Open Bible Data Home About News OET Key
OET OET-RV OET-LV ULT UST BSB MSB BLB AICNT OEB WEBBE WMBB NET LSV FBV TCNT T4T LEB BBE Moff JPS Wymth ASV DRA YLT Drby RV SLT Wbstr KJB-1769 KJB-1611 Bshps Gnva Cvdl TNT Wycl SR-GNT UHB BrLXX BrTr Related Topics Parallel Interlinear Reference Dictionary Search
ParallelVerse GEN EXO LEV NUM DEU JOB JOS JDG RUTH 1 SAM 2 SAM PSA AMOS HOS 1 KI 2 KI 1 CHR 2 CHR PROV ECC SNG JOEL MIC ISA ZEP HAB JER LAM YNA (JNA) NAH OBA DAN EZE EZRA EST NEH HAG ZEC MAL LAO GES LES ESG DNG 2 PS TOB JDT WIS SIR BAR LJE PAZ SUS BEL MAN 1 MAC 2 MAC 3 MAC 4 MAC YHN (JHN) MARK MAT LUKE ACTs YAC (JAM) GAL 1 TH 2 TH 1 COR 2 COR ROM COL PHM EPH PHP 1 TIM TIT 1 PET 2 PET 2 TIM HEB YUD (JUD) 1 YHN (1 JHN) 2 YHN (2 JHN) 3 YHN (3 JHN) REV
Num Intro C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 C9 C10 C11 C12 C13 C14 C15 C16 C17 C18 C19 C20 C21 C22 C23 C24 C25 C26 C27 C28 C29 C30 C31 C32 C33 C34 C35 C36
Num 33 V1 V3 V5 V9 V11 V13 V15 V17 V19 V21 V23 V25 V27 V29 V31 V33 V35 V37 V39 V41 V43 V45 V47 V49 V51 V53 V55
Note: This view shows ‘verses’ which are not natural language units and hence sometimes only part of a sentence will be visible—click on any Bible version abbreviation down the left-hand side to see the verse in more of its context. Normally the OET discourages the reading of individual ‘verses’, but this view is only designed as a tool for doing comparisons of different translations—the older translations are further down the page (so you can read up from the bottom to trace the English translation history). The OET segments on this page are still very early looks into the unfinished texts of the Open English Translation of the Bible—please double-check these texts in advance before using in public.
Text critical issues=none Clarity of original=clear Importance to us=normal (All still tentative.)
OET-LV And_set_out from_Etham and_turned_back to Pi- hahiroth which is_on the_face_of Baˊal- Zephon and_camped to_(the)_face_of/in_front_of/before Migdōl.
![]()
UHB וַיִּסְעוּ֙ מֵֽאֵתָ֔ם וַיָּ֨שָׁב֙ עַל־פִּ֣י הַחִירֹ֔ת אֲשֶׁ֥ר עַל־פְּנֵ֖י בַּ֣עַל צְפ֑וֹן וַֽיַּחֲנ֖וּ לִפְנֵ֥י מִגְדֹּֽל׃ ‡
(vayyişˊū mēʼētām vayyāshāⱱ ˊal-piy haḩīrot ʼₐsher ˊal-pənēy baˊal ʦəfōn vayyaḩₐnū lifənēy migdol.)
Key: khaki:verbs.
Note: Automatic aligning of the OET-RV to the LV is done by some temporary software, hence the OET-RV alignments are incomplete (and may occasionally be wrong).
BrLXX Καὶ ἀπῇραν ἐκ Βουθὰν, καὶ παρενέβαλον ἐπὶ τὸ στόμα Εἰρὼθ, ὅ ἐστιν ἀπέναντι Βεελσεπφὼν, καὶ παρενέβαλον ἀπέναντι Μαγδώλου.
(Kai apaʸran ek Bouthan, kai parenebalon epi to stoma Eirōth, ho estin apenanti Beʼelsepfōn, kai parenebalon apenanti Magdōlou. )
BrTr And they departed from Buthan and encamped at the mouth of Iroth, which is opposite Beel-sepphon, and encamped opposite Magdol.
ULT And they set out from Etham and turned back to Pi Hahiroth, which is on the face of Baal Zephon, and they camped before the face of Migdol.
UST Then they left Etham and returned to Pi Hahiroth, to the east of Baal Zephon, and set up their tents near Migdol.
