Open Bible Data Home About News OET Key
OET OET-RV OET-LV ULT UST BSB MSB BLB AICNT OEB WEBBE WMBB NET LSV FBV TCNT T4T LEB BBE Moff JPS Wymth ASV DRA YLT Drby RV SLT Wbstr KJB-1769 KJB-1611 Bshps Gnva Cvdl TNT Wycl SR-GNT UHB BrLXX BrTr Related Topics Parallel Interlinear Reference Dictionary Search
ParallelVerse GEN EXO LEV NUM DEU JOB JOS JDG RUTH 1 SAM 2 SAM PSA AMOS HOS 1 KI 2 KI 1 CHR 2 CHR PROV ECC SNG JOEL MIC ISA ZEP HAB JER LAM YNA (JNA) NAH OBA DAN EZE EZRA EST NEH HAG ZEC MAL LAO GES LES ESG DNG 2 PS TOB JDT WIS SIR BAR LJE PAZ SUS BEL MAN 1 MAC 2 MAC 3 MAC 4 MAC YHN (JHN) MARK MAT LUKE ACTs YAC (JAM) GAL 1 TH 2 TH 1 COR 2 COR ROM COL PHM EPH PHP 1 TIM TIT 1 PET 2 PET 2 TIM HEB YUD (JUD) 1 YHN (1 JHN) 2 YHN (2 JHN) 3 YHN (3 JHN) REV
1 Ki Intro C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 C9 C10 C11 C12 C13 C14 C15 C16 C17 C18 C19 C20 C21 C22
1 Ki 9 V1 V2 V3 V4 V5 V6 V7 V8 V9 V10 V11 V12 V13 V14 V15 V16 V17 V18 V19 V21 V22 V23 V24 V25 V26 V27 V28
Note: This view shows ‘verses’ which are not natural language units and hence sometimes only part of a sentence will be visible—click on any Bible version abbreviation down the left-hand side to see the verse in more of its context. Normally the OET discourages the reading of individual ‘verses’, but this view is only designed as a tool for doing comparisons of different translations—the older translations are further down the page (so you can read up from the bottom to trace the English translation history). The OET segments on this page are still very early looks into the unfinished texts of the Open English Translation of the Bible—please double-check these texts in advance before using in public.
Text critical issues=none Clarity of original=clear Importance to us=normal (All still tentative.)
OET (OET-RV) All the remaining Amorite, Hittite, Perizzite, Hivite, and Yebusite people (they weren’t descendants of Yisrael),![]()
OET-LV All_of the_people the_left of the_ʼAmorī the_Ḩittiy the_Pərizzī the_Ḩiūī and_the_Yəⱱūşī/(Yəⱱūşī/(Jebusite)s) who not from_(the)_sons of_Yisrāʼēl/(Israel) they.
![]()
UHB כָּל־הָ֠עָם הַנּוֹתָ֨ר מִן־הָאֱמֹרִ֜י הַחִתִּ֤י הַפְּרִזִּי֙ הַחִוִּ֣י וְהַיְבוּסִ֔י אֲשֶׁ֛ר לֹֽא־מִבְּנֵ֥י יִשְׂרָאֵ֖ל הֵֽמָּה׃ ‡
(kāl-hāˊām hannōtār min-hāʼₑmoriy haḩittiy hapərizzī haḩiūiy vəhayəⱱūşiy ʼₐsher loʼ-mibənēy yisrāʼēl hēmmāh.)
Key: khaki:verbs, red:negative.
Note: Automatic aligning of the OET-RV to the LV is done by some temporary software, hence the OET-RV alignments are incomplete (and may occasionally be wrong).
BrLXX No BrLXX 1 KI 9:20 verse available
BrTr No BrTr 1 KI 9:20 verse available
ULT All of the people, the ones being left from the Amorite, the Hittite, the Perizzite, the Hivite, and the Jebusite, they who were not from the sons of Israel,
UST There were many people living in Solomon’s kingdom who were not Israelites. Rather, they were Amorites, Hittites, Perizzites, Hivites, and Jebusites.
BSB As for all the people who remained of the Amorites, Hittites, Perizzites, Hivites, and Jebusites ( the people who were not Israelites )—
MSB (Same as BSB above)
OEB No OEB 1 KI book available
WEBBE As for all the people who were left of the Amorites, the Hittites, the Perizzites, the Hivites, and the Jebusites, who were not of the children of Israel—
WMBB (Same as above)
NET Now several non-Israelite peoples were left in the land after the conquest of Joshua, including the Amorites, Hittites, Perizzites, Hivites, and Jebusites.
