Open Bible Data Home About News OET Key
OET OET-RV OET-LV ULT UST BSB MSB BLB AICNT OEB WEBBE WMBB NET LSV FBV TCNT T4T LEB BBE Moff JPS Wymth ASV DRA YLT Drby RV SLT Wbstr KJB-1769 KJB-1611 Bshps Gnva Cvdl TNT Wycl SR-GNT UHB BrLXX BrTr Related Topics Parallel Interlinear Reference Dictionary Search
ParallelVerse GEN EXO LEV NUM DEU JOB JOS JDG RUTH 1 SAM 2 SAM PSA AMOS HOS 1 KI 2 KI 1 CHR 2 CHR PROV ECC SNG JOEL MIC ISA ZEP HAB JER LAM YNA (JNA) NAH OBA DAN EZE EZRA EST NEH HAG ZEC MAL LAO GES LES ESG DNG 2 PS TOB JDT WIS SIR BAR LJE PAZ SUS BEL MAN 1 MAC 2 MAC 3 MAC 4 MAC YHN (JHN) MARK MAT LUKE ACTs YAC (JAM) GAL 1 TH 2 TH 1 COR 2 COR ROM COL PHM EPH PHP 1 TIM TIT 1 PET 2 PET 2 TIM HEB YUD (JUD) 1 YHN (1 JHN) 2 YHN (2 JHN) 3 YHN (3 JHN) REV
1 Sam Intro C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 C9 C10 C11 C12 C13 C14 C15 C16 C17 C18 C19 C20 C21 C22 C23 C24 C25 C26 C27 C28 C29 C30 C31
1 Sam 30 V1 V2 V3 V4 V5 V6 V7 V8 V9 V10 V11 V12 V13 V14 V15 V16 V17 V18 V19 V20 V21 V22 V23 V24 V25 V26 V27 V29 V30 V31
Note: This view shows ‘verses’ which are not natural language units and hence sometimes only part of a sentence will be visible—click on any Bible version abbreviation down the left-hand side to see the verse in more of its context. Normally the OET discourages the reading of individual ‘verses’, but this view is only designed as a tool for doing comparisons of different translations—the older translations are further down the page (so you can read up from the bottom to trace the English translation history). The OET segments on this page are still very early looks into the unfinished texts of the Open English Translation of the Bible—please double-check these texts in advance before using in public.
Text critical issues=none Clarity of original=clear Importance to us=normal (All still tentative.)
OET (OET-RV) Aroer, Sifmot, Eshtemoa,![]()
OET-LV And_to_those in/on/at/with_ˊArōˊēr and_for_those in/on/at/with_Sifmōt and_for_those in/on/at/with_ʼEshtəmoˊa.
![]()
UHB וְלַאֲשֶׁ֧ר בַּעֲרֹעֵ֛ר וְלַאֲשֶׁ֥ר בְּשִֽׂפְמ֖וֹת וְלַאֲשֶׁ֥ר בְּאֶשְׁתְּמֹֽעַ׃ס ‡
(vəlaʼₐsher baˊₐroˊēr vəlaʼₐsher bəsifmōt vəlaʼₐsher bəʼeshtəmoˊa.§)
Key: .
Note: Automatic aligning of the OET-RV to the LV is done by some temporary software, hence the OET-RV alignments are incomplete (and may occasionally be wrong).
BrLXX καὶ τοῖς ἐν Ἀροὴρ, καὶ τοῖς ἐν Ἀμμαδὶ, καὶ τοῖς ἐν Σαφὶ, καὶ τοῖς ἐν Ἐσθιὲ,
(kai tois en Aroaʸr, kai tois en Ammadi, kai tois en Safi, kai tois en Esthie, )
BrTr And to those in Aroer, and to those in Ammadi, and to those in Saphi, and to those in Esthie,
ULT and to who was in Aroer and to who was in Siphmoth and to who was in Eshtemoa
UST Aroer, Siphmoth, Eshtemoa,
BSB to those in Aroer, Siphmoth, and Eshtemoa;
MSB (Same as BSB above)
OEB No OEB 1 SAM book available
WEBBE to those who were in Aroer, to those who were in Siphmoth, to those who were in Eshtemoa,
WMBB (Same as above)
NET for those in Aroer, Siphmoth, Eshtemoa,
LSV and to those in Aroer, and to those in Siphmoth, and to those in Eshtemoa,
FBV Aroer, Siphmoth, Eshtemoa,
T4T Aroer, Siphmoth, Eshtemoa,
LEB for those in Aroer, for those in Siphmoth, for those in Eshtemoa,
BBE And to those in Arara and Eshtemoa
Moff No Moff 1 SAM book available
JPS and to them that were in Aroer, and to them that were in Siphmoth, and to them that were in Eshtemoa;
ASV and to them that were in Aroer, and to them that were in Siphmoth, and to them that were in Eshtemoa,
DRA And to them that were in Aroer and that were in Sephamoth, and that were in Esthamo,
YLT and to those in Aroer, and to those in Siphmoth, and to those in Eshtemoa,
Drby and to those in Aroer, and to those in Siphmoth, and to those in Eshtemoa,
RV and to them which were in Aroer, and to them which were in Siphmoth, and to them which were in Eshtemoa;
SLT And to those in Aroer, and to those in Siphmoth, and to those in Eshtemoa.