BSB • They set out from Etham and turned back to Pi-hahiroth, opposite Baal-zephon, and they camped near Migdol.
MSB (Same as BSB above)
OEB No OEB NUM book available
WEBBE They travelled from Etham, and turned back to Pihahiroth, which is before Baal Zephon, and they encamped before Migdol.
WMBB (Same as above)
NET They traveled from Etham, and turned again to Pi-hahiroth, which is before Baal-Zephon; and they camped before Migdal.
LSV And they journey from Etham and turn back over Pi-Hahiroth, which [is] on the front of Ba‘al-Zephon, and they encamp before Migdol.
FBV They moved on from Etham, turning back towards Pi-hahiroth, opposite Baal-zephon, and set up camp near Migdol.
T4T Then they/we left Etham and returned to Pi-Hahiroth, to the east of Baal-Zephon, and set up their/our tents near Migdol.
LEB Then they set out from Etham and returned to Pi-Hahiroth, which faces Baal Zephon, and they camped before Migdol.
BBE And from Etham, turning back to Pi-hahiroth which is before Baal-zephon, they put up their tents before Migdol.
Moff No Moff NUM book available
JPS And they journeyed from Etham, and turned back unto Pihahiroth, which is before Baal-zephon; and they pitched before Migdol.
ASV And they journeyed from Etham, and turned back unto Pi-hahiroth, which is before Baal-zephon: and they encamped before Migdol.
DRA Departing from thence they came over against Phihahiroth, which looketh towards Beelsephon, and they camped before Magdalum.
YLT and they journey from Etham, and turn back on Pi-Hahiroth, which [is] on the front of Baal-Zephon, and they encamp before Migdol.
Drby And they removed from Etham, and turned back to Pi-hahiroth, which is opposite Baal-Zephon, and encamped before Migdol.
RV And they journeyed from Etham, and turned back unto Pi-hahiroth, which is before Baal-zephon: and they pitched before Migdol.
SLT And they will remove from Etham, and dwell upon the mouth of Hiroth, which is before Baal-Zephon: and they will encamp before Migdol.
Wbstr And they removed from Etham, and turned again to Pi-hahiroth, which is before Baal-zephon: and they encamped before Migdol.
KJB-1769 And they removed from Etham, and turned again unto Pi-hahiroth, which is before Baal-zephon: and they pitched before Migdol.
KJB-1611 And they remoued from Etham, and turned againe vnto Pihahiroth, which is before Baal-zephon: and they pitched before Migdol.
(And they removed from Etham, and turned again unto Pihahiroth, which is before Baal-zephon: and they pitched before Migdol.)
Bshps And they remoued from Etham, and turned agayne vnto Pihairoth, which is before Baal Zephon: and they pitched before Migdol.
(And they removed from Etham, and turned again unto Pihairoth, which is before Baal Zephon: and they pitched before Migdol.)
Gnva And they remoued from Etham, and turned againe vnto Pi-hahiroth, which is before Baal-zephon, and pitched before Migdol.
(And they removed from Etham, and turned again unto Pi-hahiroth, which is before Baal-zephon, and pitched before Migdol. )
Cvdl Fro Etham they departed, and abode in the valley of Hiroth (which lyeth towarde Baal Zephon) & pitched ouer agaynst Migdol.
(From Etham they departed, and abode/stayed in the valley of Hiroth (which lieth/lies toward Baal Zephon) and pitched over against Migdol.)
Wycl and camen ayens Phiayroth, whiche biholdith Beelsephon, and settiden tentis bifor Magdalun.
(and came against Phiayroth, which beholdeth/beholds Beelsephon, and set/placed tents before Magdalun.)
Luth Von Etham zogen sie aus und blieben im Grunde Hiroth, welches liegt gegen Baal-Zephon, und lagerten sich gegen Migdol.
(From Etham pulled they/she/them out_of and remained in_the Grunde Hiroth, which lies(v) to/against Baal-Zephon, and stored itself/yourself/themselves to/against Migdol.)
ClVg Inde egressi venerunt contra Phihahiroth, quæ respicit Beelsephon, et castrametati sunt ante Magdalum.
