Open Bible Data Home About News OET Key
OET OET-RV OET-LV ULT UST BSB MSB BLB AICNT OEB WEBBE WMBB NET LSV FBV TCNT T4T LEB BBE Moff JPS Wymth ASV DRA YLT Drby RV SLT Wbstr KJB-1769 KJB-1611 Bshps Gnva Cvdl TNT Wycl SR-GNT UHB BrLXX BrTr Related Topics Parallel Interlinear Reference Dictionary Search
ParallelVerse GEN EXO LEV NUM DEU JOB JOS JDG RUTH 1 SAM 2 SAM PSA AMOS HOS 1 KI 2 KI 1 CHR 2 CHR PROV ECC SNG JOEL MIC ISA ZEP HAB JER LAM YNA (JNA) NAH OBA DAN EZE EZRA EST NEH HAG ZEC MAL LAO GES LES ESG DNG 2 PS TOB JDT WIS SIR BAR LJE PAZ SUS BEL MAN 1 MAC 2 MAC 3 MAC 4 MAC YHN (JHN) MARK MAT LUKE ACTs YAC (JAM) GAL 1 TH 2 TH 1 COR 2 COR ROM COL PHM EPH PHP 1 TIM TIT 1 PET 2 PET 2 TIM HEB YUD (JUD) 1 YHN (1 JHN) 2 YHN (2 JHN) 3 YHN (3 JHN) REV
Gen Intro C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 C9 C10 C11 C12 C13 C14 C15 C16 C17 C18 C19 C20 C21 C22 C23 C24 C25 C26 C27 C28 C29 C30 C31 C32 C33 C34 C35 C36 C37 C38 C39 C40 C41 C42 C43 C44 C45 C46 C47 C48 C49 C50
Gen 25 V1 V2 V3 V4 V5 V6 V7 V8 V9 V10 V11 V13 V14 V15 V16 V17 V18 V19 V20 V21 V22 V23 V24 V25 V26 V27 V28 V29 V30 V31 V32 V33 V34
Note: This view shows ‘verses’ which are not natural language units and hence sometimes only part of a sentence will be visible—click on any Bible version abbreviation down the left-hand side to see the verse in more of its context. Normally the OET discourages the reading of individual ‘verses’, but this view is only designed as a tool for doing comparisons of different translations—the older translations are further down the page (so you can read up from the bottom to trace the English translation history). The OET segments on this page are still very early looks into the unfinished texts of the Open English Translation of the Bible—please double-check these texts in advance before using in public.
Text critical issues=none Clarity of original=clear Importance to us=normal (All still tentative.)
OET (OET-RV) Now these are the generations of Yishma’el the son of Abraham, whom Hagar the Egyptian, Sarah’s female slave, had given birth to for Abraham.![]()
OET-LV and_these are_the_accounts_of Yishmāˊʼēl/(Ishmael) the_son_of ʼAⱱrāhām whom she_bore Hāgār the_from_Miʦrayim/(Miʦrayim/(Egypt)) the_maidservant_of Sārāh to_ʼAⱱrāhām.
![]()
UHB וְאֵ֛לֶּה תֹּלְדֹ֥ת יִשְׁמָעֵ֖אל בֶּן־אַבְרָהָ֑ם אֲשֶׁ֨ר יָלְדָ֜ה הָגָ֧ר הַמִּצְרִ֛ית שִׁפְחַ֥ת שָׂרָ֖ה לְאַבְרָהָֽם׃ ‡
(vəʼēlleh toldot yishmāˊēʼl ben-ʼaⱱrāhām ʼₐsher yālədāh hāgār hammiʦrit shifḩat sārāh ləʼaⱱrāhām.)
Key: khaki:verbs.
Note: Automatic aligning of the OET-RV to the LV is done by some temporary software, hence the OET-RV alignments are incomplete (and may occasionally be wrong).
BrLXX Αὗται δὲ αἱ γενέσεις Ἰσμαὴλ τοῦ υἱοῦ Ἁβραὰμ, ὃν ἔτεκεν Ἄγαρ ἡ Αἰγυπτία, ἡ παιδίσκη Σάῤῥας, τῷ Ἁβραάμ.
(Hautai de hai geneseis Ismaaʸl tou huiou Habraʼam, hon eteken Agar haʸ Aiguptia, haʸ paidiskaʸ Saɽɽas, tōi Habraʼam. )
BrTr And these are the generations of Ismael the son of Abraam, whom Agar the Egyptian the hand-maid of Sarrha bore to Abraam.
