Open Bible Data Home About News OET Key
OET OET-RV OET-LV ULT UST BSB MSB BLB AICNT OEB WEBBE WMBB NET LSV FBV TCNT T4T LEB BBE Moff JPS Wymth ASV DRA YLT Drby RV SLT Wbstr KJB-1769 KJB-1611 Bshps Gnva Cvdl TNT Wycl SR-GNT UHB BrLXX BrTr Related Topics Parallel Interlinear Reference Dictionary Search
ParallelVerse GEN EXO LEV NUM DEU JOB JOS JDG RUTH 1 SAM 2 SAM PSA AMOS HOS 1 KI 2 KI 1 CHR 2 CHR PROV ECC SNG JOEL MIC ISA ZEP HAB JER LAM YNA (JNA) NAH OBA DAN EZE EZRA EST NEH HAG ZEC MAL LAO GES LES ESG DNG 2 PS TOB JDT WIS SIR BAR LJE PAZ SUS BEL MAN 1 MAC 2 MAC 3 MAC 4 MAC YHN (JHN) MARK MAT LUKE ACTs YAC (JAM) GAL 1 TH 2 TH 1 COR 2 COR ROM COL PHM EPH PHP 1 TIM TIT 1 PET 2 PET 2 TIM HEB YUD (JUD) 1 YHN (1 JHN) 2 YHN (2 JHN) 3 YHN (3 JHN) REV
2 Sam Intro C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 C9 C10 C11 C12 C13 C14 C15 C16 C17 C18 C19 C20 C21 C22 C23 C24
2 Sam 12 V1 V2 V3 V4 V5 V6 V7 V8 V9 V10 V11 V12 V13 V14 V15 V16 V17 V18 V19 V20 V22 V23 V24 V25 V26 V27 V28 V29 V30 V31
Note: This view shows ‘verses’ which are not natural language units and hence sometimes only part of a sentence will be visible—click on any Bible version abbreviation down the left-hand side to see the verse in more of its context. Normally the OET discourages the reading of individual ‘verses’, but this view is only designed as a tool for doing comparisons of different translations—the older translations are further down the page (so you can read up from the bottom to trace the English translation history). The OET segments on this page are still very early looks into the unfinished texts of the Open English Translation of the Bible—please double-check these texts in advance before using in public.
Text critical issues=small word differences Clarity of original=clear Importance to us=normal (All still tentative.)
OET (OET-RV) His servants queried him, “We don’t understand what just happened: when the baby was alive you fasted and wept, but yet when he dies, you get up and have a meal?”![]()
OET-LV servants_of_his And_they_said to_him/it what the_thing the_this which you_have_done in_account_of the_child was_alive you_fasted and_wept and_just_as_that he_died the_child you_arose and_she/it_ate food.
![]()
UHB וַיֹּאמְר֤וּ עֲבָדָיו֙ אֵלָ֔יו מָֽה־הַדָּבָ֥ר הַזֶּ֖ה אֲשֶׁ֣ר עָשִׂ֑יתָה בַּעֲב֞וּר הַיֶּ֤לֶד חַי֙ צַ֣מְתָּ וַתֵּ֔בְךְּ וְכַֽאֲשֶׁר֙ מֵ֣ת הַיֶּ֔לֶד קַ֖מְתָּ וַתֹּ֥אכַל לָֽחֶם׃ ‡
(vayyoʼmərū ˊₐⱱādāyv ʼēlāyv māh-haddāⱱār hazzeh ʼₐsher ˊāsitāh baˊₐⱱūr hayyeled ḩay ʦamtā vattēⱱəⱪə vəkaʼₐsher mēt hayyeled qamtā vattoʼkal lāḩem.)
Key: khaki:verbs.
Note: Automatic aligning of the OET-RV to the LV is done by some temporary software, hence the OET-RV alignments are incomplete (and may occasionally be wrong).
