Open Bible Data Home About News OET Key
OET OET-RV OET-LV ULT UST BSB MSB BLB AICNT OEB WEBBE WMBB NET LSV FBV TCNT T4T LEB BBE Moff JPS Wymth ASV DRA YLT Drby RV SLT Wbstr KJB-1769 KJB-1611 Bshps Gnva Cvdl TNT Wycl SR-GNT UHB BrLXX BrTr Related Topics Parallel Interlinear Reference Dictionary Search
ParallelVerse GEN EXO LEV NUM DEU JOB JOS JDG RUTH 1 SAM 2 SAM PSA AMOS HOS 1 KI 2 KI 1 CHR 2 CHR PROV ECC SNG JOEL MIC ISA ZEP HAB JER LAM YNA (JNA) NAH OBA DAN EZE EZRA EST NEH HAG ZEC MAL LAO GES LES ESG DNG 2 PS TOB JDT WIS SIR BAR LJE PAZ SUS BEL MAN 1 MAC 2 MAC 3 MAC 4 MAC YHN (JHN) MARK MAT LUKE ACTs YAC (JAM) GAL 1 TH 2 TH 1 COR 2 COR ROM COL PHM EPH PHP 1 TIM TIT 1 PET 2 PET 2 TIM HEB YUD (JUD) 1 YHN (1 JHN) 2 YHN (2 JHN) 3 YHN (3 JHN) REV
2 Ki Intro C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 C9 C10 C11 C12 C13 C14 C15 C16 C17 C18 C19 C20 C21 C22 C23 C24 C25
2 Ki 18 V1 V2 V3 V4 V6 V7 V8 V9 V10 V11 V12 V13 V14 V15 V16 V17 V18 V19 V20 V21 V22 V23 V24 V25 V26 V27 V28 V29 V30 V31 V32 V33 V34 V35 V36 V37
Note: This view shows ‘verses’ which are not natural language units and hence sometimes only part of a sentence will be visible—click on any Bible version abbreviation down the left-hand side to see the verse in more of its context. Normally the OET discourages the reading of individual ‘verses’, but this view is only designed as a tool for doing comparisons of different translations—the older translations are further down the page (so you can read up from the bottom to trace the English translation history). The OET segments on this page are still very early looks into the unfinished texts of the Open English Translation of the Bible—please double-check these texts in advance before using in public.
Text critical issues=none Clarity of original=clear Importance to us=normal (All still tentative.)
OET (OET-RV) Hizkiyah fully trusted in Yisrael’s god Yahweh, and no other king was like him among all the kings of Yehudah that either preceded or followed him.![]()
OET-LV In/on/at/with_LORD the_god_of Yisrāʼēl/(Israel) he_trusted and_after_him not anyone_was like_him in/on/at/with_all_of the_kings_of Yəhūdāh and_which they_were before_face/front_him.
![]()
UHB בַּיהוָ֥ה אֱלֹהֵֽי־יִשְׂרָאֵ֖ל בָּטָ֑ח וְאַחֲרָ֞יו לֹא־הָיָ֣ה כָמֹ֗הוּ בְּכֹל֙ מַלְכֵ֣י יְהוּדָ֔ה וַאֲשֶׁ֥ר הָי֖וּ לְפָנָֽיו׃ ‡
(bayhvāh ʼₑlohēy-yisrāʼēl bāţāḩ vəʼaḩₐrāyv loʼ-hāyāh kāmohū bəkol malkēy yəhūdāh vaʼₐsher hāyū ləfānāyv.)
Key: khaki:verbs, red:negative, blue:Elohim, green:YHWH.
Note: Automatic aligning of the OET-RV to the LV is done by some temporary software, hence the OET-RV alignments are incomplete (and may occasionally be wrong).
BrLXX Ἐν Κυρίῳ Θεῷ Ἰσραὴλ ἤλπισεν, καὶ μετʼ αὐτὸν οὐκ ἐγενήθη ὅμοιος αὐτῷ ἐν βασιλεῦσιν Ἰούδα, καὶ ἐν τοῖς γενομένοις ἔμπροσθεν αὐτοῦ.
