Open Bible Data Home About News OET Key
OET OET-RV OET-LV ULT UST BSB MSB BLB AICNT OEB WEBBE WMBB NET LSV FBV TCNT T4T LEB BBE Moff JPS Wymth ASV DRA YLT Drby RV SLT Wbstr KJB-1769 KJB-1611 Bshps Gnva Cvdl TNT Wycl SR-GNT UHB BrLXX BrTr Related Topics Parallel Interlinear Reference Dictionary Search
ParallelVerse GEN EXO LEV NUM DEU JOB JOS JDG RUTH 1 SAM 2 SAM PSA AMOS HOS 1 KI 2 KI 1 CHR 2 CHR PROV ECC SNG JOEL MIC ISA ZEP HAB JER LAM YNA (JNA) NAH OBA DAN EZE EZRA EST NEH HAG ZEC MAL LAO GES LES ESG DNG 2 PS TOB JDT WIS SIR BAR LJE PAZ SUS BEL MAN 1 MAC 2 MAC 3 MAC 4 MAC YHN (JHN) MARK MAT LUKE ACTs YAC (JAM) GAL 1 TH 2 TH 1 COR 2 COR ROM COL PHM EPH PHP 1 TIM TIT 1 PET 2 PET 2 TIM HEB YUD (JUD) 1 YHN (1 JHN) 2 YHN (2 JHN) 3 YHN (3 JHN) REV
2 Ki Intro C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 C9 C10 C11 C12 C13 C14 C15 C16 C17 C18 C19 C20 C21 C22 C23 C24 C25
2 Ki 18 V1 V2 V3 V4 V5 V6 V7 V8 V10 V11 V12 V13 V14 V15 V16 V17 V18 V19 V20 V21 V22 V23 V24 V25 V26 V27 V28 V29 V30 V31 V32 V33 V34 V35 V36 V37
Note: This view shows ‘verses’ which are not natural language units and hence sometimes only part of a sentence will be visible—click on any Bible version abbreviation down the left-hand side to see the verse in more of its context. Normally the OET discourages the reading of individual ‘verses’, but this view is only designed as a tool for doing comparisons of different translations—the older translations are further down the page (so you can read up from the bottom to trace the English translation history). The OET segments on this page are still very early looks into the unfinished texts of the Open English Translation of the Bible—please double-check these texts in advance before using in public.
Text critical issues=none Clarity of original=clear Importance to us=normal (All still tentative.)
OET (OET-RV) Then in the fourth year of King Hizkiyah’s reign (it was the seventh year of Elah’s son Hoshea’s reign over Yisrael), the Assyrian King Shalmaneser had attacked Shomron (Samaria) and besieged it.![]()
OET-LV and_he/it_was in/on/at/with_year the_fourth to/for_the_king Ḩizqiyyāh it the_year the_seventh of_Hōshēˊa the_son_of ʼĒlāh the_king_of Yisrāʼēl/(Israel) Shalmanʼeşer he_came_up the_king_of ʼAshshūr on Shomrōn and_he/it_laid_siege against_it.
![]()
UHB וַֽיְהִ֞י בַּשָּׁנָ֤ה הָֽרְבִיעִית֙ לַמֶּ֣לֶךְ חִזְקִיָּ֔הוּ הִ֚יא הַשָּׁנָ֣ה הַשְּׁבִיעִ֔ית לְהוֹשֵׁ֥עַ בֶּן־אֵלָ֖ה מֶ֣לֶךְ יִשְׂרָאֵ֑ל עָלָ֞ה שַׁלְמַנְאֶ֧סֶר מֶֽלֶךְ־אַשּׁ֛וּר עַל־שֹׁמְר֖וֹן וַיָּ֥צַר עָלֶֽיהָ׃ ‡
(vayəhiy bashshānāh hārəⱱīˊīt lammelek ḩizqiyyāhū hiyʼ hashshānāh hashshəⱱīˊit ləhōshēˊa ben-ʼēlāh melek yisrāʼēl ˊālāh shalmanʼeşer melek-ʼashshūr ˊal-shomrōn vayyāʦar ˊāleyhā.)
Key: khaki:verbs.
Note: Automatic aligning of the OET-RV to the LV is done by some temporary software, hence the OET-RV alignments are incomplete (and may occasionally be wrong).