BrLXX Καὶ εἶπαν οἱ παῖδες αὐτοῦ πρὸς αὐτόν, τί τὸ ῥῆμα τοῦτο ὃ ἐποίησας ἕνεκα τοῦ παιδαρίου; ἔτι ζῶντος ἐνήστευες καὶ ἔκλαιες καὶ ἠγρύπνεις, καὶ ἡνίκα ἀπέθανε τὸ παιδάριον, ἀνέστης, καὶ ἔφαγες ἄρτον, καὶ πέπωκας;
(Kai eipan hoi paides autou pros auton, ti to ɽaʸma touto ho epoiaʸsas heneka tou paidariou; eti zōntos enaʸsteues kai eklaies kai aʸgrupneis, kai haʸnika apethane to paidarion, anestaʸs, kai efages arton, kai pepōkas; )
BrTr And his servants said to him, What is this thing that thou hast done concerning the child? while it was yet living thou didst fast, and weep, and watch: and when the child was dead thou didst rise up, and didst eat bread, and drink.
ULT And his servants said to him, “What is this thing that you have done? For the sake of the living child you fasted and wept, but when the child died, you arose and ate bread.”
UST Then his servants said to him, “We do not understand why you have done this! While the baby was still alive, you cried for him and refused to eat. But now that the baby has died, you have gotten up and eaten some food!”
BSB “What [is] this you have done?” his servants asked. “While the child was alive, you fasted and wept, but when he died, you got up and ate.”
MSB (Same as BSB above)
OEB No OEB 2 SAM book available
WEBBE Then his servants said to him, “What is this that you have done? You fasted and wept for the child while he was alive, but when the child was dead, you rose up and ate bread.”
WMBB (Same as above)
NET His servants said to him, “What is this that you have done? While the child was still alive, you fasted and wept. Once the child was dead you got up and ate food!”
LSV And his servants say to him, “What [is] this thing you have done? Because of the living boy you have fasted and you weep, and when the boy is dead you have risen and eat bread.”
FBV “Why are you acting like this?” his officials asked him. “While the child was still alive, you fasted and cried aloud, but now that he's dead, you get up and eat.”
T4T Then his servants said to him, “We do not understand [RHQ] why you have done this! While the baby was still alive, you cried for him and refused to eat anything. But now that the baby has died, you are not crying any more! You got up and ate some food!”
LEB Then his servants said to him, “What is this thing that you have done? While the child was alive, you fasted and wept; now that the child has died, you get up and eat food!”
BBE Then his servants said to him, Why have you been acting in this way? you were weeping and going without food while the child was still living; but when the child was dead, you got up and had a meal.
Moff No Moff 2 SAM book available
JPS Then said his servants unto him: 'What thing is this that thou hast done? thou didst fast and weep for the child, while it was alive; but when the child was dead, thou didst rise and eat bread.'
ASV Then said his servants unto him, What thing is this that thou hast done? thou didst fast and weep for the child, while it was alive; but when the child was dead, thou didst rise and eat bread.
DRA And his servants said to him: What thing is this that thou hast done? thou didst fast and weep for the child, while it was alive, but when the child was dead, thou didst rise up, and eat bread.
YLT And his servants say unto him, 'What [is] this thing thou hast done? because of the living lad thou hast fasted and dost weep, and when the lad is dead thou hast risen and dost eat bread.'
Drby And his servants said to him, What thing is this which thou hast done? thou didst fast and weep for the child alive; but as soon as the child is dead, thou dost rise and eat bread.
RV Then said his servants unto him, What thing is this that thou hast done? thou didst fast and weep for the child, while it was alive; but when the child was dead, thou didst rise and eat bread.
(Then said his servants unto him, What thing is this that thou/you hast done? thou/you didst/did fast and weep for the child, while it was alive; but when the child was dead, thou/you didst/did rise and eat bread. )
SLT And his servants will say to him, What this word which thou didst? for sake of the child living thou didst fast and weep, and when the child died thou didst rise and thou wilt eat bread.
Wbstr Then said his servants to him, What thing is this that thou hast done? thou didst fast and weep for the child, while it was alive; but after the child was dead, thou didst rise and eat bread.
KJB-1769 Then said his servants unto him, What thing is this that thou hast done? thou didst fast and weep for the child, while it was alive; but when the child was dead, thou didst rise and eat bread.
