts in advance before using in public.
Text critical issues=none Clarity of original=clear Importance to us=normal (All still tentative.)
OET (OET-RV) • the descendants of Bazlut, Mehida, and Harsha,![]()
OET-LV The_descendants_of Baʦlūt the_descendants_of Məḩīdāʼ the_descendants_of Ḩarshāʼ.
![]()
UHB בְּנֵי־בַצְל֥וּת בְּנֵי־מְחִידָ֖א בְּנֵ֥י חַרְשָֽׁא׃ ‡
(bənēy-ⱱaʦlūt bənēy-məḩīdāʼ bənēy ḩarshāʼ.)
Key: .
Note: Automatic aligning of the OET-RV to the LV is done by some temporary software, hence the OET-RV alignments are incomplete (and may occasionally be wrong).
BrLXX υἱοὶ Βασαλὼθ, υἱοὶ Μαουδὰ, υἱοὶ Ἀρσὰ,
(huioi Basalōth, huioi Maouda, huioi Arsa, )
BrTr the children of Basaloth, the children of Mauda, the children of Arsa,
ULT the sons of Bazluth, the sons of Mehida, the sons of Harsha,
UST Bazluth, Mehida, Harsha,
BSB • the descendants of Bazluth,[fn]
• the descendants of Mehida,
• the descendants of Harsha,
2:52 Bazluth is a variant of Bazlith; see Nehemiah 7:54.
MSB (Same as BSB above including footnotes)
OEB No OEB EZRA book available
WEBBE the children of Bazluth, the children of Mehida, the children of Harsha,
WMBB (Same as above)
NET the descendants of Bazluth, the descendants of Mehida, the descendants of Harsha,
LSV sons of Bazluth, sons of Mehida, sons of Harsha,
FBV Bazluth, Mehida, Harsha,
T4T • Bazluth, Mehida, Harsha,
LEB the descendants[fn] of Bazluth, the descendants[fn] of Mehida, the descendants[fn] of Harsha,
BBE The children of Bazluth, the children of Mehida, the children of Harsha,
Moff Bazluth, Mehida, Harsha,
JPS the children of Bazluth, the children of Mehida, the children of Harsha;
ASV the children of Bazluth, the children of Mehida, the children of Harsha,
DRA The children of Besluth, the children of Mahida, the children of Harsa,
YLT Sons of Bazluth, sons of Mehida, sons of Harsha,
Drby the children of Bazluth, the children of Mehida, the children of Harsha,
RV the children of Bazluth, the children of Mehida, the children of Harsha;
SLT The sons of Bazluth, the sons of Mehida, the sons of Harsha,
Wbstr The children of Bazluth, the children of Mehida, the children of Harsha,
KJB-1769 The children of Bazluth, the children of Mehida, the children of Harsha,[fn]
2.52 Bazluth: also called, Bazlith
KJB-1611 [fn]The children of Bazluth, the children of Mehida, the children of Harsha,
(Same as from KJB-1769 above apart from footnotes)
2:52 Or, Bazlith, in Nehem.
Bshps The children of Bazluth, the children of Mehida, the children of Harsa,
Gnva The sonnes of Bazluth, the sonnes of Mehida, the sonnes of Harsha,
(The sons of Bazluth, the sons of Mehida, the sons of Harsha, )
Cvdl ye childre of Hazeluth, ye childre of Mehira, the children of Harsa,
(ye/you_all children of Hazeluth, ye/you_all children of Mehira, the children of Harsa,)
Wycl sones of Maida, sones of Arsa,
(sons of Maida, sons of Arsa,)
Luth die Kinder Bazeluth, die Kinder Mehida, die Kinder Harsa,
(the children Bazeluth, the children Mehida, the children Harsa,)
ClVg filii Besluth, filii Mahida, filii Harsa,
(children Besluth, children Mahida, children Harsa, )
2:1-70 This chapter is the first of Ezra’s major digressions from the main story line. The returning exiles needed to keep track of who the true Jews were so that the community could maintain its identity (by knowing whom they could marry) and theological purity (by knowing who could worship at the Temple). This list is not an initial list (cp. Neh 7:6-73) of all the Jews who returned to Jerusalem but a slightly later list (after Sheshbazzar had died) of people who had settled in their towns.