BrLXX Καὶ ἐγένετο ἐν τῷ ἔτει τῷ τετάρτῳ βασιλεῖ Ἐζεκίᾳ, αὐτὸς ἐνιαυτὸς ὁ ἕβδομος τῷ Ὠσηὲ υἱῷ Ἠλὰ βασιλεῖ Ἰσραήλ, ἀνέβη Σαλαμανασσὰρ βασιλεὺς Ἀσσυρίων ἐπὶ Σαμάρειαν, καὶ ἐπολιόρκει ἐπʼ αὐτὴν,
(Kai egeneto en tōi etei tōi tetartōi basilei Ezekia, autos eniautos ho hebdomos tōi Ōsaʸe huiōi Aʸla basilei Israaʸl, anebaʸ Salamanassar basileus Assuriōn epi Samareian, kai epoliorkei epʼ autaʸn, )
BrTr And it came to pass in the fourth year of king Ezekias (this is the seventh year of Osee son of Ela king of Israel,) that Salamanassar king of the Assyrians came up against Samaria, and besieged it.
ULT And it happened in the fourth year of King Hezekiah—it was the seventh year of Hoshea the son of Elah, the king of Israel—Shalmaneser the king of Assyria went up against Samaria, and he laid siege against it.
UST After King Hezekiah had been ruling Judah for almost four years, and when King Hoshea had been ruling Israel for almost seven years, the army of King Shalmaneser of Assyria invaded Israel and surrounded the city of Samaria.
BSB In the fourth year of Hezekiah’s reign, which was the seventh year of the reign of Hoshea son of Elah over Israel, Shalmaneser king of Assyria marched against Samaria and besieged it.
MSB (Same as BSB above)
OEB No OEB 2 KI book available
WEBBE In the fourth year of King Hezekiah, which was the seventh year of Hoshea son of Elah king of Israel, Shalmaneser king of Assyria came up against Samaria and besieged it.
WMBB (Same as above)
NET In the fourth year of King Hezekiah’s reign (it was the seventh year of the reign of Israel’s King Hoshea, son of Elah), King Shalmaneser of Assyria marched up against Samaria and besieged it.
LSV And it comes to pass, in the fourth year of King Hezekiah—it [is] the seventh year of Hoshea son of Elah, king of Israel—Shalmaneser king of Asshur has come up against Samaria and lays siege to it,
FBV In the fourth year of Hezekiah's reign, equivalent to the seventh year of the reign of Hoshea, son of Elah, king of Israel, Shalmaneser, king of Assyria, attacked Samaria, besieging it.
T4T After King Hezekiah had been ruling Judah for almost four years, and when King Hoshea had been ruling Israel for almost seven years, the army of King Shalmaneser of Assyria invaded Israel and surrounded Samaria city.
LEB It happened in the fourth year of King Hezekiah, that is, the seventh year of Hoshea the son of Elah king of Israel, Shalmaneser king of Assyria came against Samaria and laid siege against her.
BBE Now in the fourth year of King Hezekiah, which was the seventh year of Hoshea, son of Elah, king of Israel, Shalmaneser, king of Assyria, came up against Samaria, shutting it in with his armies.
Moff No Moff 2 KI book available
JPS And it came to pass in the fourth year of king Hezekiah, which was the seventh year of Hoshea son of Elah king of Israel, that Shalmaneser king of Assyria came up against Samaria, and besieged it.
ASV And it came to pass in the fourth year of king Hezekiah, which was the seventh year of Hoshea son of Elah king of Israel, that Shalmaneser king of Assyria came up against Samaria, and besieged it.
DRA In the fourth year of king Ezechias, which was the seventh year of Osee the son of Ela king of Israel, Salmanasar king of the Assyrians came up to Samaria, and besieged it,
YLT And it cometh to pass, in the fourth year of king Hezekiah — it [is] the seventh year of Hoshea son of Elah king of Israel — come up hath Shalmaneser king of Asshur against Samaria, and layeth siege to it,
Drby And it came to pass in the fourth year of king Hezekiah, which was the seventh year of Hoshea the son of Elah, king of Israel, [that] Shalmaneser king of Assyria came up against Samaria and besieged it.
RV And it came to pass in the fourth year of king Hezekiah, which was the seventh year of Hoshea son of Elah king of Israel, that Shalmaneser king of Assyria came up against Samaria, and besieged it.
SLT And it will be in the fourth year to king Hezekiah, this the seventh year to Hoshea son of Elah, king of Israel, Shalmaneser, king of Assur, came up against Shomeron and pressed, upon it.
Wbstr And it came to pass in the fourth year of king Hezekiah, which was the seventh year of Hoshea son of Elah king of Israel, that Shalmaneser king of Assyria came up against Samaria, and besieged it.