(Then said his servants unto him, What thing is this that thou/you hast done? thou/you didst/did fast and weep for the child, while it was alive; but when the child was dead, thou/you didst/did rise and eat bread. )
KJB-1611 Then said his seruants vnto him, What thing is this that thou hast done? thou didst fast and weepe for the childe, while it was aliue, but when the childe was dead, thou didst rise and eat bread.
(Modernised spelling is same as from KJB-1769 above, apart from punctuation)
Bshps Then said his seruauntes vnto him: What thing is this that thou hast done? Thou diddest fast & weepe for the childe while it was alyue, & assoone as it was dead, thou diddest ryse vp & eate meate.
(Then said his servants unto him: What thing is this that thou/you hast done? Thou/You didst/did fast and weep for the child while it was alive, and as soon as it was dead, thou/you didst/did rise up and eat meat.)
Gnva Then saide his seruants vnto him, What thing is this, that thou hast done? thou diddest fast and weepe for the childe while it was aliue, but when the childe was dead, thou diddest rise vp, and eate meate.
(Then said his servants unto him, What thing is this, that thou/you hast done? thou/you didst/did fast and weep for the child while it was alive, but when the child was dead, thou/you didst/did rise up, and eat meat. )
Cvdl Then sayde his seruauntes vnto him: What maner of thinge is this that thou doest? Whan the childe was alyue, thou fastedst and weptest: but now that it is deed, thou stodest up and eatest?
(Then said his servants unto him: What manner of thing is this that thou/you doest? When the child was alive, thou/you fasted and weptst: but now that it is deed, thou/you stoodst up and eatest?)
Wycl Sothely his seruauntis seiden to hym, What is the word which thou hast do? Thou fastidist, and weptist for the yong child, whanne he lyuede yit; sotheli whanne the child was deed, thou risidist and etist breed?
(Sothely his servants said to him, What is the word which thou/you hast do? Thou/You fastidist, and weptist for the young child, when he lived yit; truly when the child was deed, thou/you rised and etist breed?)
Luth Da sprachen seine Knechte zu ihm: Was ist das für ein Ding, das du tust? Da das Kind lebte, fastetest du und weinetest; nun es aber gestorben ist, stehest du auf und issest?
