Open Bible Data Home About News OET Key
OET OET-RV OET-LV ULT UST BSB MSB BLB AICNT OEB WEBBE WMBB NET LSV FBV TCNT T4T LEB BBE Moff JPS Wymth ASV DRA YLT Drby RV SLT Wbstr KJB-1769 KJB-1611 Bshps Gnva Cvdl TNT Wycl SR-GNT UHB BrLXX BrTr Related Topics Parallel Interlinear Reference Dictionary Search
ParallelVerse GEN EXO LEV NUM DEU JOB JOS JDG RUTH 1 SAM 2 SAM PSA AMOS HOS 1 KI 2 KI 1 CHR 2 CHR PROV ECC SNG JOEL MIC ISA ZEP HAB JER LAM YNA (JNA) NAH OBA DAN EZE EZRA EST NEH HAG ZEC MAL LAO GES LES ESG DNG 2 PS TOB JDT WIS SIR BAR LJE PAZ SUS BEL MAN 1 MAC 2 MAC 3 MAC 4 MAC YHN (JHN) MARK MAT LUKE ACTs YAC (JAM) GAL 1 TH 2 TH 1 COR 2 COR ROM COL PHM EPH PHP 1 TIM TIT 1 PET 2 PET 2 TIM HEB YUD (JUD) 1 YHN (1 JHN) 2 YHN (2 JHN) 3 YHN (3 JHN) REV
2 Ki Intro C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 C9 C10 C11 C12 C13 C14 C15 C16 C17 C18 C19 C20 C21 C22 C23 C24 C25
2 Ki 25 V1 V3 V4 V5 V6 V7 V8 V9 V10 V11 V12 V13 V14 V15 V16 V17 V18 V19 V20 V21 V22 V23 V24 V25 V26 V27 V28 V29 V30
Note: This view shows ‘verses’ which are not natural language units and hence sometimes only part of a sentence will be visible—click on any Bible version abbreviation down the left-hand side to see the verse in more of its context. Normally the OET discourages the reading of individual ‘verses’, but this view is only designed as a tool for doing comparisons of different translations—the older translations are further down the page (so you can read up from the bottom to trace the English translation history). The OET segments on this page are still very early looks into the unfinished texts of the Open English Translation of the Bible—please double-check these texts in advance before using in public.
Text critical issues=none Clarity of original=clear Importance to us=normal (All still tentative.)
OET (OET-RV) and besieged the city for two years.![]()
OET-LV And_came the_city in/on/at/with_siege until one_plus_of ten year to/for_the_king Tsidqiyyāh.
![]()
UHB וַתָּבֹ֥א הָעִ֖יר בַּמָּצ֑וֹר עַ֚ד עַשְׁתֵּ֣י עֶשְׂרֵ֣ה שָׁנָ֔ה לַמֶּ֖לֶךְ צִדְקִיָּֽהוּ׃ ‡
(vattāⱱoʼ hāˊir bammāʦōr ˊad ˊashtēy ˊesrēh shānāh lammelek ʦidqiyyāhū.)
Key: khaki:verbs.
Note: Automatic aligning of the OET-RV to the LV is done by some temporary software, hence the OET-RV alignments are incomplete (and may occasionally be wrong).
BrLXX Καὶ ἦλθεν ἡ πόλις ἐν περιοχῇ ἕως τοῦ ἑνδεκάτου ἔτους τοῦ βασιλέως Σεδεκίου ἐννάτῃ τοῦ μηνός.
(Kai aʸlthen haʸ polis en perioⱪaʸ heōs tou hendekatou etous tou basileōs Sedekiou ennataʸ tou maʸnos. )
BrTr And the city was besieged until the eleventh year of king Sedekias on the ninth day of the month.
ULT And the city came into the siege until the eleventh year of King Zedekiah.
UST It took them two years to do that.
BSB And the city was kept under siege until King Zedekiah’s eleventh year.
MSB (Same as BSB above)
OEB No OEB 2 KI book available
WEBBE So the city was besieged until the eleventh year of King Zedekiah.