(Inde having_gone_out they_came on_the_contrary Phihahiroth, which looks_back Beelsephon, and camped are before Magdalum. )
33:1-56 This review of the entire wilderness period contains the longest integrated list of place-names in the Old Testament, from Israel’s departure from Egypt (33:3; cp. Exod 12:37) until their arrival in the plains of Moab, opposite Jericho (Num 33:49; cp. 22:1). The forty-two way stations on this itinerary represent far more than a geographical journey; they recall Israel’s forty-year spiritual pilgrimage. In their travels between Rameses in Egypt (33:3) and AcaciaAbel-shittim on the plains of Moab (33:49), Israel finally became the people who could invade the land of Canaan and claim the promises God made to Abraham.
• This itinerary does not provide enough data to plot an accurate, specific route. Most of the places cannot be identified with certainty; many of the sites appear nowhere else in the Hebrew Bible, and there are not enough clues to pinpoint their locations precisely. Furthermore, this list is partial or selective, omitting some of the place-names mentioned earlier in the journey.
Numbers 13-14; 20-21; 33; Deuteronomy 1-2; 10:6-9
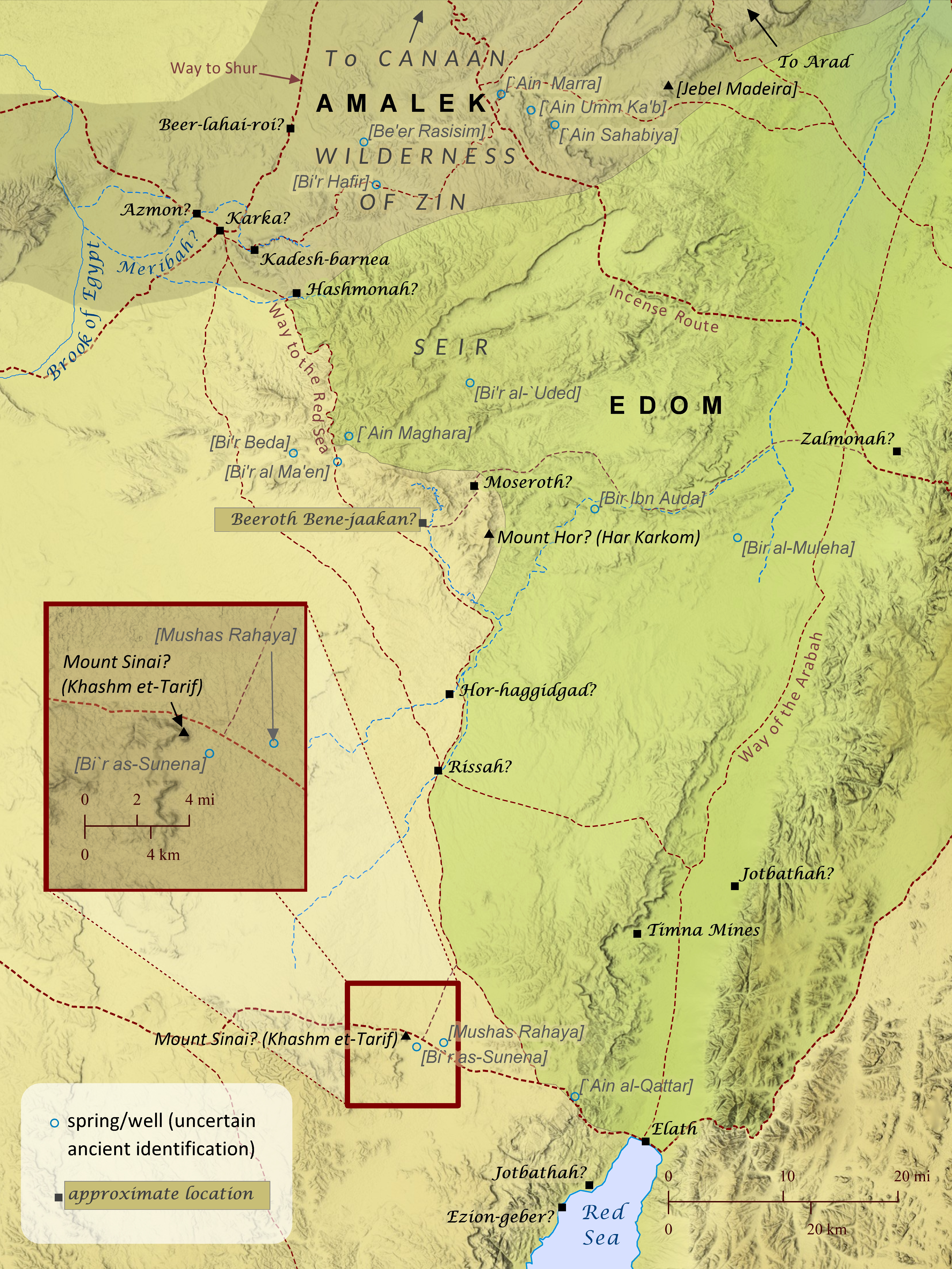
After the Israelites received the law on Mount Sinai, which may have been located at Khashm et-Tarif (see also “The Route of the Exodus”), they traveled to Kadesh-barnea, a distance that took eleven days “by the way of Mount Seir” (Deuteronomy 1:2). The phrase “by the way of Mount Seir” suggests that more than one route existed between Mount Sinai and Kadesh, as shown here, but the road the Israelites took probably ran alongside the mountainous region of Seir. This route would have offered greater access to water from wells, natural springs, and seasonal streams flowing from the hills of Seir–a critical necessity for a large group traveling through this very arid region. Nearly every location identified on this map was essentially a small community centered around one of these life-enabling sources of water. After reaching Kadesh in the wilderness of Zin, the Israelites prepared to enter Canaan by sending spies to scout out the land. But when ten of the twelve spies brought back news about the strength of the Canaanites, the people became afraid to enter the land, so the Lord punished them by condemning them to travel in the wilderness for forty years until that generation died off. Some Israelites repented and tried to enter the land, but they were beaten back to Hormah by the Amalekites and Canaanites. So for forty years the Israelites traveled from place to place, probably in the general area of Kadesh-barnea, though very few locations mentioned are able to be established with much certainty. As the forty years of traveling drew to a close, the Israelites prepared again to travel to Canaan by requesting permission from the king of Edom to pass through his land. When the king refused, the Israelites “turned away” from the Edomites and set out from Kadesh to travel to Mount