15:1 Azaryah was also known as Uzziyah, especially from v13 onwards.![]()
Open Bible Data Home About News OET Key
OET OET-RV OET-LV ULT UST BSB MSB BLB AICNT OEB WEBBE WMBB NET LSV FBV TCNT T4T LEB BBE Moff JPS Wymth ASV DRA YLT Drby RV SLT Wbstr KJB-1769 KJB-1611 Bshps Gnva Cvdl TNT Wycl SR-GNT UHB BrLXX BrTr Related Topics Parallel Interlinear Reference Dictionary Search
ParallelVerse GEN EXO LEV NUM DEU JOB JOS JDG RUTH 1 SAM 2 SAM PSA AMOS HOS 1 KI 2 KI 1 CHR 2 CHR PROV ECC SNG JOEL MIC ISA ZEP HAB JER LAM YNA (JNA) NAH OBA DAN EZE EZRA EST NEH HAG ZEC MAL LAO GES LES ESG DNG 2 PS TOB JDT WIS SIR BAR LJE PAZ SUS BEL MAN 1 MAC 2 MAC 3 MAC 4 MAC YHN (JHN) MARK MAT LUKE ACTs YAC (JAM) GAL 1 TH 2 TH 1 COR 2 COR ROM COL PHM EPH PHP 1 TIM TIT 1 PET 2 PET 2 TIM HEB YUD (JUD) 1 YHN (1 JHN) 2 YHN (2 JHN) 3 YHN (3 JHN) REV
2 Ki Intro C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 C9 C10 C11 C12 C13 C14 C15 C16 C17 C18 C19 C20 C21 C22 C23 C24 C25
2 Ki 15 V2 V3 V4 V5 V6 V7 V8 V9 V10 V11 V12 V13 V14 V15 V16 V17 V18 V19 V20 V21 V22 V23 V24 V25 V26 V27 V28 V29 V30 V31 V32 V33 V34 V35 V36 V37 V38
Note: This view shows ‘verses’ which are not natural language units and hence sometimes only part of a sentence will be visible—click on any Bible version abbreviation down the left-hand side to see the verse in more of its context. Normally the OET discourages the reading of individual ‘verses’, but this view is only designed as a tool for doing comparisons of different translations—the older translations are further down the page (so you can read up from the bottom to trace the English translation history). The OET segments on this page are still very early looks into the unfinished texts of the Open English Translation of the Bible—please double-check these texts in advance before using in public.
Text critical issues=none Clarity of original=clear Importance to us=normal (All still tentative.)
OET (OET-RV) In the twenty-seventh year of King Yarave’am’s reign over Yisrael, Amatsyah’s son Azaryah[fn] became king of Yehudah.
15:1 Azaryah was also known as Uzziyah, especially from v13 onwards.![]()
OET-LV in_year twenty and_seven year of_Yārāⱱəˊām/(Jeroboam) the_king_of Yisrāʼēl/(Israel) ˊAzaryāh he_became_king the_son_of ʼAmaʦyāh the_king_of Yəhūdāh/(Judah).
![]()
UHB בִּשְׁנַ֨ת עֶשְׂרִ֤ים וָשֶׁ֨בַע֙ שָׁנָ֔ה לְיָרָבְעָ֖ם מֶ֣לֶךְ יִשְׂרָאֵ֑ל מָלַ֛ךְ עֲזַרְיָ֥ה בֶן־אֲמַצְיָ֖ה מֶ֥לֶךְ יְהוּדָֽה׃ ‡
(bishənat ˊesrim vāsheⱱaˊ shānāh ləyārāⱱəˊām melek yisrāʼēl mālak ˊₐzaryāh ⱱen-ʼₐmaʦyāh melek yəhūdāh.)
Key: khaki:verbs.
Note: Automatic aligning of the OET-RV to the LV is done by some temporary software, hence the OET-RV alignments are incomplete (and may occasionally be wrong).
BrLXX Ἐν ἔτει εἰκοστῷ καὶ ἑβδόμῳ τῷ Ἱεροβοὰμ βασιλεῖ Ἰσραὴλ ἐβασίλευσεν Ἀζαρίας υἱὸς Ἀμεσσίου βασιλέως Ἰούδα.
(En etei eikostōi kai hebdomōi tōi Hieroboam basilei Israaʸl ebasileusen Azarias huios Amessiou basileōs Youda. )
BrTr In the twenty-seventh year of Jeroboam king of Israel Azarias the son of Amessias king of Juda [fn]began to reign.