KJB-1769 ¶ And it came to pass in the fourth year of king Hezekiah, which was the seventh year of Hoshea son of Elah king of Israel, that Shalmaneser king of Assyria came up against Samaria, and besieged it.
KJB-1611 ¶ And it came to passe in the fourth yeere of king Hezekiah, (which was the seuenth yeere of Hoshea, sonne of Elah king of Israel) that Shalmaneser king of Assyria came vp against Samaria, and besieged it.
(Modernised spelling is same as from KJB-1769 above, apart from punctuation)
Bshps And in the fourth yere of king Hezekia, (whiche was the seuenth yere of Hosea sonne of Ela king of Israel) it fortuned that Salmanazar king of Assyria came vp against Samaria, and besieged it.
(And in the fourth year of king Hezekia, (which was the seventh year of Hosea son of Ela king of Israel) it fortuned that Salmanazar king of Assyria came up against Samaria, and besieged it.)
Gnva And in the fourth yere of King Hezekiah, (which was the seuenth yeere of Hoshea sonne of Elah King of Israel) Shalmaneser King of Asshur came vp against Samaria, and besieged it.
(And in the fourth year of King Hezekiah, (which was the seventh year of Hoshea son of Elah King of Israel) Shalmaneser King of Asshur came up against Samaria, and besieged it. )
Cvdl In the fourth yeare of Ezechias kynge of Iuda (yt was the seuenth yeare of Oseas the sonne of Ela kynge of Israel) came Salmanasar the kynge of Assiria vp agaynst Samaria, and layed sege vnto it,
(In the fourth year of Ezechias king of Yudah (yt was the seventh year of Oseas the son of Ela king of Israel) came Salmanasar the king of Assiria up against Samaria, and laid siege unto it,)
Wycl In the fourthe yeer of kyng Ezechie, that was the seuenthe yeer of Osee, sone of Hela, kyng of Israel, Salmanazar, kyng of Assiriens, stiede to Samarie,
(In the forth year of king Ezechie, that was the seventh year of Osee, son of Hela, king of Israel, Salmanazar, king of Assiriens, stayed to Samaria,)
Luth Im vierten Jahr Hiskias, des Königs Judas (das war das siebente Jahr Hoseas, des Sohns Elas, des Königs Israels), da zog Salmanesser, der König zu Assyrien, herauf wider Samaria und belagerte sie;
(In_the fourth year Hiskias, the kings Yudas (the what/which the seventh year Hoseas, the son Elas, the kings Israels), there pulled Salmanesser, the/of_the king to/for Assyrien, up against Samaria and besieged they/she/them;)
ClVg Anno quarto regis Ezechiæ, qui erat annus septimus Osee filii Ela regis Israël, ascendit Salmanasar rex Assyriorum in Samariam, et oppugnavit eam,
(In_the_year quarto king Hezekiah, who was year the_seventh Osee children Ela king Israel, went_up Salmanasar king Assyriorum in/into/on Samariam, and oppugnavit her, )
18:1-12 The accession statement concerning Hezekiah’s reign (18:1-2) is accompanied by a lengthy evaluation of Hezekiah’s spiritual commitment (18:3-7a), followed by background details of the political situation in his time (18:7b-12).
Note 1 topic: translate-names
(Occurrence 0) Hoshea … Elah … Shalmaneser
(Some words not found in UHB: and=he/it_was in/on/at/with,year the,fourth to/for=the_king Ḩizqiyyāh she/it the,year the,seventh of,Hoshea son_of ʼĒlāh king Yisrael came_up Shalmanʼeşer king ʼAshshūr on/upon/above/on_account_of//he/it_went_in Shomrōn and=he/it_laid_siege against,it )
These are the names of men.