Hor. The Jewish historian Josephus located Mount Hor at Jebel Nebi Harun, a very tall mountain in eastern Edom, but this has been rejected by many scholars in favor of other sites such as Jebel Madeira to the northeast of Kadesh. This author is convinced, however, that any candidate for Mount Hor must be sought to the south of Kadesh-barnea. Numbers 33:30 and Deuteronomy 10:6 mention that, during their wilderness travels, the Israelites camped at Moseroth/Moserah, which was apparently located at Mount Hor, since both Moseroth/Moserah and Mount Hor are cited as the place where Aaron died (Numbers 21:29-29; 33:37-39; Deuteronomy 10:6-9). It is difficult to envision the Israelites traveling back to the edge of Canaan after suffering defeat there the last time they attempted to enter the land. These same passages also note that after their stay at Moseroth/Moserah the Israelites traveled to Hor-haggidgad/Gudgodah (probably located along the Wadi Khadakhid) and then to Jotbathah, with no mention of passing through Kadesh, which they would have had to do if Mount Hor was north of Kadesh (since they were avoiding the land of Edom). Also, in Deuteronomy 2:1 Moses says that after the Israelites left Kadesh, “we journeyed back into the wilderness, in the direction of the Red Sea, as the Lord had told me and skirted Mount Seir for many days,” and Aaron’s death on Mount Hor fits best during this time. Similarly, Numbers 21:4 says “from Mount Hor they set out by the way to the Red Sea, to go around the land of Edom,” but there would have been no way to the Red Sea around the land of Edom if Mount Hor were located northeast of Kadesh. One element of the wilderness narratives that appears to favor a northeast location for Mount Hor, however, is the story of the king of Arad, which the book of Numbers (chapters 21 and 33) places immediately after the death of Aaron on Mount Hor. At first glance, the narrative seems to imply that the king attacked the Israelites at Mount Hor, which fits better with a northern location. Yet, it is also possible that the story is simply noting that it was after the Israelites’ arrival at Mount Hor that the king of Arad first learned of the Israelites’ renewed intentions to enter Canaan, perhaps as a result of their request to pass through Edom. But it may have been later that the king of Arad actually engaged them in battle, perhaps as they were passing north of Zalmonah and appeared to be ready to enter Canaan by way of Arad (see Numbers 33:41-42 and the map “The Journey to Abel-shittim”). For these reasons, this author believes that Har Karkom is the best candidate for the location of Mount Hor. The site is appropriately located at the edge of Seir and along the way to the Red Sea. This site’s role as an ancient cultic center is also well established. Perhaps Aaron’s priestly duties and authority in Israel had grown out of a similar role he had previously held at Mount Hor (see also Numbers 12:1-2; Deuteronomy 33:2; Judges 5:4-5), where he was eventually buried.