LSV The whole of the people that is left of the Amorite, the Hittite, the Perizzite, the Hivite, and the Jebusite, who [are] not of the sons of Israel—
FBV The descendants of the Amorites, Hittites, Perizzites, Hivites and Jebusites (people who were not Israelites)
T4T There were many people who belonged to the Amor people-group, the Heth people-group, the Periz people-group, the Hiv people-group, and the Jebus people-group who were not killed when the Israelis captured their land.
LEB All of the people who were remaining from the Amorites, the Hittites, the Perizzites, the Hivites, and the Jebusites who were not of the ⌊Israelites⌋,[fn]
9:20 Literally “sons/children of Israel”
BBE As for the rest of the Amorites, the Hittites, the Perizzites, the Hivites, and the Jebusites, who were not children of Israel;
Moff No Moff 1 KI book available
JPS All the people that were left of the Amorites, the Hittites, the Perizzites, the Hivites, and the Jebusites, who were not of the children of Israel;
ASV As for all the people that were left of the Amorites, the Hittites, the Perizzites, the Hivites, and the Jebusites, who were not of the children of Israel;
DRA All the people that were left of the Amorrhites, and Hethites, and Pherezites, and Hevites, and Jebusites, that are not of the children of Israel:
YLT The whole of the people that is left of the Amorite, the Hittite, the Perizzite, the Hivite, and the Jebusite, who [are] not of the sons of Israel —
Drby All the people that were left of the Amorites, the Hittites, the Perizzites, the Hivites, and the Jebusites, who were not of the children of Israel,
RV As for all the people that were left of the Amorites, the Hittites, the Perizzites, the Hivites, and the Jebusites, which were not of the children of Israel;
SLT All the people remaining of the Amorites, the Hittites, the Perizzites, the Hivites and the Jebusites, which were not of the sons of Israel;
Wbstr And all the people that were left of the Amorites, Hittites, Perizzites, Hivites, and Jebusites, who were not of the children of Israel,
KJB-1769 And all the people that were left of the Amorites, Hittites, Perizzites, Hivites, and Jebusites, which were not of the children of Israel,
KJB-1611 And all the people that were left of the Amorites, Hittittes, Perizzites, Hiuites, and Iebusites, which were not of the children of Israel,
(Modernised spelling is same as from KJB-1769 above)
Bshps And al the people that were left of the Amorites, Hethites, Pherezites, Heuites and Iebusites, whiche were not of the children of Israel,
(Modernised spelling is same as from KJB-1769 above, apart from marking of added words (and possibly capitalisation and punctuation))
Gnva Al the people that were left of the Amorites, Hittites, Perizzites, Hiuites, and Iebusites, which were not of the children of Israel:
(All the people that were left of the Amorites, Hittites, Perizzites, Hivites, and Yebusites, which were not of the children of Israel: )
Cvdl And all the remnaunt of the people of the Amorytes, Hethites, Pheresites, Heuites and Iebusites, which were not of the children of Israel,
(And all the remnant of the people of the Amorytes, Hittites, Perizzites, Hivites and Yebusites, which were not of the children of Israel,)
Wycl Salomon made tributaries `til to this dai al the puple, that lefte of Ammorreis, Etheis, and Fereseis, and Eueys, and Jebuseys, that ben not of the sones of Israel,
(Solomon made tributaries till to this day all the people, that left of Ammorreis, Hittites, and Fereseis, and Hivites, and Yebuseys, that been not of the sons of Israel,)
Luth Und alles übrige Volk von den Amoritern, Hethitern, Pheresitern, Hevitern und Jebusitern, die nicht von den Kindern Israel waren,
(And all/everything rest people from the Amoritern, Hethitern, Pheresitern, Hevitern and Yebusitern, the not from the children Israel were,)
ClVg Universum populum qui remanserat de Amorrhæis, et Hethæis, et Pherezæis, et Hevæis, et Jebusæis, qui non sunt de filiis Israël:[fn]
(Universum the_people who remanserat from/about Amorrhæis, and Hethæis, and Pherezæis, and Hevæis, and Yebusæis, who not/no are from/about to_the_children Israel: )
9.20 Universum. RAB. ubi supra. Qui non fuerat de filiis Isræl, fecit Pacificus noster tributarios, cum eis qui non sunt in filiorum numero; sed in servili conditione utitur ad proprium servitium. Tales licet in multis adversentur, tamen frequenter usibus serviunt Ecclesiæ, cum in præsenti tempore de rebus suis solatia præbent. De filiis. ID., ibid. Eos qui non ancillæ filii sunt, sed liberæ, etc., usque ad et in semitas justitiæ ducant.