WMBB (Same as above)
NET The city remained under siege until King Zedekiah’s eleventh year.
LSV And the city enters into siege until the eleventh year of King Zedekiah.
FBV The city remained under siege until the eleventh year of King Zedekiah.
T4T They did that for two years.
LEB So the city came under siege until the eleventh year of the king.
BBE And the town was shut in by their forces till the eleventh year of King Zedekiah.
Moff No Moff 2 KI book available
JPS So the city was besieged unto the eleventh year of king Zedekiah.
ASV So the city was besieged unto the eleventh year of king Zedekiah.
DRA And the city was shut up and besieged till the eleventh year of king Sedecias,
YLT And the city entereth into siege till the eleventh year of king Zedekiah,
Drby And the city was besieged until the eleventh year of king Zedekiah.
RV So the city was besieged unto the eleventh year of king Zedekiah.
SLT And the city will go into siege till the eleventh year to king Zedekiah.
Wbstr And the city was besieged to the eleventh year of king Zedekiah.
KJB-1769 And the city was besieged unto the eleventh year of king Zedekiah.
KJB-1611 And the citie was besieged vnto the eleuenth yeere of king Zedekiah.
(Modernised spelling is same as from KJB-1769 above)
Bshps And the citie was besieged vnto the eleuenth yere of king Zedekia.
(And the city was besieged unto the eleventh year of king Zedekia.)
Gnva So the citie was besieged vnto the eleueth yeere of King Zedekiah.
(So the city was besieged unto the eleventh year of King Zedekiah. )
Cvdl Thus was the cite beseged vnto the eleuenth yeare of kynge Sedechias.
(Thus was the cite besieged unto the eleventh year of king Sedechias.)
Wycl And the citee was closid, and cumpassid, `til to the eleuenthe yeer of king Sedechie,