(So said his servant(s) to/for him: What is the for/in_favour_of a thing, the you(sg) do/act? So the child lived, fastingest you(sg) and criedst; now it but died is, standst you(sg) on/in/to and issest?)
ClVg Dixerunt autem ei servi sui: Quis est sermo quem fecisti? propter infantem, cum adhuc viveret, jejunasti et flebas: mortuo autem puero, surrexisti, et comedisti panem.
(They_said however to_him slaves self: Who it_is speech which you_did? because infantem, when/with still would_live, yeyunasti and flebas: dead however to_a_boy, surrexisti, and comedisti bread/food. )
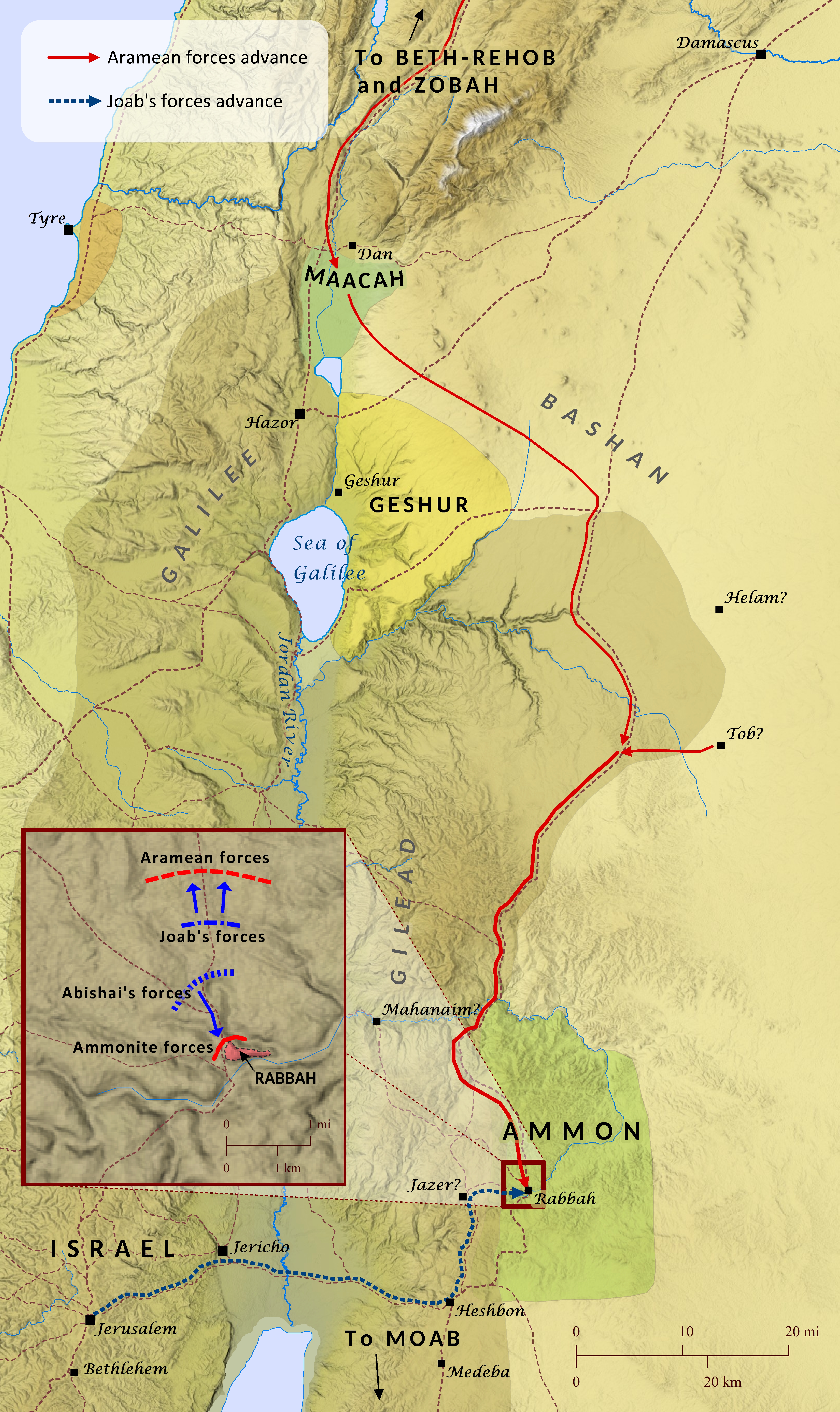
2 Samuel 8:1-8; 10:1-19; 12:21-31; 1 Chronicles 18:2-11; 19:1-19; 20:1-3
The accounts of David’s greatest military victories stand like bookends around the record of David’s most grievous sins. Sometime after David brought the Ark of the Covenant into Jerusalem and the Lord promised to establish his dynasty over Israel, David achieved a series of victories over virtually all of Israel’s neighboring nations. These began with David’s capture of Metheg-ammah (likely Gath) and all of Philistia and was followed by his victory over Moab. Then Nahash king of Ammon died, and David sent envoys to express his condolences to Nahash’s son Hanun, who had now become king. Hanun, however, intentionally humiliated David’s envoys, shaving off half their beards and cutting off the bottom half of their garments before sending them back to Israel. When David heard of it, he sent word to his envoys to remain at Jericho until their beards grew back. In the meantime, the Ammonites called upon several Aramean nations to help them fight against Israel, which was likely their original intent for humiliating David’s envoys. Warriors came from Beth-rehob and Zobah, which lay between Israel and Hamath farther north, as well as from Maacah (see “Geshur and Maacah” map) and Tob. The writer of 1 Chronicles also notes that soldiers came from Mesopotamia as well. David sent his commander Joab to fight this coalition at Rabbah. The writer of 1 Chronicles consistently speaks of the battle occurring at Medeba, rather than Rabbah, but the town of Medeba south of Heshbon seems an unlikely location for the battle. Perhaps Rabbah was also referred to at times as Medeba. In any case, Joab and his brother Abishai divided their forces into two groups, with Joab leading the fight