15:1 Gr. reigned.
ULT In the year of the 27th year of Jeroboam the king of Israel, Azariah the son of Amaziah, the king of Judah, became king.
UST After Jeroboam had been ruling Israel for almost twenty-seven years, Azariah, son of Amaziah king of Judah, began to rule.
BSB In the twenty-seventh year of Jeroboam’s reign over Israel, Azariah[fn] son of Amaziah became king of Judah.
15:1 Azariah is also called Uzziah; also in verses 6, 7, 8, 17, 23, and 27; see 2 Chronicles 26:1.
MSB (Same as BSB above including footnotes)
OEB No OEB 2 KI book available
WEBBE In the twenty-seventh year of Jeroboam king of Israel, Azariah son of Amaziah king of Judah began to reign.
WMBB (Same as above)
NET In the twenty-seventh year of King Jeroboam’s reign over Israel, Amaziah’s son Azariah became king over Judah.
LSV In the twenty-seventh year of Jeroboam king of Israel, Azariah son of Amaziah, king of Judah, has reigned;
FBV Azariah, son of Amaziah, became king of Judah in the twenty-seventh year of the reign of Jeroboam, king of Israel.
T4T After Jeroboam #2 had been ruling Israel for almost twenty-seven years, Uzziah, the son of King Amaziah of Judah, began to rule.
LEB In the twenty-seventh year of Jeroboam king of Israel, Azariah the son of Amaziah king of Judah began to reign.
BBE In the twenty-seventh year of the rule of Jeroboam, king of Israel, Azariah, son of Amaziah, became king of Judah.
Moff No Moff 2 KI book available
JPS In the twenty and seventh year of Jeroboam king of Israel began Azariah son of Amaziah king of Judah to reign.
ASV In the twenty and seventh year of Jeroboam king of Israel began Azariah son of Amaziah king of Judah to reign.
DRA In the seven and twentieth year of Jeroboam king of Israel reigned Azarias son of Amasias, king of Juda.
YLT In the twenty and seventh year of Jeroboam king of Israel reigned hath Azariah son of Amaziah king of Judah,
Drby In the twenty-seventh year of Jeroboam king of Israel, Azariah son of Amaziah, king of Judah, began to reign.
RV In the twenty and seventh year of Jeroboam king of Israel began Azariah son of Amaziah king of Judah to reign.
(In the twenty and seventh year of Jeroboam king of Israel began Azariah son of Amaziah king of Yudah to reign. )
SLT In the twentieth year and seventh year to Jeroboam king of Israel, reigned Azariah son of Amaziah king of Judah.
Wbstr In the twenty and seventh year of Jeroboam king of Israel began Azariah son of Amaziah king of Judah to reign.
KJB-1769 In the twenty and seventh year of Jeroboam king of Israel began Azariah son of Amaziah king of Judah to reign.[fn]
(In the twenty and seventh year of Jeroboam king of Israel began Azariah son of Amaziah king of Yudah to reign. )
15.1 Azariah: also called, Uzziah
KJB-1611 ¶ In the twenty and seuenth yeere of Ieroboam king of Israel, began Azariah sonne of Amaziah king of Iudah to reigne.
(Modernised spelling is same as from KJB-1769 above, apart from punctuation)
Bshps In the twentie and seuenth yere of Ieroboam king of Israel, began Azaria sonne of Amazia king of Iuda to raigne.
(In the twenty and seventh year of Yeroboam king of Israel, began Azaria son of Amazia king of Yudah to reign.)
Gnva In the seuen and twentieth yeere of Ieroboam King of Israel, began Azariah, sonne of Amaziah King of Iudah to reigne.
(In the seven and twentieth year of Yeroboam King of Israel, began Azariah, son of Amaziah King of Yudah to reign. )
Cvdl In the seuen & twentieth yeare of Ieroboam kynge of Israel, reigned Asarias the sonne of Amasias kynge of Iuda:
(In the seven and twentieth year of Yeroboam king of Israel, reigned Asarias the son of Amasias king of Yuda:)
Wycl In the seuenthe and twentithe yeer of Jeroboam, king of Israel, Azarie, sone of Amasie, kyng of Juda, regnede;
(In the seventh and twentieth year of Yeroboam, king of Israel, Azarie, son of Amasie, king of Yuda, reigned;)
Luth Im siebenundzwanzigsten Jahr Jerobeams, des Königs Israels, ward König Asarja, der Sohn Amazias, des Königs Judas.