(En Kuriōi Theōi Israaʸl aʸlpisen, kai metʼ auton ouk egenaʸthaʸ homoios autōi en basileusin Youda, kai en tois genomenois emprosthen autou. )
BrTr He [fn]trusted in the Lord God of Israel; and after him there was not any like him among the kings of Juda, [fn]nor among those that were before him.
ULT In Yahweh the God of Israel he trusted, and after him none was like him among all the kings of Judah, nor those who were before him.
UST Hezekiah trusted in Yahweh, the God whom the Israelites worshiped. There was no king who ruled Judah before him or after him who was as devoted to Yahweh as he was.
BSB Hezekiah trusted in the LORD, the God of Israel. No king of Judah was like him, either before him or after him.
MSB (Same as BSB above)
OEB No OEB 2 KI book available
WEBBE He trusted in the LORD, the God of Israel, so that after him was no one like him amongst all the kings of Judah, nor amongst them that were before him.
WMBB (Same as above)
NET He trusted in the Lord God of Israel; in this regard there was none like him among the kings of Judah either before or after.
LSV In YHWH, God of Israel, he has trusted, and after him there has not been like him among all the kings of Judah, nor [among any] who were before him;
FBV Hezekiah put his trust in the Lord, the God of Israel. Among the kings of Judah there was no one like him, neither before him nor after him.
T4T Hezekiah trusted in Yahweh, the God whom the Israelis worshiped. There was no king who ruled Judah before him or after him who was as devoted to Yahweh as he was.
LEB He trusted in Yahweh the God of Israel; there was no one like him, before or after, among all the kings of Judah.
BBE He had faith in the Lord, the God of Israel; so that there was no one like him among all the kings of Judah who were before him.
Moff No Moff 2 KI book available
JPS He trusted in the LORD, the God of Israel; so that after him was none like him among all the kings of Judah, nor among them that were before him.
ASV He trusted in Jehovah, the God of Israel; so that after him was none like him among all the kings of Judah, nor among them that were before him.
DRA He trusted in the Lord the God of Israel: so that after him there was none like him among all the kings of Juda, nor any of them that were before him:
YLT In Jehovah, God of Israel, he hath trusted, and after him there hath not been like him among all the kings of Judah, nor [among any] who were before him;
Drby He trusted in Jehovah the [fn]God of Israel; so that after him was none like him among all the kings of Judah, nor [among any] that were before him.
18.5 Elohim
RV He trusted in the LORD, the God of Israel; so that after him was none like him among all the kings of Judah, nor among them that were before him.
(He trusted in the LORD, the God of Israel; so that after him was none like him among all the kings of Yudah, nor among them that were before him. )
SLT And he trusted in Jehovah the God of Israel; and after him was not like him among all the kings of Judah, and who were before him.
Wbstr He trusted in the LORD God of Israel; so that after him was none like him among all the kings of Judah, nor any that were before him.
KJB-1769 He trusted in the LORD God of Israel; so that after him was none like him among all the kings of Judah, nor any that were before him.
(He trusted in the LORD God of Israel; so that after him was none like him among all the kings of Yudah, nor any that were before him. )
KJB-1611 He trusted in the LORD God of Israel, so that after him was none like him among all the kings of Iudah, nor any that were before him.
(Modernised spelling is same as from KJB-1769 above, apart from punctuation)
Bshps He trusted in the Lorde God of Israel, so that after him was none lyke him among all the kinges of Iuda, neither were there any such before him.
(He trusted in the Lord God of Israel, so that after him was none like him among all the kings of Yuda, neither were there any such before him.)
Gnva He trusted in the Lord God of Israel: so that after him was none like him among all the Kings of Iudah, neither were there any such before him.