ULT Now these are the generations of Ishmael the son of Abraham, whom Hagar the Egyptian, the maidservant of Sarah, had born for Abraham.
UST What follows is a record of the descendants of Abraham’s son Ishmael, the son Abraham had with Sarah’s Egyptian slave woman Hagar.
BSB This is the account of Abraham’s son Ishmael, whom Hagar the Egyptian, Sarah’s maidservant, bore to Abraham.
MSB (Same as BSB above)
OEB This is a list of descendants of Ishmael, Abraham’s son whom Hagar the Egyptian, Sarah’s maid-servant gave to Abraham.
WEBBE Now this is the history of the generations of Ishmael, Abraham’s son, whom Hagar the Egyptian, Sarah’s servant, bore to Abraham.
WMBB (Same as above)
NET This is the account of Abraham’s son Ishmael, whom Hagar the Egyptian, Sarah’s servant, bore to Abraham.
LSV And these [are] the generations of Ishmael, Abraham’s son, whom Hagar the Egyptian, Sarah’s handmaid, has borne to Abraham;
FBV This is the genealogy of Abraham's son Ishmael. His mother Hagar was Sarah's Egyptian slave.
T4T ◄These are/I will now give a list of► the descendants of Abraham’s son, Ishmael, to whom Sarah’s female slave, Hagar from Egypt, had given birth.
LEB Now these are the generations[fn] of Ishmael, the son of Abraham, that Hagar the Egyptian, the maidservant of Sarah, bore to Abraham.
25:12 Or “family records”
BBE Now these are the generations of Ishmael, the son of Abraham, whose mother was Hagar the Egyptian, the servant of Sarah:
Moff No Moff GEN book available
JPS Now these are the generations of Ishmael, Abraham's son, whom Hagar the Egyptian, Sarah's handmaid, bore unto Abraham.
ASV Now these are the generations of Ishmael, Abraham’s son, whom Hagar the Egyptian, Sarah’s handmaid, bare unto Abraham:
DRA These are the generations of Ismael the son of Abraham, whom Agar the Egyptian, Sara’s servant, bore unto him:
YLT And these [are] births of Ishmael, Abraham's son, whom Hagar the Egyptian, Sarah's handmaid, hath borne to Abraham;
Drby And these are the generations of Ishmael, Abraham's son, whom Hagar the Egyptian, Sarah's bondwoman, bore to Abraham.
RV Now these are the generations of Ishmael, Abraham’s son, whom Hagar the Egyptian, Sarah’s handmaid, bare unto Abraham:
SLT These the generations of Ishmael, son of Abraham, whom Hagar brought forth, the Egyptian, Sarah’s maid, to Abraham.
Wbstr Now these are the generations of Ishmael, Abraham's son, whom Hagar the Egyptian, Sarah's handmaid, bore to Abraham.
KJB-1769 ¶ Now these are the generations of Ishmael, Abraham’s son, whom Hagar the Egyptian, Sarah’s handmaid, bare unto Abraham:
KJB-1611 ¶ Now these are the generations of Ishmael Abrahams sonne, whom Hagar the Egyptian Sarahs handmayd, bare vnto Abraham:
(¶ Now these are the generations of Ishmael Abrahams son, whom Hagar the Egyptian Sarahs handmayd, bare unto Abraham:)
Bshps These are the generations of Ismael Abrahams sonne, whiche Hagar the Egyptian Saraes handmayde bare vnto Abraham.
(These are the generations of Ismael Abrahams son, which Hagar the Egyptian Saraes handmaid bare unto Abraham.)
Gnva Nowe these are the generations of Ishmael Abrahams sonne, whome Hagar the Egyptian Sarahs handmayde bare vnto Abraham.
(Now these are the generations of Ishmael Abrahams son, whom Hagar the Egyptian Sarahs handmaid bare unto Abraham. )
Cvdl This is the generacion of Ismael Abrahams sonne, whom Agar Saras mayde the Egipcian bare vnto him.
(This is the generation of Ismael Abrahams son, whom Agar Saras maid the Egipcian bare unto him.)