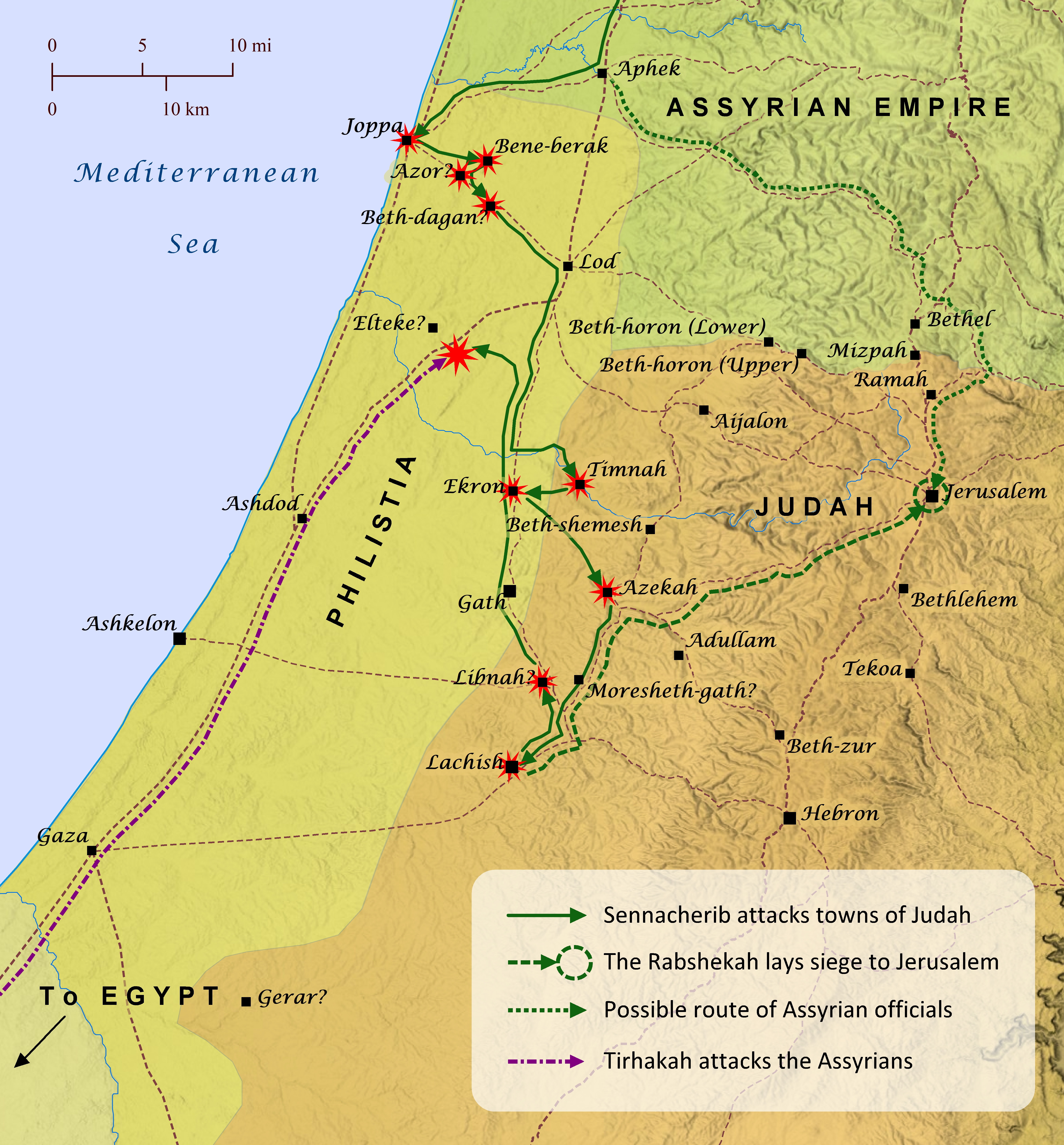
Isaiah 36-37; 2 Kings 18-19; 2 Chronicles 32
The harrowing experience of the attack on Judah by King Sennacherib of Assyria during Hezekiah’s reign is recorded by three different writers of Scripture and even by Sennacherib himself. Many scholars also suspect that this event formed the basis for Herodotus’s story regarding an army of mice eating the bow strings of the Assyrian army during their campaign against the Egyptians (Histories, 2.141). The origins of this event stretch back into the reign of Hezekiah’s father Ahaz, who enticed the Assyrians to attack Israel and Aram in exchange for making Judah a vassal of Assyria (2 Kings 16-17; 2 Chronicles 28; Isaiah 7-8; also see “The Final Days of the Northern Kingdom of Israel” map). Judah continued to be a vassal of Assyria through the early part of Hezekiah’s reign, but Hezekiah also quietly made extensive preparations to throw off the yoke of Assyria one day (2 Kings 18:1-12; 1 Chronicles 4:39-43; 2 Chronicles 29-31; also see “Hezekiah Strengthens Judah” map). Hezekiah also appears to have been hoping for support from Babylon and Egypt regarding his efforts to revolt against Assyria’s rule, but the prophet Isaiah warned Judah against placing their hopes in these foreign powers (Isaiah 30:1-5; 31:1-3; 39:1-8; 40:10-15; 2 Kings 20:12-19). After a few years spent quashing rebellion among the Babylonians, the Kassites, and the Medes in the east, Sennacherib turned his sights westward and began a campaign to subdue the various vassal nations that were refusing to submit to Assyria’s rule any longer. He first reconquered the Phoenician cities of Sidon and Tyre and then moved south to Philistia. He subdued Joppa, Beth-dagon, Bene-berak, and Azor and then moved to capture the cities of the Shephelah, which guarded the entrances to the valleys leading into the central hill country of Judah. While Sennacherib was attacking Lachish he sent his officers to demand Hezekiah’s surrender. This may be the Assyrian advance upon Jerusalem from the north described in Isaiah 10:28-32, but this is not certain (see “Assyria Advances on Jerusalem” map). Hezekiah sent officers back to Sennacherib with gold and silver taken from Temple