(In_the twenty-seventh year Yerobeams, the kings Israels, what/which king Asarya, the/of_the son Amazias, the kings Yudas.)
ClVg Anno vigesimo septimo Jeroboam regis Israël, regnavit Azarias filius Amasiæ regis Juda.[fn]
(In_the_year twentieth seventh Yeroboam king Israel, reigned Azarias son Amasiæ king Yuda. )
15.1 Anno vicesimo Azarias. RAB., in lib. Reg., tom. 3. Ipse est Ozias, etc., usque ad superius porta Ephraim dicitur.
15.1 In_the_year twentieth Azarias. RAB., in/into/on lib. Reg., tom. 3. Exactly_that it_is Ozias, etc., until to above gate/door Ephraim it_is_said.
15:1-3 The name Uzziah means Yahweh is my strength.
• fifty-two years: The length of Uzziah’s reign (792–740 BC) reflects changed conditions in the early 700s BC. Assyria was in decline and relations between Israel and Judah were cordial. Uzziah’s spiritual convictions earned God’s blessing so that Judah enjoyed its greatest prosperity since the days of Solomon (2 Chr 26:9-10).
Note 1 topic: figures-of-speech / explicit
(Occurrence 0) In the twenty-seventh year of Jeroboam
(Some words not found in UHB: in=year twenty and,seven year of,Jeroboam king Yisrael reign ˊAzaryāh son_of ʼAmaʦyāh king Yehuda )
It can be stated clearly that this is the twenty-seventh year of his reign. Alternate translation: “In year 27 of the reign of Jeroboam” (See also: translate-numbers)
(Occurrence 0) Azariah
(Some words not found in UHB: in=year twenty and,seven year of,Jeroboam king Yisrael reign ˊAzaryāh son_of ʼAmaʦyāh king Yehuda )
This king is better known today by the name “Uzziah.”
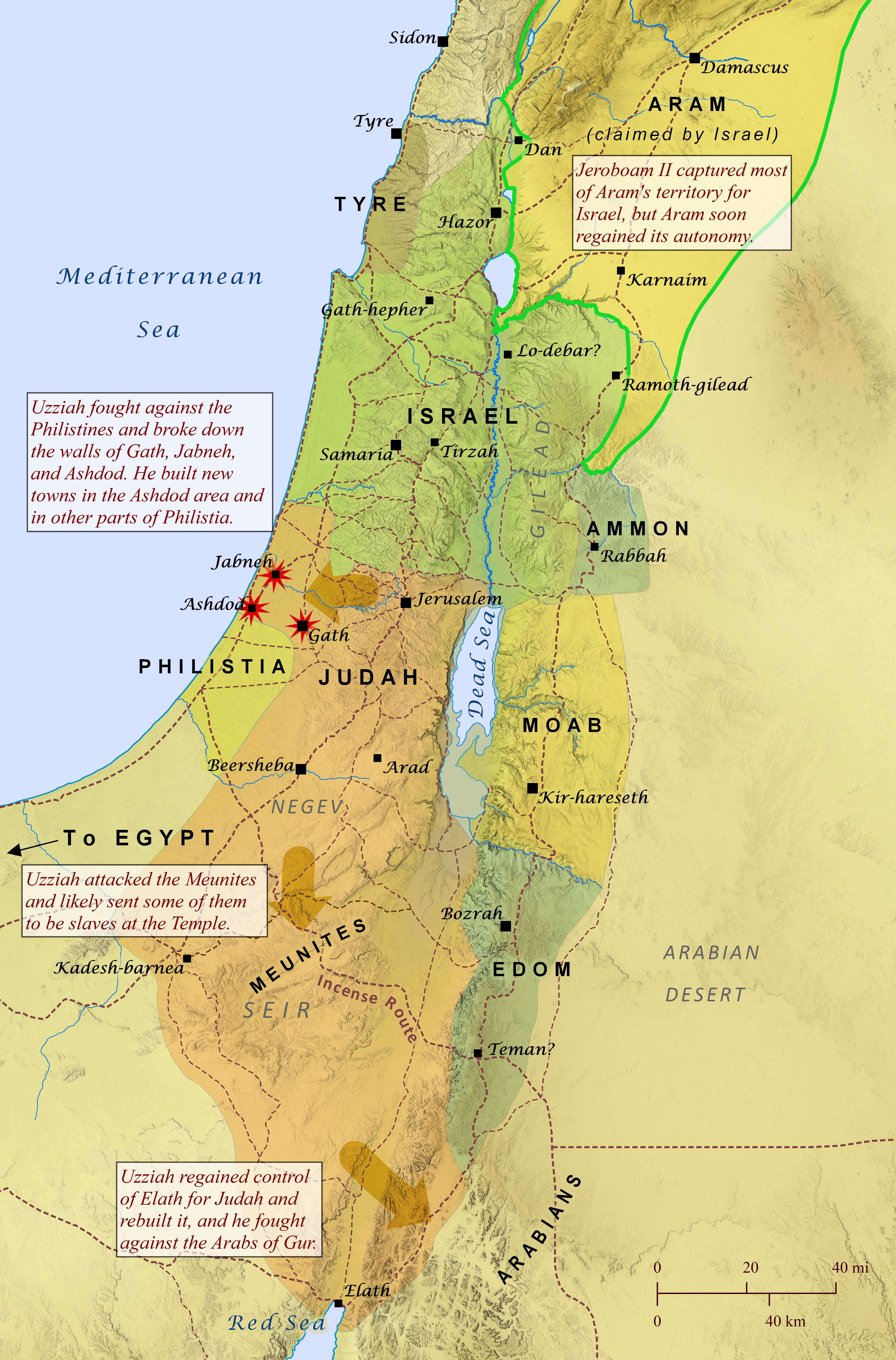
2 Kings 14:23-29; 15:1-7; 2 Chronicles 26
The long, concurrent reigns of Jeroboam II of Israel and Uzziah (also called Azariah) of Judah marked a period of resurgence after their nations had suffered nearly sixty years of decline and unrest. By the time both kings ascended to the throne in 793 B.C. and 792 B.C., Moab had revolted from Israel and seized land belonging to the tribe of Reuben (2 Kings 1:1; see “The Nation of Moab and the Tribe of Reuben”), and Edom and Libnah had revolted from Judah (2 Kings 8:16-24; 2 Chronicles 21:1-11; see “Edom and Libnah Revolt”). Jehu then brutally overthrew Ahab’s dynasty, but he later suffered the loss of all Gilead to the rising power