(And the city was closed, and compassed/surrounded, till to the eleventh year of king Sedechie,)
Luth Also ward die Stadt belagert bis ins elfte Jahr des Königs Zidekia.
(So what/which the city belagert until into_the elfte year the kings Zidekia.)
ClVg Et clausa est civitas atque vallata usque ad undecimum annum regis Sedeciæ,
(And clausa it_is city and_yet vallata until to elevenum a_year king Sedeciæ, )
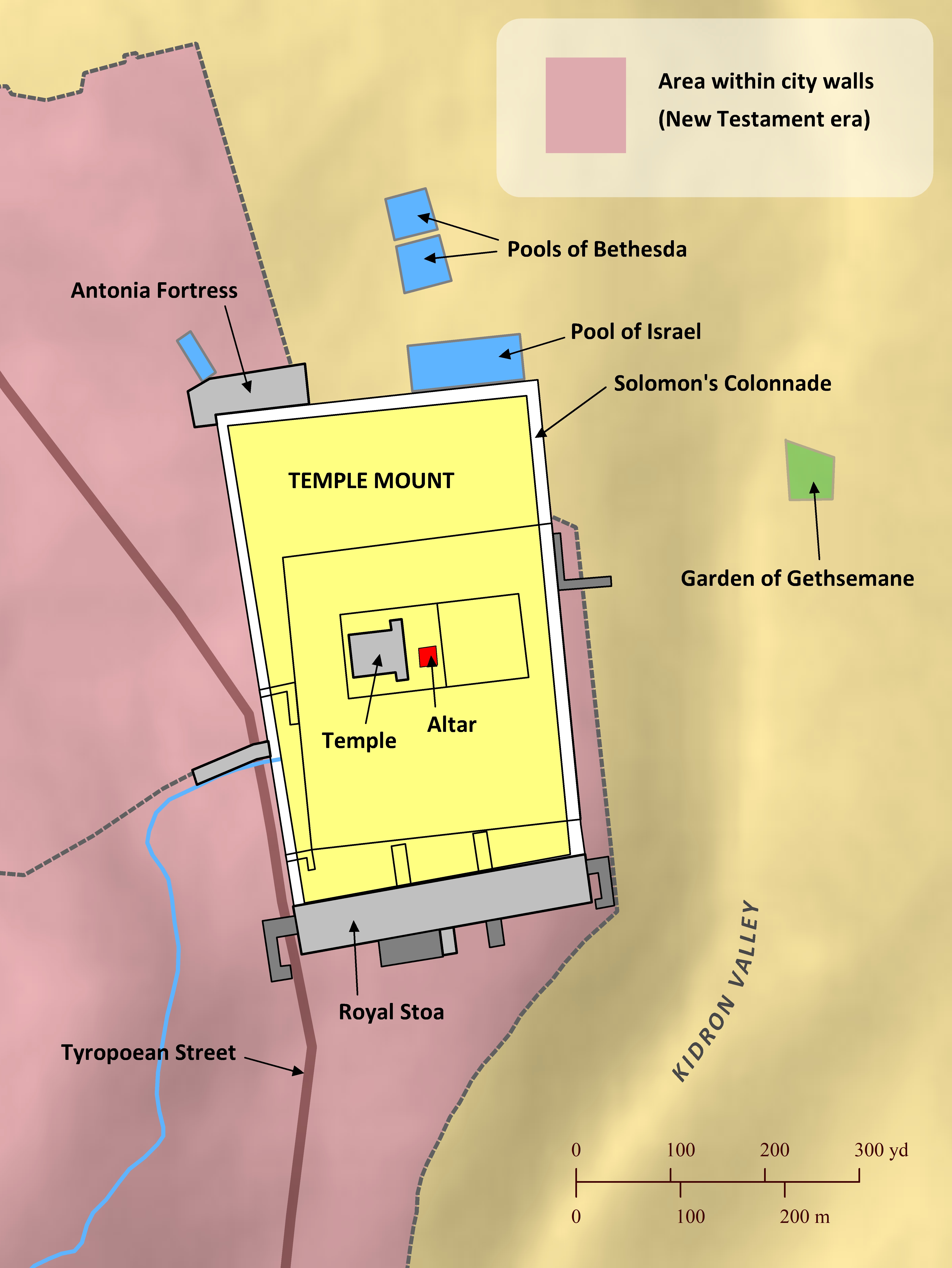
The Temple of the Lord in Jerusalem, where all Israelite males were commanded to offer sacrifices to the Lord (Exodus 23:14-19; Deuteronomy 16:16-17), underwent several stages of reconstruction and development over hundreds of years. The first Temple was built by King Solomon to replace the aging Tabernacle, and it was constructed on a threshing floor on high ground on the north side of the city (2 Samuel 24; 1 Chronicles 21). Hundreds of years later King Hezekiah expanded the platform surrounding the Temple. When Jerusalem fell to the Babylonians in 586 B.C., the Temple was completely destroyed (2 Kings 25:1-21; 2 Chronicles 36:17-21; Jeremiah 39:1-10; 52:1-30). It was rebuilt in 515 B.C. after a group of Jews returned to Judea from exile in Babylon (Ezra 1:5-6:15; Nehemiah 7:5-65). Herod the Great completely rebuilt and expanded the Temple once again around 20 B.C., making it one of the largest temples in the Roman world. Jesus’ first believers often met together in Solomon’s Colonnade, a columned porch that encircled the Temple Mount, perhaps carrying on a tradition started by Jesus himself (John 10:23; Acts 3:11; 5:12). But Herod’s Temple did not last long: After many Jews revolted against Rome, the Romans eventually recaptured Jerusalem and destroyed the Temple in A.D. 70.