Wbstr And to them who were in Aroer, and to them who were in Siphmoth, and to them who were in Eshtemoa,
KJB-1769 And to them which were in Aroer, and to them which were in Siphmoth, and to them which were in Eshtemoa,
KJB-1611 And to them which were in Aroer, and to them which were in Siphmoth, and to them which were in Eshtemoa,
(Same as from KJB-1769 above)
Bshps To them of Aroer, to them of Sephamoth, to them of Esthema,
Gnva And to them of Aroer, and to them of Siphmoth, and to them of Eshtemoa,
Cvdl vnto them at Aroer, vnto them at Siphamoth, vnto them at Eschemoa,
(unto them at Aroer, unto them at Siphamoth, unto them at Eschemoa,)
Wycl and that weren in Jether, and that weren in Aroer, and that weren in Sephamoth, and that weren in Escama, and that weren in Rethala,
(and that were in Yether, and that were in Aroer, and that were in Sephamoth, and that were in Escama, and that were in Rethala,)
Luth denen zu Aroer, denen zu Siphamoth, denen zu Esthemoa,
(those to/for Aroer, those to/for Siphamoth, those to/for Esthemoa,)
ClVg et qui in Aroër, et qui in Sephamoth, et qui in Esthamo,
(and who in/into/on Aroër, and who in/into/on Sephamoth, and who in/into/on Esthamo, )
30:21-31 David generously divided the spoils among those who participated in the battle and those who were too exhausted to take part.
Connecting Statement:
The writer continues the list that began in [1 Samuel 30:27](../30/27.md) of towns whose elders received gifts from David.
Note 1 topic: translate-names
(Occurrence 0) Aroer … Siphmoth … Eshtemoa
(Some words not found in UHB: and,to,those in/on/at/with,Aroer and,for,those in/on/at/with,Siphmoth and,for,those in/on/at/with,Eshtemoa )
These are names of towns.
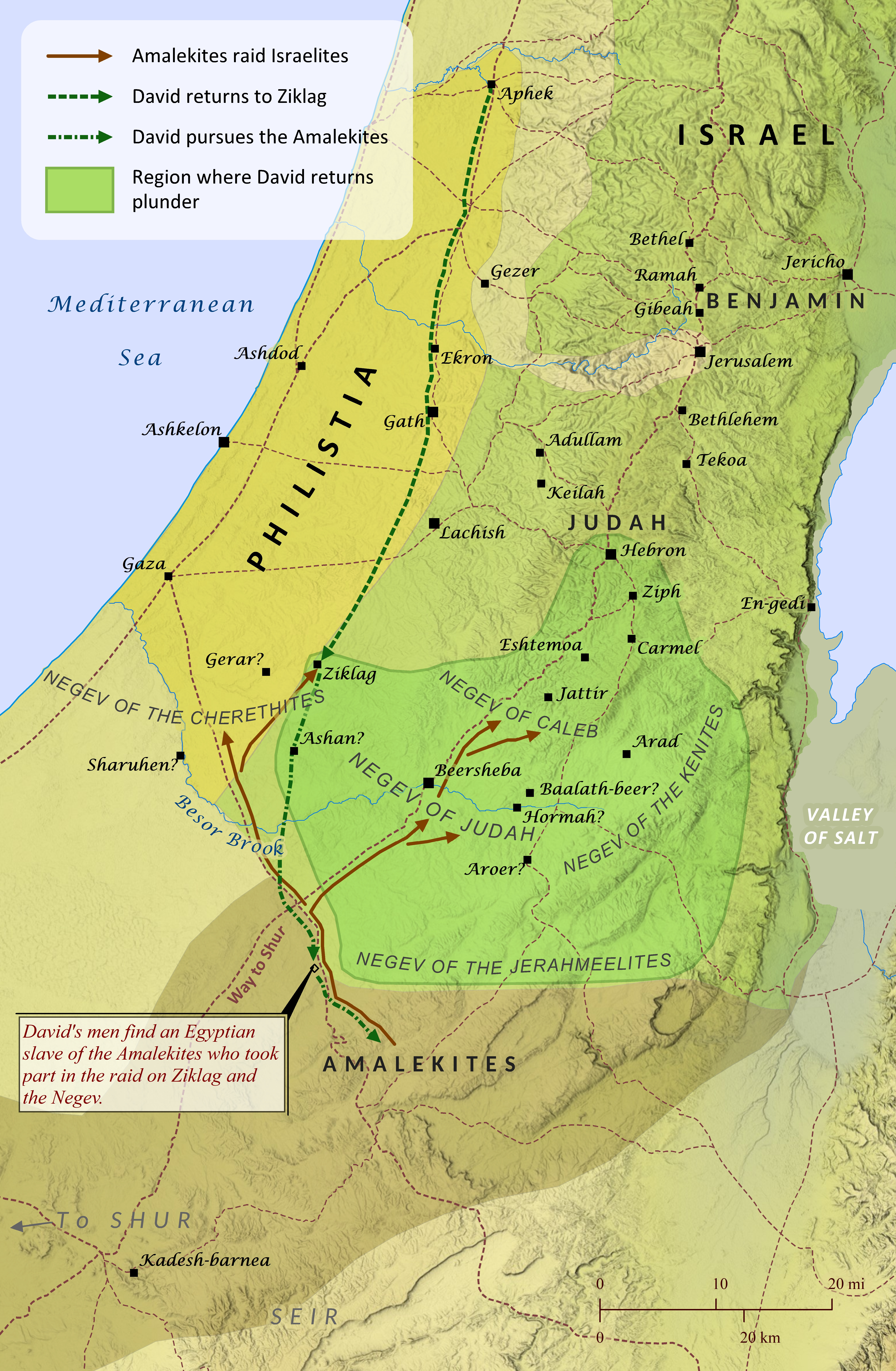
1 Samuel 27-30
The Bible makes it clear that David was specially chosen and raised up by God to be Israel’s next king (1 Samuel 16:1-13), but Scripture also makes it clear that David’s rise to power came about through several shrewd maneuvers on his part. Among these shrewd maneuvers were David’s clandestine attacks on hostile peoples to the south of Judah and his distribution of Amalekite plunder among the towns of southern Judah. These actions by David strengthened southern Judah against their enemies and no doubt cemented Judah’s loyalty to him as a champion for their well-being. It should be noted that the Bible affirms King Saul’s effectiveness at attacking Israel’s enemies (1 Samuel 14:47-52), especially the Philistines, but various character flaws and bad choices by Saul led to God’s selection of David as the one who would replace Saul as king (1 Samuel 13:1-23; 15:1-35). Because of this, Saul grew jealous of David and sought to kill him, forcing David to seek refuge among various towns throughout Judah and even in Philistia (1 Samuel 16-27). After seeking asylum in Gath for a time, David asked