9.20 Universum. RAB. where above. Who not/no had_been from/about to_the_children Israel, he_did Pacificus our tributarios, when/with to_them who not/no are in/into/on of_children number; but in/into/on servili conditione uses to own servitium. Tales licet in/into/on many adversentur, nevertheless frequenter usibus they_serve Assemblies/Churches, when/with in/into/on present at_the_time from/about things to_his_own alonetia beforebent. From/About to_the_children. ID., there. Eos who not/no handmaiden children are, but liberæ, etc., until to and in/into/on path justice ducant.
9:15-24 Solomon used forced labor to complete many building projects (4:6; 5:13-18; 9:20-23; 12:4, 18-19; cp. 1 Sam 8:10-18).
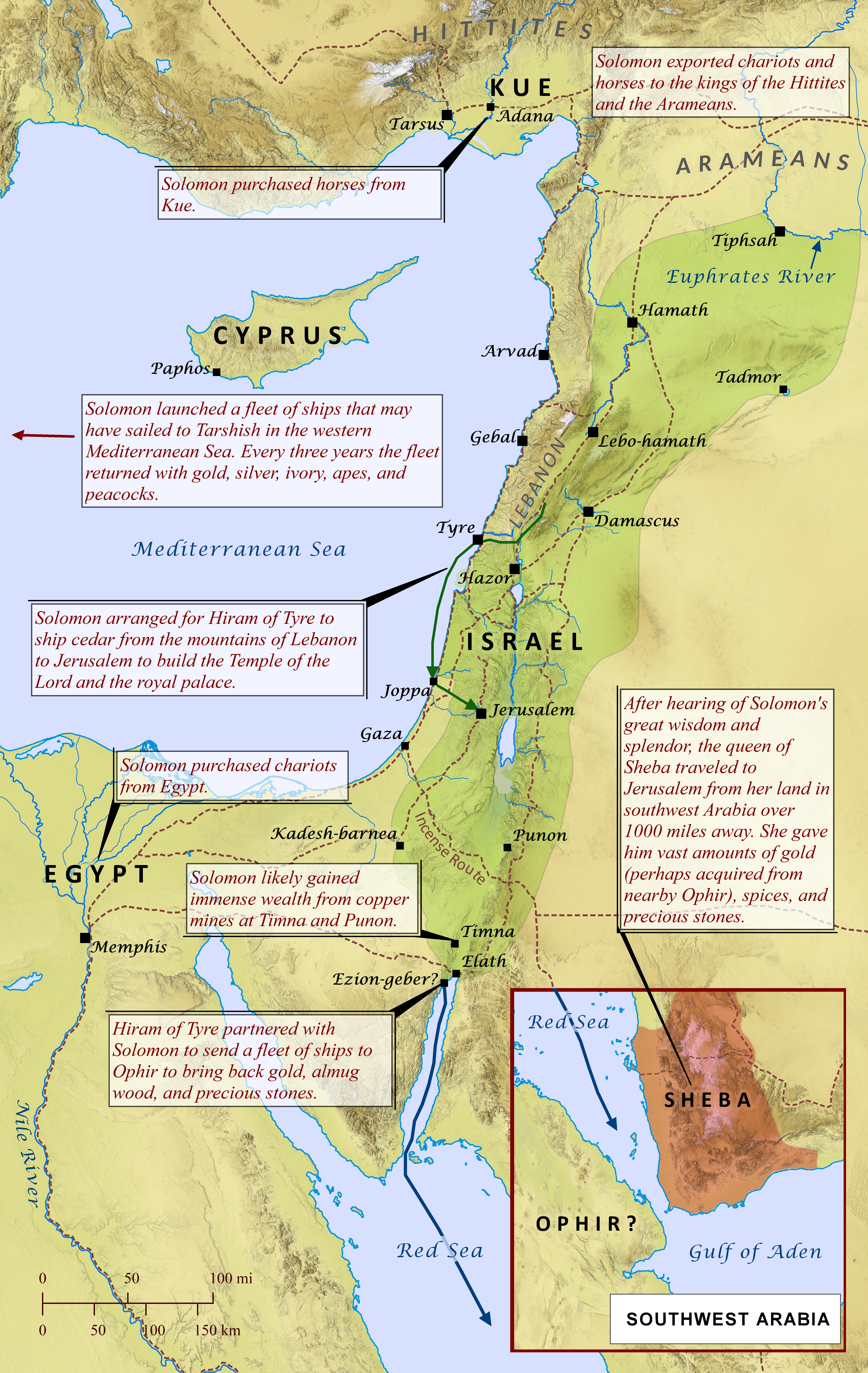
1 Kings 9-10; 2 Chronicles 2:1-18; 8:1-9:28
Near the beginning of Solomon’s reign, the Lord promised to bless him with great wisdom, riches, and honor (1 Kings 3:2-15), and the fulfillment of this promise led to great fame for Solomon throughout the Near East. Humanly speaking, Solomon had been set up for immense success by his father David, who passed on to him a powerful kingdom that stretched from the tip of the Red Sea to the Euphrates River (2 Samuel 8-10; 1 Chronicles 18-19; 2 Chronicles 8). During Solomon’s reign Israel controlled all land routes leading from Egypt and the Red Sea to the Aramean and Hittite nations to the north, and they also controlled the northern terminus of the great Incense Route leading from the peoples of southwest Arabia to the shores of the Mediterranean Sea at Gaza. Solomon appears to have capitalized on his strategic control over travel and shipping throughout the region by setting up a very lucrative international arms dealership, through which he paired chariots bought from Egypt with horses bought from Kue (the term sometimes translated as “Egypt” should probably be translated “Muzur,” a district near Kue) and sold them to the kings of the Hittites and Arameans. Solomon also likely gained immense wealth from very productive copper mines at Punon, Timna, and elsewhere (see “Southern Arabah Valley” map). All this won him great renown among all the rulers of the Near East, including the queen of Sheba, who traveled over a thousand miles to see for herself Solomon’s great wisdom and splendor. She brought with her luxurious gifts from her land, including spices, precious stones, and gold, which she may have