Daniel 1; 2 Kings 24-25; 2 Chronicles 36; Jeremiah 39; 52
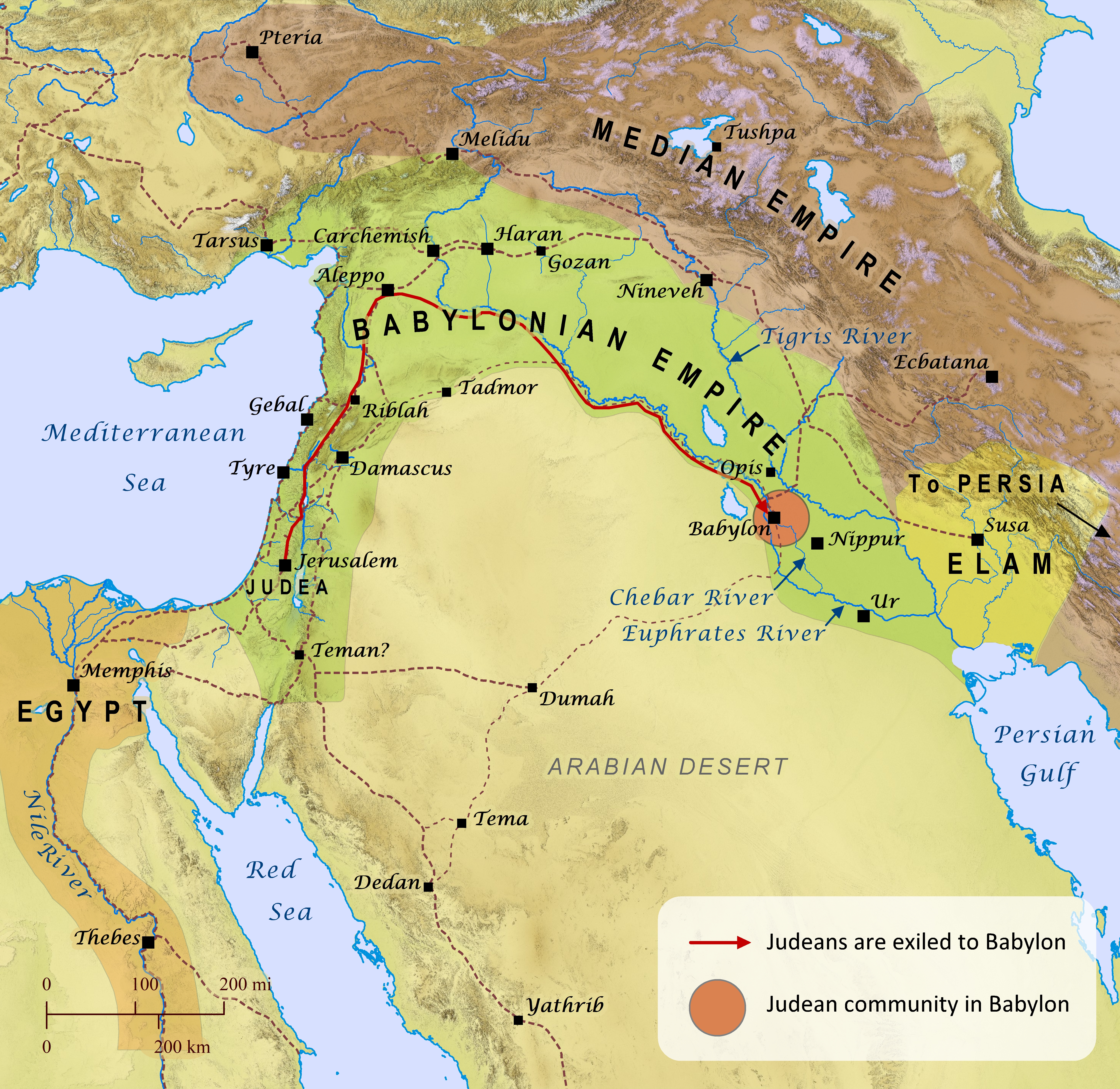
One of the most significant events in the story of the Old Testament is the exile of Judah to Babylon in 586 B.C. This event–actually the third in a series of exiles to Babylon (the others occurring in 605 B.C. and 597 B.C.)–precipitated several crises in the nation and in Judaism. The northern kingdom of Israel had already been exiled to Assyria over a century earlier in 722 B.C. (2 Kings 15:29; 17:1-6; 1 Chronicles 5:26; see also “Israelites Are Exiled to Assyria” map), and in some ways that exile was even more devastating. Nevertheless, the Temple of the Lord remained intact in Jerusalem as a place where the faithful could continue to offer their sacrifices. With the destruction of Jerusalem and the Temple of the Lord at the hands of the Babylonians, however, sacrifices could no longer be offered at the Tabernacle or Temple of the Lord (Leviticus 17:2-4; Deuteronomy 12:5-7), and the Lord’s promise to provide a land for his people and a descendant on the throne of David no doubt seemed abandoned. At the same time, however, the Judean exiles were allowed to maintain their religious traditions in Babylon, and many even began to thrive there, including Daniel and his friends, who served at the royal court (Daniel 1; see also “The Land of Exile” map). One of the last kings of Babylon expanded Babylonia further by capturing the desert oases of Dumah, Tema, Dedan, and Yathrib (see “Oases of the Arabian Desert” map), but