of Aram (2 Kings 1:1; 3:1-27; 8:12; 10:32-33; 2 Chronicles 21:8-10; see “Aram Captures Gilead”). Soon after this, however, the Assyrian king Adad-nirari III (who may be the “savior” of 2 Kings 13:5) attacked Aram, but then he withdrew, thus creating a power vacuum to the north. Jeroboam of Israel took advantage of this opportunity and captured much of Aram, though it is unclear how firmly he held Aram or for how long. During this same time, king Uzziah of Judah captured the Red Sea port city of Elath in the far south, which belonged to Edom, and he also attacked the Arabs of Gur, who were likely located nearby. He also attacked the Meunites who lived in Seir, the formerly Edomite region south of the Judean Negev, though the Meunites themselves do not appear to have been Edomites. The Meunites are probably the same as the “Maonites” mentioned in Judges 10:12, and they also joined the Moabite alliance that attacked king Jehoshaphat of Judah (2 Chronicles 20). About a century after Uzziah’s time, during the reign of Hezekiah, some Simeonites attacked some Meunites in the Negev and seized their land (1 Chronicles 4:41-43). According to the Septuagint, the Meunites also paid Uzziah tribute (2 Chronicles 26:7-8), and Uzziah likely captured some of the Meunites and gave them as servants for the Temple of the Lord, which appears to have been a common practice in Israel since the time of Moses and Joshua (see Numbers 31:30; Joshua 9:27; Ezra 8:20). Their descendants are listed among the “Nethinim,” who served at the Temple during time of Ezra and Nehemiah (Ezra 2:50; Nehemiah 7:52). Uzziah also attacked the Philistine cities of Gath, Ashdod, and Jabneh and established other cities throughout Philistia. He built towers in Jerusalem at the Corner Gate, the Valley Gate, and the Angle as well as towers in the wilderness. He also dug many cisterns to store water for his large herds, both in the Shephelah (the foothills near Gath) and in the plain. He also had large farms and vineyards and strengthened Judah’s army. As far as moral leadership, the writer of Kings deems Jeroboam as a bad king for allowing idolatry to continue in Israel, but Uzziah is deemed as good, though he later sinned and was afflicted with leprosy for making an offering on the altar of incense.