and the royal treasury, but he would not surrender. The officers then traveled to Libnah to meet with Sennacherib, for he gone to fight there by that time. In the meantime King Tirhakah of Cush, who was ruling over Egypt at this time, came to attack Sennacherib, so Sennacherib sent his officials back to Hezekiah with a message that Jerusalem would be taken if he resisted. Hezekiah laid the letter from the officials before the Lord and prayed, and the Lord sent word through the prophet Isaiah that Jerusalem would not be taken. Then that very night the angel of the Lord killed 185,000 Assyrian soldiers (probably those with Sennacherib fighting the Egyptians), and Sennacherib went back to Assyria. There while he was worshiping in the temple of Nisroch, Sennacherib’s sons killed him and fled to Ararat (see “Ararat” map).
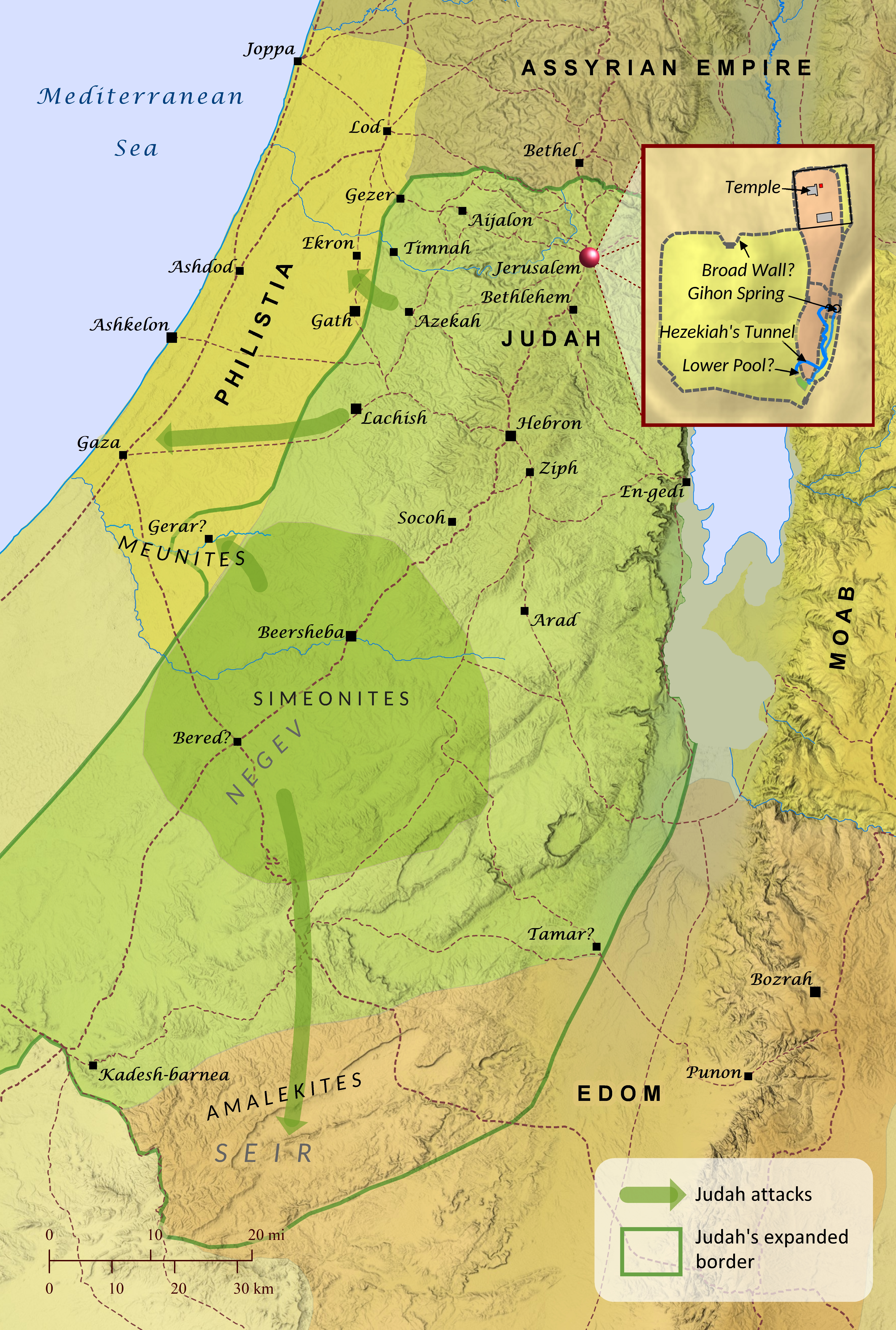
2 Kings 18:1-12; 1 Chronicles 4:39-43; 2 Chronicles 29-31
Throughout his reign, Hezekiah strengthened Judah by restoring proper worship of the Lord and preparing the nation for revolt against Assyria. Though the Bible does not clearly say, both of these aspects of Hezekiah’s reign may have been borne out of a desire to undo the detrimental choices of his father, Ahaz, who had promoted idolatry through Judah (2 Chronicles 28:1-4) and made Judah a vassal to the king of Assyria in exchange for help against Israel and Aram (2 Kings 16-17; 2 Chronicles 28; Isaiah 7-8; see also “The Final Days of the Northern Kingdom of Israel” map). Later, when Hezekiah was a teenager, he witnessed Assyria’s grueling three year siege to capture Samaria (2 Kings 17:1-6; 18:9-12), perhaps cementing his resolve to throw off Judah’s yolk of servitude to Assyria (2 Kings 18:7). Whatever the reasons for his actions as king, Hezekiah spent considerable resources promoting the worship of the Lord and preparing for the inevitable Assyrian attack that would follow Judah’s refusal to submit to Assyria any longer. Hezekiah began by directing the priests and Levites to consecrate themselves and restore ritual purity to the Temple and all its furnishings (2 Chronicles 29). He sent word throughout all Israel and Judah to come and celebrate Passover together once again in Jerusalem (2 