eventually the Median Empire to the north merged with the Persian Empire to the southeast and conquered the Babylonian Empire. King Cyrus of Persia then decreed that the exiled Judeans, now called “Jews,” could return to their homeland if they desired (2 Chronicles 36:22-23; Ezra 1-2; see also “Jews Return from Exile” map).
2 Kings 23:19-25:30; Jeremiah 39
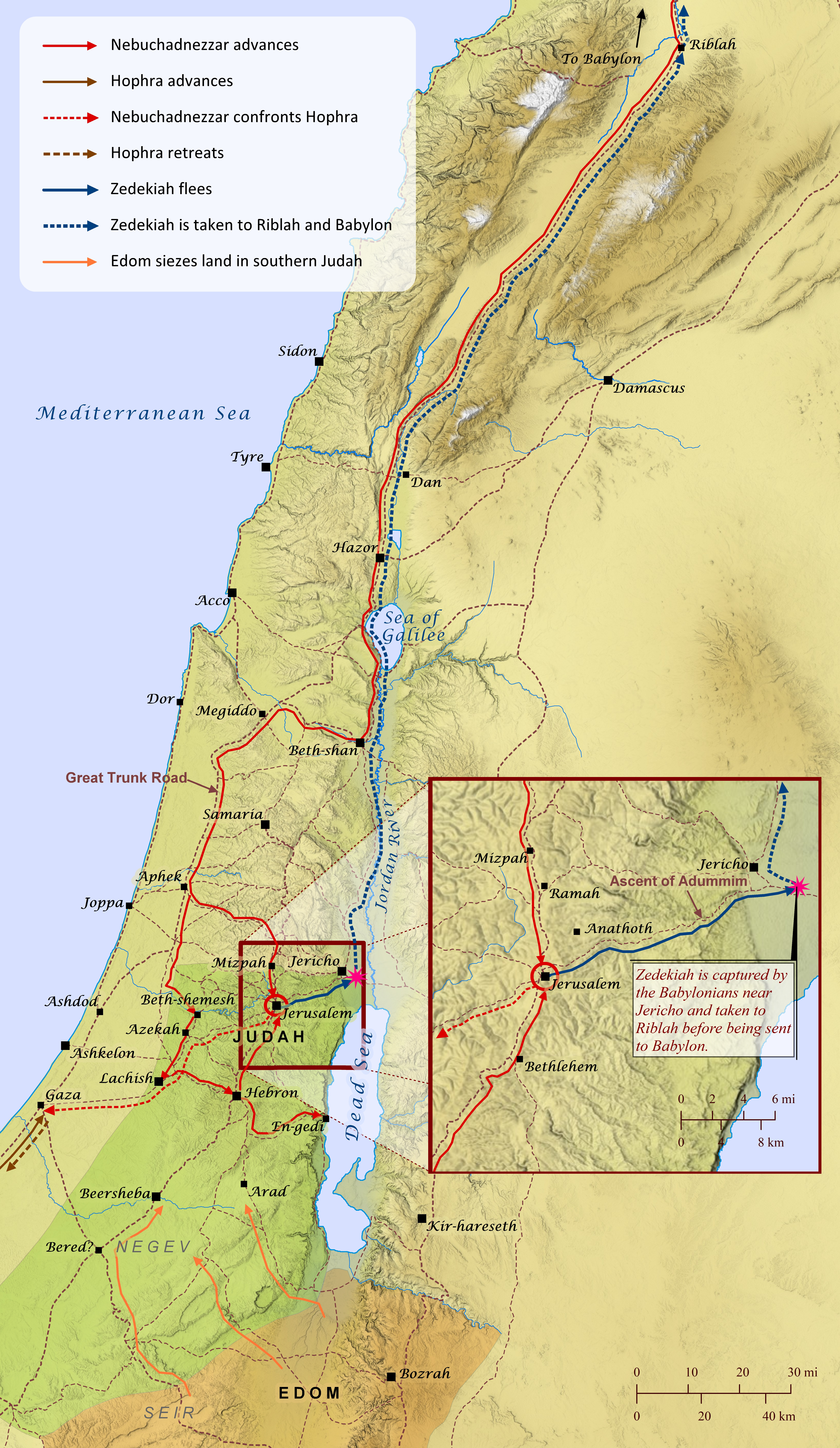
The final collapse of the southern kingdom of Judah as an independent nation came at the hands of King Nebuchadnezzar II of Babylon in 586 B.C. Judah had already become a vassal of Egypt in 609 B.C. when King Josiah was killed by Pharaoh Neco at Megiddo (see “Josiah Battles Neco” map). Then in 605 B.C., after Egypt and Assyria were defeated by Nebuchadnezzar at Carchemish, Judah’s vassal loyalty transferred to Babylon. At that time, some of the Judean nobility were sent into exile, including Daniel and his friends (Daniel 1:1-7). Several years later in 597 B.C. a second exile occurred in retaliation for King Jehoiakim’s refusal to continue paying tribute to Babylon, and this likely included the prophet Ezekiel (Ezekiel 1:1-3). Finally, in 586 B.C. Nebuchadnezzar conquered many of the fortified towns throughout Judah and destroyed Jerusalem and the Temple after King Zedekiah refused to submit to his Babylonian overlords any longer. Nebuchadnezzar began this campaign into Judah by heading south along the Great Trunk Road and dividing his forces near Aphek, sending some of them to Jerusalem from the north and others from the southwest. At