against the Arameans to the north and Abishai leading the fight against the Ammonites just outside the gates of Rabbah. As Joab advanced, the Arameans fled, which in turn led the Ammonites to retreat behind the walls of Rabbah. After this Joab (and probably his forces) returned home to Israel. But the Arameans regrouped and added more troops from Aramean nations beyond the Euphrates River. David met them in battle at Helam (likely modern Alma) and won a great victory over them, even killing their commander Shobah (or Shophach). After this the Arameans made peace with Israel. Sometime later David also subjugated the Edomites, who lived to the south of Moab. It was likely sometime after this that David engaged in adultery with the wife of Uriah, one of his own valiant warriors (see “David’s Mighty Men” map), and then he tried to cover up his sin by arranging for Uriah’s death in battle. His sin was later exposed by Nathan the prophet, and David repented. After this Joab returned to Rabbah to finish capturing the city, and when victory was close at hand he called for David to come and finish taking the city. Thus the Ammonites became subject to Israel as well. From all these conquered nations David took many spoils and dedicated them to the Lord’s service, including great amounts of bronze from the towns of Tebah (also called Betah and Tibhath), Berothai, and Cun.
The Battle with the Ammonites and the Arameans
The Battle with the Arameans
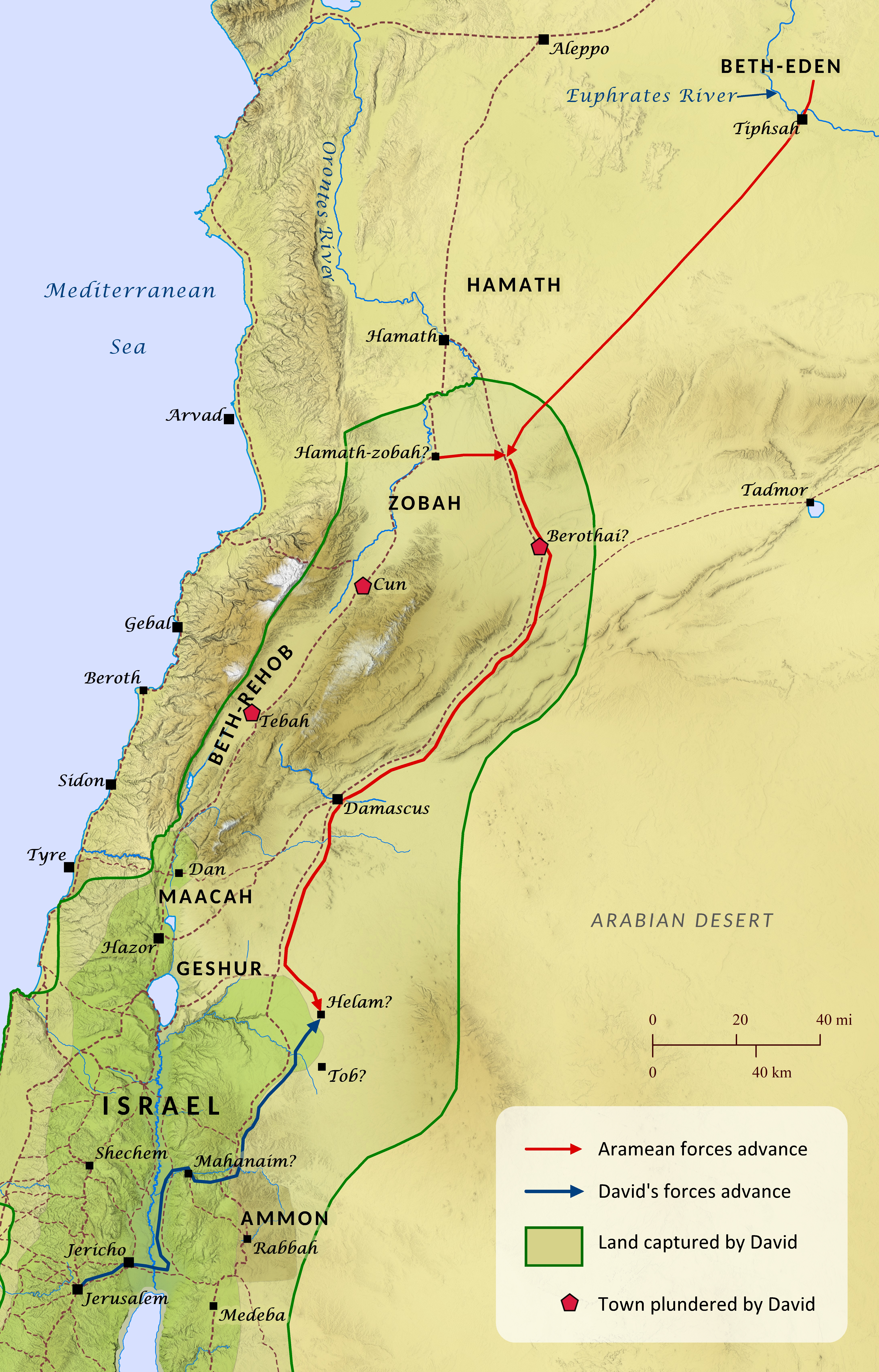
2 Samuel 8:1-8; 10:1-19; 12:21-31; 1 Chronicles 18:2-11; 19:1-19; 20:1-3
The accounts of David’s greatest military victories stand like bookends around the record of David’s most grievous sins. Sometime after David brought the Ark of the Covenant into Jerusalem and the Lord promised to establish his dynasty over Israel, David achieved a series of victories over virtually all of Israel’s neighboring nations. These began with David’s capture of Metheg-ammah (likely Gath) and all of Philistia and was followed by his victory over Moab. Then Nahash king of Ammon died, and David sent envoys to express his condolences to Nahash’s son Hanun, who had now become king. Hanun, however, intentionally humiliated David’s envoys, shaving off half their beards and cutting off the bottom half of their garments before sending them back to Israel. When David heard of