Note 1 topic: figures-of-speech / metaphor
בְּנֵי־בַצְל֥וּת בְּנֵי־מְחִידָ֖א בְּנֵ֥י חַרְשָֽׁא
sons_of Baʦlūt sons_of Məḩīdāʼ sons_of Ḩarshāʼ
Here, sons means descendants. If you continue the sentence from [2:43](../02/43.md), you can just list the names of these three men. Alternate translation: [Bazluth, Mehida, Harsha,]
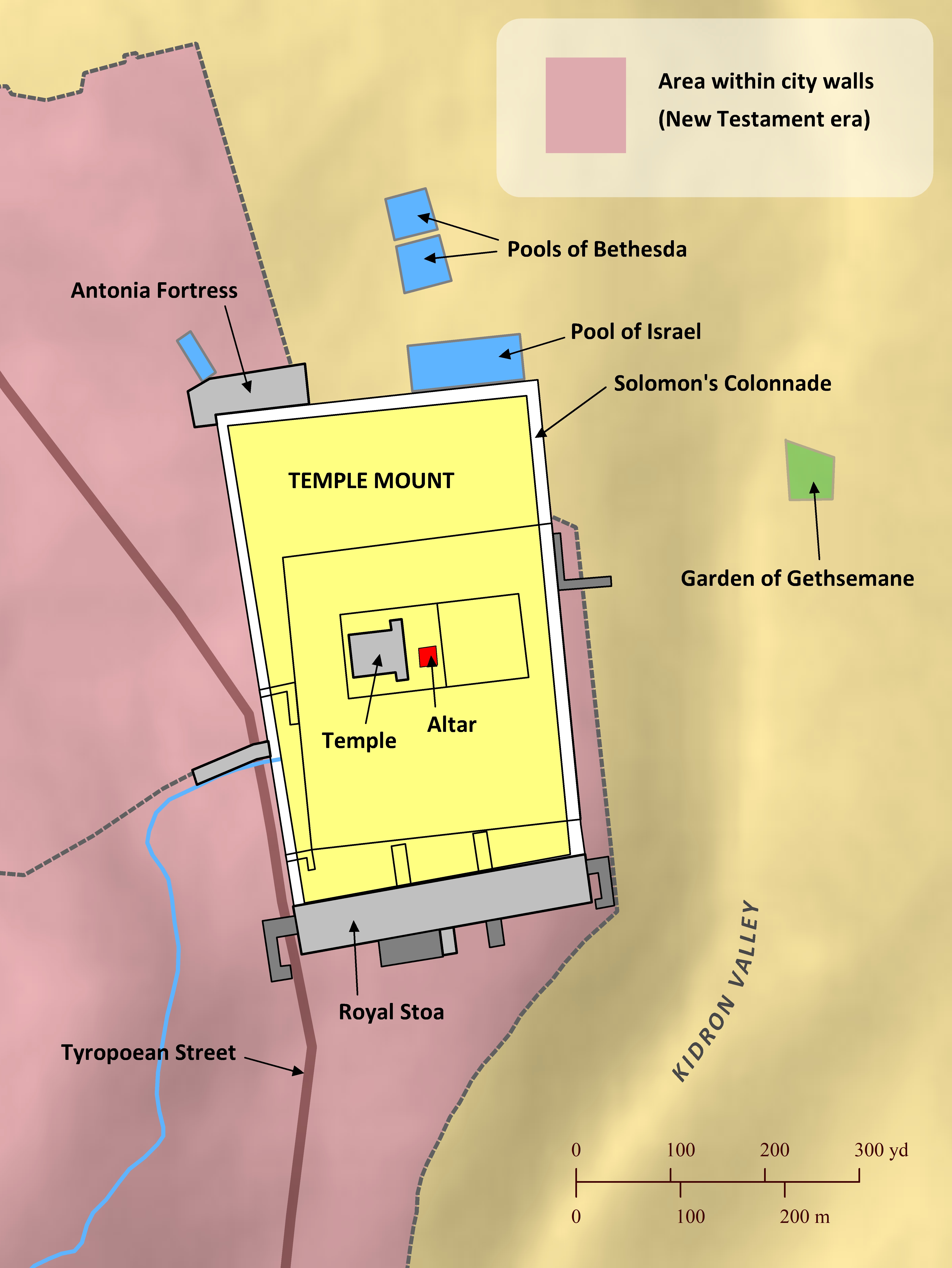
The Temple of the Lord in Jerusalem, where all Israelite males were commanded to offer sacrifices to the Lord (Exodus 23:14-19; Deuteronomy 16:16-17), underwent several stages of reconstruction and development over hundreds of years. The first Temple was built by King Solomon to replace the aging Tabernacle, and it was constructed on a threshing floor on high ground on the north side of the city (2 Samuel 24; 1 Chronicles 21). Hundreds of years later King Hezekiah expanded the platform surrounding the Temple. When Jerusalem fell to the Babylonians in 586 B.C., the Temple was completely destroyed (2 Kings 25:1-21; 2 Chronicles 36:17-21; Jeremiah 39:1-10; 52:1-30). It was rebuilt in 515 B.C. after a group of Jews returned to Judea from exile in Babylon (Ezra 1:5-6:15; Nehemiah 7:5-65). Herod the Great completely rebuilt and expanded the Temple once again around 20 B.C., making it one of the largest temples in the Roman world. Jesus’ first believers often met together in Solomon’s Colonnade, a columned porch that encircled the Temple Mount, perhaps carrying on a tradition started by Jesus himself (John 10:23; Acts 3:11; 5:12). But Herod’s Temple did not last long: After many Jews revolted against Rome, the Romans eventually recaptured Jerusalem and destroyed the Temple in A.D. 70.