some point during his siege of Jerusalem, King Hophra of Egypt advanced toward Judah to support Judah’s rebellion against Babylon, and Nebuchadnezzar lifted the siege to confront Hophra (Jeremiah 37:5-8). It is unclear exactly what transpired between Hophra’s forces and Nebuchadnezzar’s forces, but apparently Hophra’s forces returned to Egypt, and Nebuchadnezzar’s forces returned to finish besieging Jerusalem. When the Babylonians finally breached the main northern wall, it became clear that all hope was lost, and King Zedekiah and his sons fled on horseback through a gate at the southeastern corner of Jerusalem (see “Jerusalem during the Early Old Testament” map). They followed the Ascent of Adummim toward Jericho, perhaps seeking to escape to Ammon, but the Babylonians captured Zedekiah and his sons on the plains of Jericho and sent them to Riblah. There they killed Zedekiah’s sons, blinded Zedekiah, and sent him to Babylon to die in exile. After completely destroying Jerusalem and the Temple, the Babylonians sent many other Judean nobles and their families to Babylon (see “Judah Is Exiled to Babylon” map) and appointed a Judean named Gedaliah as governor over the region at Mizpah, thus bringing an end to the independent kingdom of Judah. Around this time it also appears that the Edomites took advantage of Judah’s vulnerable situation and captured territory for themselves in the Negev. In response, the prophets Obadiah and Ezekiel pronounced blistering curses upon the Edomites (Obadiah 1:1-21; Ezekiel 25:12-14).