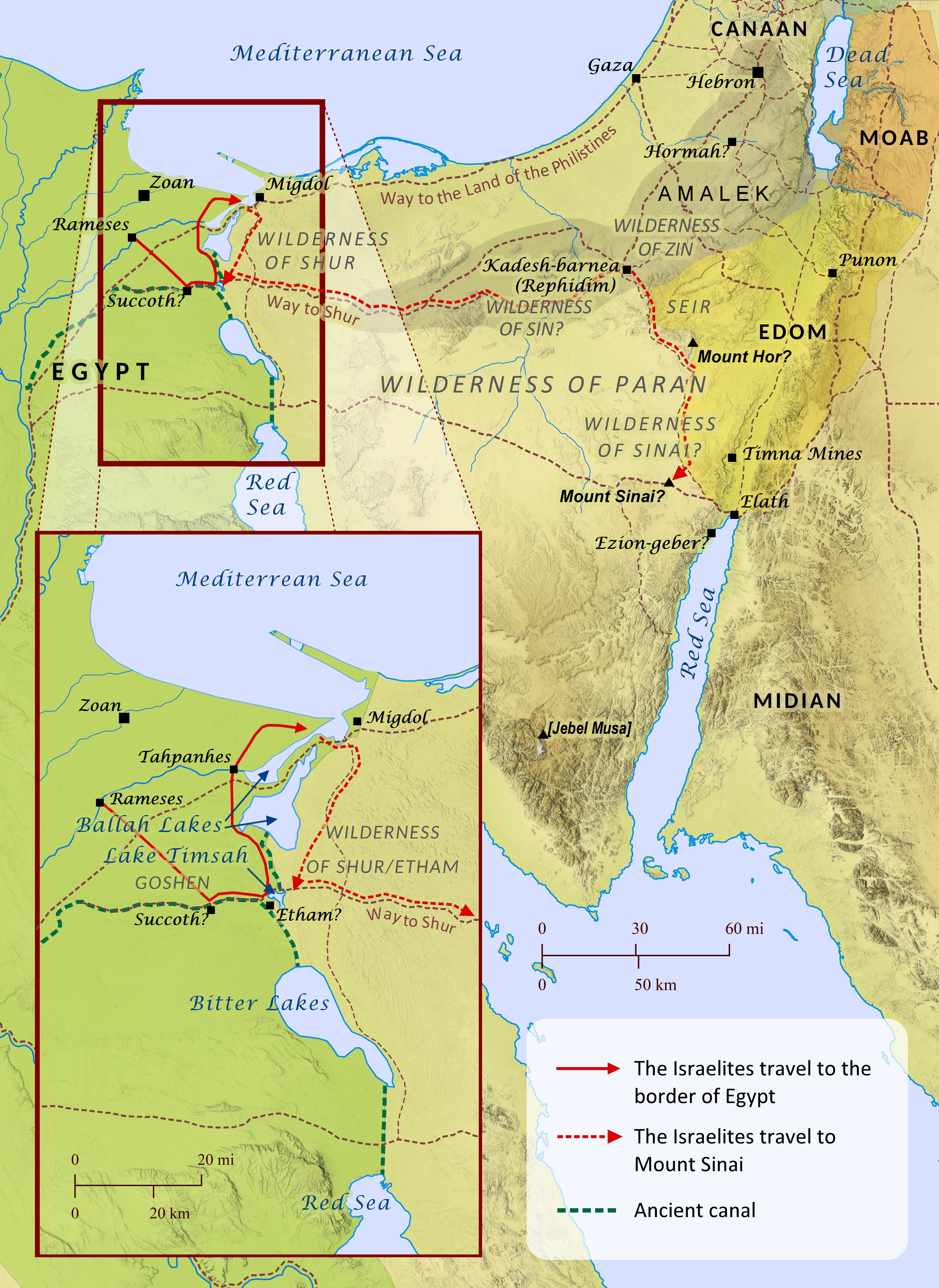
Exodus 13-19; Numbers 33
Like several other events recorded in Scripture, the Bible’s account of the Israelites’ journey from Egypt to Mount Sinai includes an abundance of geographical references, yet it remains one of the most hotly debated topics among scholars, and numerous theories have been offered. The vast majority of geographical references provided in the story are disputed, including the place where the Israelites crossed the Red Sea, the location of Mount Sinai (see Proposed Locations for Mount Sinai map), and the various stops along the Israelites’ journey. A few locations have been established with some degree of scholarly consensus, but even these are not without opposing viewpoints. Amidst this incredible diversity of opinion, however, a single verse provides one of the most helpful clues for weighing the merits of one viewpoint over another: “By the way of Mount Seir it takes eleven days to reach Kadesh-barnea from Horeb” (Deuteronomy 1:2). For those who assume the Bible’s account to be trustworthy, this verse appears to require the following for any theory to be considered viable: 1) Kadesh-barnea and Mount Sinai must have been located at a distance from each other that could reasonably have been expected to take eleven days for an entire nation of people with small children, flocks, equipment, and perhaps even elderly members to travel on foot; and 2) the pace established by this distance over eleven days should most likely be considered the typical pace for the Israelites as they traveled from place to place along the other parts of the journey. This two-pronged test clearly strains many of the theories put forth to this point, especially when one factors in the time references given for the start of the journey (Exodus 12:6; Numbers 33:3), the middle of the journey (Exodus 16:1; Numbers 33:8), and the end of the journey (Exodus 19:1). In short, the journey from Rameses to the Wilderness of Sin took 31 days, since it included the 15th day of the second month, and the rest of the journey took another 16 days, assuming they arrived at Mount Sinai on the 15th day (not the first day, etc.) of the third month. Along with these criteria, a theory’s overall congruence with other established geographical and archeological data should bolster its credibility over other proposals. Another consideration is the extreme similarity between the events at Rephidim (Exodus 17) and the events at