(He trusted in the Lord God of Israel: so that after him was none like him among all the Kings of Yudah, neither were there any such before him. )
Cvdl He put his trust in the LORDE God of Israel, so that after him there was not his like amoge all the kynges of Iuda nether had bene before him.
(He put his trust in the LORD God of Israel, so that after him there was not his like among all the kings of Yudah neither had been before him.)
Wycl And he hopide in the Lord God of Israel; therfor aftir hym noon was lijk hym of alle the kyngis of Juda, but `and nether in tho kyngis that weren bifor hym.
(And he hoped in the Lord God of Israel; therefore after him noon was like him of all the kings of Yuda, but and neither in those kings that were before him.)
Luth Er vertrauete dem HErr’s, dem GOtt Israels, daß nach ihm seinesgleichen nicht war unter allen Königen Judas, noch vor ihm gewesen.
(He trustede to_him LORD’s, to_him God Israels, that after him beesgleichen not what/which under all/everyone kings Yudas, still before/in_front_of him been.)
ClVg In Domino Deo Israël speravit: itaque post eum non fuit similis ei de cunctis regibus Juda, sed neque in his qui ante eum fuerunt:
(In Master to_God Israel he_hoped: therefore after him not/no it_was similar to_him from/about to_all kings Yuda, but nor in/into/on his who before him they_were: )
18:1-12 The accession statement concerning Hezekiah’s reign (18:1-2) is accompanied by a lengthy evaluation of Hezekiah’s spiritual commitment (18:3-7a), followed by background details of the political situation in his time (18:7b-12).
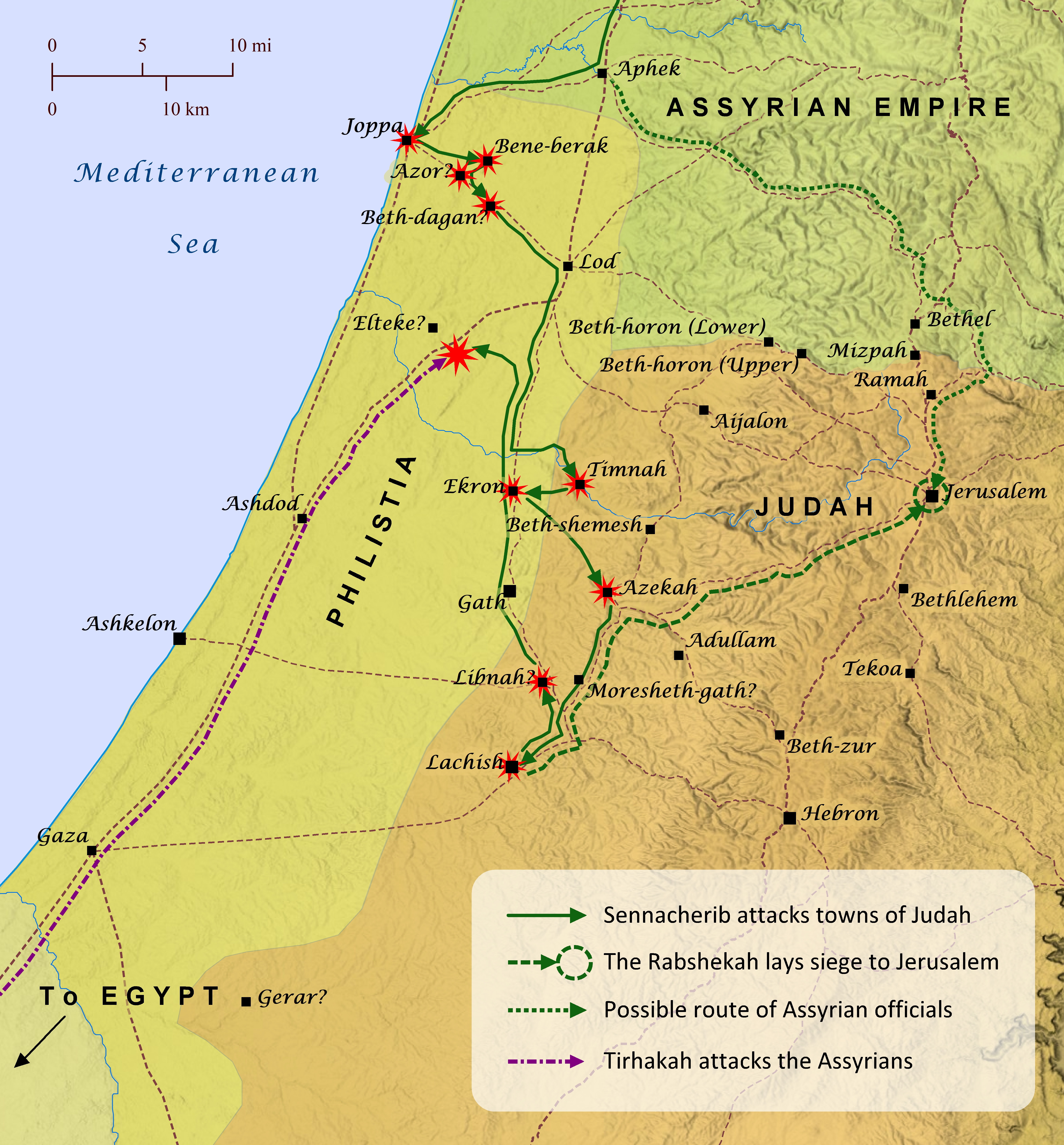
Isaiah 36-37; 2 Kings 18-19; 2 Chronicles 32
The harrowing experience of the attack on Judah by King Sennacherib of Assyria during Hezekiah’s reign is recorded by three different writers of Scripture and even by Sennacherib himself. Many scholars also suspect that this event formed the basis for Herodotus’s story regarding an army of mice eating the bow strings of the Assyrian army during their campaign against the Egyptians (Histories, 2.141). The origins of this event stretch back into the reign of Hezekiah’s father Ahaz, who enticed the Assyrians to attack Israel and Aram in exchange for making Judah a vassal of Assyria (2 Kings 16-17; 2 Chronicles 28; Isaiah 7-8; also see “The Final