obtained from nearby Ophir. Solomon also arranged for King Hiram of Tyre to provide him with cedar timbers from Lebanon to build the Temple of the Lord and his royal palace (2 Chronicles 2). The logs were bound into rafts, floated down to Joppa, and then disassembled and hauled up to Jerusalem. Solomon also launched ships to sail to faraway lands during his reign and bring back riches and exotic goods. Scholars have proposed various locations for the exact destination of the ships, and some have struggled to reconcile what can seem like confusion on the part of the biblical writers over the term Tarshish. But a careful reading of the biblical accounts indicates that there were probably two separate fleets of ships: the fleet of Hiram and Solomon’s fleet of ships of Tarshish. Both fleets are separately mentioned in 1 Kings 10:22, and the phrase “at sea with” may simply indicate that they were sailing at the same time but not necessarily together. Also, the list of goods brought back by Hiram’s fleet is somewhat different than the list of goods brought back by Solomon’s fleet (compare 1 Kings 10:11, 22; 2 Chronicles 8:17-18; 9:10, 21). Likewise, the wording of 2 Chronicles 8:17-18 is that Hiram “sent to [Solomon] by the hand of his servants ships and servants familiar with the sea,” but the implication seems to be that the ships remained Hiram’s, not Solomon’s, whereas the other fleet of ships of Tarshish appears to have belonged to Solomon, though the ships were manned by Hiram’s men as well (2 Chronicles 9:21). Thus, Hiram’s fleet set sail from Ezion-geber, traveled the length of the Red Sea, and acquired gold from Ophir. Solomon’s fleet, on the other hand, could have sailed either the Red Sea or the Mediterranean Sea, since the term ships of Tarshish seems to have been used at times to indicate a class of trading or refinery ships rather than a specific destination (see article for “Tarshish” map). It is also possible, however, that the term Tarshish referred to the ships’ actual destination, which during Solomon’s reign appears to have been located in the far western Mediterranean Sea. This is supported by isotopic studies of silver found in Israel during Solomon’s time, which have traced the source to Tharros on the island of Sardinia. This also fits well with the length of time given for the voyage of Solomon’s fleet, which returned every three years with their exotic goods.