Chronicles 30). Though only a few from Israel accepted Hezekiah’s invitation, the Passover was a time of great celebration and worship for all who did come from Israel and Judah. After this, the worshipers went throughout Israel and Judah and destroyed the pagan worship centers (2 Kings 18:4; 2 Chronicles 31:1). Hezekiah also conducted a series of actions to strengthen Judah against the coming Assyrian attack. On the west he attacked the Philistines as far as Gaza (2 Kings 18:8). Part of this effort may have included a Simeonite attack on some Meunites in the valley of Gerar (as in the Septuagint; the Hebrew reading Gedor is likely due to a misreading of the letter r as the similarly shaped letter d), which is recounted in 1 Chronicles 4:39-41. Elsewhere in Scripture the Meunites appear to have lived in the region of Seir (2 Chronicles 20), south of Judah, but a remnant of them may have fled toward Gerar during Uzziah’s time when he attacked them and likely took some of them captive to serve at the Temple of the Lord in Jerusalem (Ezra 2:50; Nehemiah 7:52; also see “Resurgence of Israel and Judah” map). Other Simeonites attacked a remnant of Amalekites living in Seir, thus providing increased protection on Judah’s southern border (1 Chronicles 4:39-43). Hezekiah also fortified Jerusalem and redirected various sources of water away from enemies who might lay siege to the city (2 Chronicles 32:1-8). As part of these preparations Hezekiah commissioned the hewing of a tunnel that channeled water from the Gihon spring (probably also called the “waters of Shiloah” in Isaiah 8:6) away from the eastern side of the city and deposited it in the Lower Pool (also called the Pool of Siloam) further inside the city walls. Hezekiah also repaired portions of the wall that were broken down and built a second wall outside it, likely in the Kidron Valley. He also produced many weapons and shields. The writer of Chronicles appears to portray these preparations as being in keeping with Hezekiah’s other acts of faithfulness and righteousness. Some scholars, however, suspect that Isaiah 22:1-14 may reflect another perspective regarding Hezekiah’s preparations, though it is not certain that this passage refers to Hezekiah’s efforts.