it, he sent word to his envoys to remain at Jericho until their beards grew back. In the meantime, the Ammonites called upon several Aramean nations to help them fight against Israel, which was likely their original intent for humiliating David’s envoys. Warriors came from Beth-rehob and Zobah, which lay between Israel and Hamath farther north, as well as from Maacah (see “Geshur and Maacah” map) and Tob. The writer of 1 Chronicles also notes that soldiers came from Mesopotamia as well. David sent his commander Joab to fight this coalition at Rabbah. The writer of 1 Chronicles consistently speaks of the battle occurring at Medeba, rather than Rabbah, but the town of Medeba south of Heshbon seems an unlikely location for the battle. Perhaps Rabbah was also referred to at times as Medeba. In any case, Joab and his brother Abishai divided their forces into two groups, with Joab leading the fight against the Arameans to the north and Abishai leading the fight against the Ammonites just outside the gates of Rabbah. As Joab advanced, the Arameans fled, which in turn led the Ammonites to retreat behind the walls of Rabbah. After this Joab (and probably his forces) returned home to Israel. But the Arameans regrouped and added more troops from Aramean nations beyond the Euphrates River. David met them in battle at Helam (likely modern Alma) and won a great victory over them, even killing their commander Shobah (or Shophach). After this the Arameans made peace with Israel. Sometime later David also subjugated the Edomites, who lived to the south of Moab. It was likely sometime after this that David engaged in adultery with the wife of Uriah, one of his own valiant warriors (see “David’s Mighty Men” map), and then he tried to cover up his sin by arranging for Uriah’s death in battle. His sin was later exposed by Nathan the prophet, and David repented. After this Joab returned to Rabbah to finish capturing the city, and when victory was close at hand he called for David to come and finish taking the city. Thus the Ammonites became subject to Israel as well. From all these conquered nations David took many spoils and dedicated them to the Lord’s service, including great amounts of bronze from the towns of Tebah (also called Betah and Tibhath), Berothai, and Cun.
The Battle with the Ammonites and the Arameans
The Battle with the Arameans