Wycl These ben the generaciouns of Ismael, sone of Abraham, whom Agar Egipcian, seruauntesse of Sare, childide to Abraham;
(These been the generations of Ismael, son of Abraham, whom Agar Egipcian, servantsse of Sara, childed/bore to Abraham;)
Luth Dies ist das Geschlecht Ismaels, Abrahams Sohns, den ihm Hagar gebar, die Magd Saras aus Ägypten;
(This/These is the descendant Ismaels, Abrahams son, the him Hagar gave_birth, the maid Saras out_of Egypt;)
ClVg Hæ sunt generationes Ismaël filii Abrahæ, quem peperit ei Agar Ægyptia, famula Saræ: et[fn]
(These are generations Ismaël children Abrahæ, which gave_birth to_him Agar of_Egypta, famula Saræ: and )
25.12 Hæ sunt generationes, etc. Hi populi ante filios Isaac computantur, qui cum sint de semine Abrahæ, non tamen computantur in semine, quia prius est quod animæ est, deinde quod spirituale. Unde post computationem carnalium, ponitur genealogia Isaac, de quo facta est promissio, et electorum propaganda successio.
25.12 These are generations, etc. They of_the_people before children Isaac computantur, who when/with let_them_be from/about with_seed Abrahæ, not/no nevertheless computantur in/into/on with_seed, because first/before it_is that soul it_is, then/next that spiritual. From_where/who after computationem carnalum, is_placed genealogia Isaac, from/about where facts it_is promise, and of_the_elect propaganda successio.
25:12-18 This record lists Ishmael’s descendants before tracing Isaac’s (25:19–35:29), which is in keeping with the literary arrangement of Genesis (see Genesis Book Introduction, “Summary”).
Note 1 topic: writing-newevent
וְאֵ֛לֶּה תֹּלְדֹ֥ת
and=these generations_of
Consider what is the best way in your language to introduce the new topic that begins here. See how you translated this clause in Gen 11:10. Alternate translation: [Here is the genealogy of] or [Here is the list of the descendants of] or [What follows is the record of the descendants of]
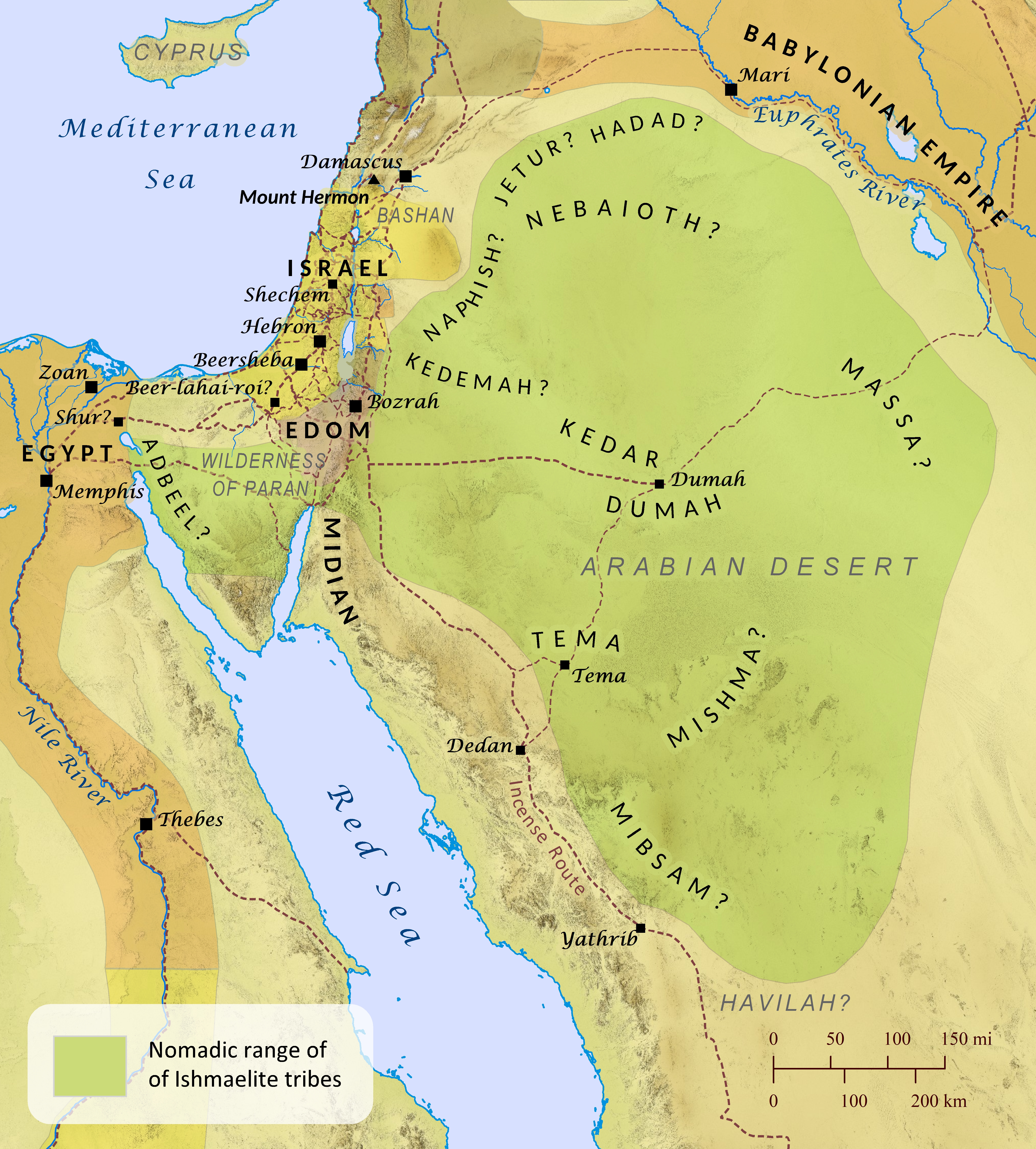
Genesis 21:1-21; 25:1-18; 1 Chronicles 5:3-22
The book of Genesis twice records the origin of the Ishmaelites, who were descended from Ishmael, the son of Abraham by Sarah’s handmaiden Hagar. Ishmael lived in the wilderness of Paran (Genesis 21:20-21), and his descendants eventually ranged from Shur near Egypt all the way around to Havilah on the Arabian peninsula (Genesis 25:12-18), as shown on this map that depicts the region around the time of the Judges. Yet the term Ishmaelite also appears to have referred in a more general sense to any of the nomadic groups that roamed the deserts of Sinai and Arabia, because the Midianites (another group descended from Abraham by his second wife Keturah; Genesis 25:1-2) are twice referred to as Ishmaelites: once when Joseph is sold to