Kadesh-barnea (Numbers 20:1-13; 27:12-14; Deuteronomy 32:51; Ezekiel 47:19; 48:28), raising the question of whether Rephidim (meaning “resting places”) is in fact Kadesh-barnea. With these things in mind, the map below proposes a route for the exodus that meets virtually all of these criteria. A careful analysis and explanation of all the elements of the map is far beyond the scope of this article, but a few key points should be noted. The term Red Sea, in addition to referring to what we now regard it, must have also applied to the interconnected lakes and marshlands that lay along what is now the Suez Canal. Also, the portion of the journey that passed through the wilderness for three days without water (Exodus 15:22; Numbers 33:8) may have been comprised of a partial first day, a full second day, and a partial third day, much like Jesus’ time in the tomb is reckoned as three days in Matthew 12:40. Most notably, Mount Sinai is placed on this map at Gebel Khashm et-Tarif, which is appropriately located near, but not in, Midian (Exodus 3:1; 18:5; Numbers 10:29-30). It is also located 89 miles from Kadesh-barnea (assuming Kadesh is at Tall al-Quderat), which establishes a reasonable pace of 7.6 miles (12.2 km) per day to travel between them in 11 days. This lines up well with several known sources of water along that route (e.g., `Ain Qedeis [Hazar-addar?], Tamilat Suwelima [Hor-haggiggad?], and the spring at Kuntillet al-Girafi [unknown ancient identification]). This general pace then synchronizes very well with the timetable and distances required by this map for the other parts of the journey. The distance from Rameses to the Wilderness of Sin (where it is located here) could be completed in under 26 days, leaving an acceptable buffer of about 5 days for the parting of the Red Sea and perhaps a slower pace through the Wilderness of Shur/Etham. The entire journey took about 60 days, and the journey from the Wilderness of Sin to Mount Sinai took about 29 days. This leaves an acceptable buffer of time to complete the rest of the journey (about 16 days of travel) with a very adequate two weeks of extra time for Jethro to visit Moses and the Israelites to do battle with the Amalekites (Exodus 17-18). It should be noted that this timetable generally assumes (but does not necessarily require) that travel continued on sabbath days, but Scripture does not make clear whether travel was prohibited as work prior to the giving of the law at Mount Sinai.