Days of the Northern Kingdom of Israel” map). Judah continued to be a vassal of Assyria through the early part of Hezekiah’s reign, but Hezekiah also quietly made extensive preparations to throw off the yoke of Assyria one day (2 Kings 18:1-12; 1 Chronicles 4:39-43; 2 Chronicles 29-31; also see “Hezekiah Strengthens Judah” map). Hezekiah also appears to have been hoping for support from Babylon and Egypt regarding his efforts to revolt against Assyria’s rule, but the prophet Isaiah warned Judah against placing their hopes in these foreign powers (Isaiah 30:1-5; 31:1-3; 39:1-8; 40:10-15; 2 Kings 20:12-19). After a few years spent quashing rebellion among the Babylonians, the Kassites, and the Medes in the east, Sennacherib turned his sights westward and began a campaign to subdue the various vassal nations that were refusing to submit to Assyria’s rule any longer. He first reconquered the Phoenician cities of Sidon and Tyre and then moved south to Philistia. He subdued Joppa, Beth-dagon, Bene-berak, and Azor and then moved to capture the cities of the Shephelah, which guarded the entrances to the valleys leading into the central hill country of Judah. While Sennacherib was attacking Lachish he sent his officers to demand Hezekiah’s surrender. This may be the Assyrian advance upon Jerusalem from the north described in Isaiah 10:28-32, but this is not certain (see “Assyria Advances on Jerusalem” map). Hezekiah sent officers back to Sennacherib with gold and silver taken from Temple and the royal treasury, but he would not surrender. The officers then traveled to Libnah to meet with Sennacherib, for he gone to fight there by that time. In the meantime King Tirhakah of Cush, who was ruling over Egypt at this time, came to attack Sennacherib, so Sennacherib sent his officials back to Hezekiah with a message that Jerusalem would be taken if he resisted. Hezekiah laid the letter from the officials before the Lord and prayed, and the Lord sent word through the prophet Isaiah that Jerusalem would not be taken. Then that very night the angel of the Lord killed 185,000 Assyrian soldiers (probably those with Sennacherib fighting the Egyptians), and Sennacherib went back to Assyria. There while he was worshiping in the temple of Nisroch, Sennacherib’s sons killed him and fled to Ararat (see “Ararat” map).