King Achish if he could move his family outside of the city, and Achish gave him the border town of Ziklag. Apparently Achish still tried to keep tabs on David’s activities, however, periodically asking him where he had recently raided. David would answer that he had been raiding the Negev of Judah, the Negev of the Jerahmeelites (see 1 Chronicles 2:42), or the Negev of the Kenites (Judges 1:16; see “Saul Attacks the Amalekites” map), which were inhabited by people loyal to Israel. In reality, however, David had been raiding the Amalekites (longtime enemies of Israel; see Genesis 14:7; Exodus 17; Numbers 13:29; 14:45; Deuteronomy 25:17-19), the Geshurites, and the Girzites. These peoples lived to the south of Israel’s territory and along the Way to Shur leading to Egypt. Soon after this King Achish mustered his men at Aphek to head to battle against the Israelites in the Jezreel Valley further north. As they set off for battle and the other Philistine rulers realized David and his men were accompanying them, the rulers protested and insisted that David would turn on them in battle. So Achish sent David home and continued on to Jezreel. When David and his men arrived at Ziklag, they found that Amalekites had burned the town and carried off their wives and children. David and his men set out to attack the Amalekites and recover their families. When they reached the Besor Brook, two hundred of the men were too exhausted to go on and stayed with the other equipment while the remaining four hundred men continued toward Amalek. Along the way, David’s men found an abandoned Egyptian slave of the Amalekites who had participated in the attack on Ziklag and on other locations in southern Judah. The man led David’s men to the Amalekite camp, and then they attacked the Amalekites and retrieved all the captives and plunder that had been taken. Only four hundred Amalekites were able to escape, fleeing on camels. David’s men then rejoined their fellow warriors at the Besor Brook and returned to Ziklag. David sent some of the plunder to the leaders of Ziklag as well as to other towns where David had roamed during the time when he was fleeing from Saul. Many of these towns were located in territory formerly inhabited by Amalekites (Numbers 13:29; 14:25, 43-45; Judges 1:16; see also Judges 12:15) and were likely among those attacked by the Amalekites and other hostile peoples to the south. After this, the Amalekites are only mentioned again in Scripture to note that David killed an Amalekite who himself had killed Saul (to fulfill what Saul requested of him), to note that Amalekite plunder was among the treasures that David dedicated to the Temple of the Lord (2 Samuel 8:9-12), and to recount how in the days of Hezekiah some Simeonites went to Mount Seir and destroyed the remnant of Amalekites that had survived (1 Chronicles 4:42-43).