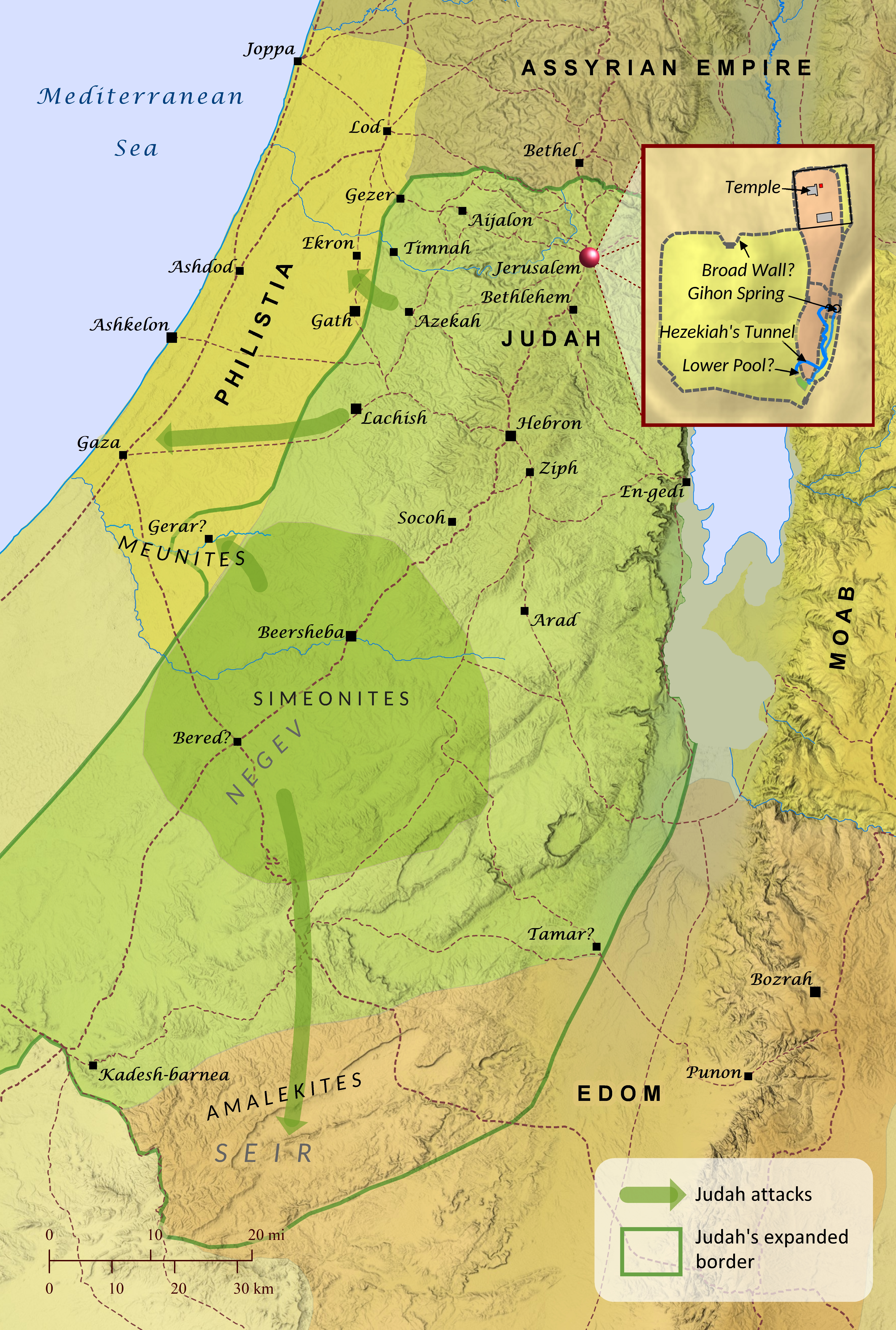
2 Kings 18:1-12; 1 Chronicles 4:39-43; 2 Chronicles 29-31
Throughout his reign, Hezekiah strengthened Judah by restoring proper worship of the Lord and preparing the nation for revolt against Assyria. Though the Bible does not clearly say, both of these aspects of Hezekiah’s reign may have been borne out of a desire to undo the detrimental choices of his father, Ahaz, who had promoted idolatry through Judah (2 Chronicles 28:1-4) and made Judah a vassal to the king of Assyria in exchange for help against Israel and Aram (2 Kings 16-17; 2 Chronicles 28; Isaiah 7-8; see also “The Final Days of the Northern Kingdom of Israel” map). Later, when Hezekiah was a teenager, he witnessed Assyria’s grueling three year siege to capture Samaria (2 Kings 17:1-6; 18:9-12), perhaps cementing his resolve to throw off Judah’s yolk of servitude to Assyria (2 Kings 18:7). Whatever the reasons for his actions as king, Hezekiah spent considerable resources promoting the worship of the Lord and preparing for the inevitable Assyrian attack that would follow Judah’s refusal to submit to Assyria any longer. Hezekiah began by directing the priests and Levites to consecrate themselves and restore ritual purity to the Temple and all its furnishings (2 Chronicles 29). He sent word throughout all Israel and Judah to come and celebrate Passover together once again in Jerusalem (2 Chronicles 30). Though only a few from Israel accepted Hezekiah’s invitation, the Passover was a time of great celebration and worship for all who did come from Israel and Judah. After this, the worshipers went throughout Israel and Judah and destroyed the pagan worship centers (2 Kings 18:4; 2 Chronicles 31:1). Hezekiah also conducted a series of actions to strengthen Judah against the coming Assyrian attack. On the west he attacked the Philistines as far as Gaza (2 Kings 18:8). Part of this effort may have included a Simeonite attack on some Meunites in the valley of Gerar (as in the Septuagint; the Hebrew reading Gedor is likely due to a misreading of the letter r as the similarly shaped letter d), which is recounted in 1 Chronicles 4:39-41. Elsewhere in Scripture the Meunites appear to have lived in the region of Seir (2 Chronicles 20), south of Judah, but a remnant of them may have fled toward Gerar during Uzziah’s time when he attacked them and likely took some of them captive to serve at the Temple of the Lord in Jerusalem (Ezra 2:50; Nehemiah 7:52; also see “Resurgence of Israel and Judah” map). Other Simeonites attacked a remnant of Amalekites living in Seir, thus providing increased protection on Judah’s southern border (1 Chronicles 4:39-43). Hezekiah also fortified Jerusalem and redirected various sources of water away from enemies who might lay siege to the city (2 Chronicles 32:1-8). As part of these preparations Hezekiah commissioned the hewing of a tunnel that channeled water from the Gihon spring (probably also called the “waters of Shiloah” in Isaiah 8:6) away from the eastern side of the city and deposited it in the Lower Pool (also called the Pool of Siloam) further inside the city walls. Hezekiah also repaired portions of the wall that were broken down and built a second wall outside it, likely in the Kidron Valley. He also produced many weapons and shields. The writer of Chronicles appears to portray these preparations as being in keeping with Hezekiah’s other acts of faithfulness and righteousness. Some scholars, however, suspect that Isaiah 22:1-14 may reflect another perspective regarding Hezekiah’s preparations, though it is not certain that this passage refers to Hezekiah’s efforts.