a group of Midianite traders traveling from Gilead to Egypt (Genesis 37:28-36), and again when Gideon is collecting gold earrings from the spoil taken from the Midianites (Judges 8:24). Likewise, the term Hagrites, (likely meaning those descended from Hagar), is applied at times to a tribal group that appears to have been among those descended from Ishmael, but in 1 Chronicles 27:30 the terms Ishmaelite and Hagrite are applied to two different people, indicating that the terms were not synonymous. Twelve tribes are specifically listed by Genesis as descending from Ishmael, similar to how Israel was reckoned as being comprised of twelve tribes descended from a single patriarch (Genesis 35:23-26). While some of the Ishmaelite tribes achieved political dominance during certain periods of biblical history, the twelve tribes never operated as a single, unified nation. The physical boundaries of each Ishmaelite tribe’s nomadic range is difficult to establish with much certainty, partially because nomads, by definition, continually move to new lands as needed to feed their flocks. Even so, a few clues from Scripture and other ancient sources point to the likely general range for each tribe, as shown on this map.
Nebaioth has often been speculated to be the same tribe that was later called the Nabateans, but the variance in the Hebrew spelling between the two names makes this identification unlikely. Rather, they were probably the Nabaiate of Assyrian documents, which mention them in close association with the tribe of Kedar. Nebaioth and Kedar are also mentioned together in Isaiah 60:7.
Kedar, the most prominent and powerful of the Ishmaelite tribes, lay to the southeast of Israel, and this is confirmed by Jeremiah’s comment in Jeremiah 2:10 that speaks of Cyprus and Kedar as lying on opposite sides of Israel. Kedar attained significant political strength during the ninth century B.C. until they were absorbed into the Nabatean empire in the first century B.C.
Adbeel was likely a tribe known by the Akkadians as the Idibilu, who were eventually conquered by Tiglath-pileser III of Assyria and employed to guard the approaches to Egypt’s borders.
Mibsam may be named after the word for “sweet odor,” suggesting that they may have been one of the people groups of western Arabia who produced world-renowned incense and transported it to ports along the eastern Mediterranean Sea.
Mishma may have been centered around a mountain called Jebel Mishma today.
Dumah was likely centered around the ancient Arabian city by the same name.
Massa was known to the Assyrians as Mas’a, and they were forced to pay tribute to Tiglath-pileser III. Ptolemy knew the tribe as the Masanoi and located them to the northeast of Dumah.
Hadad is somewhat unknown in ancient sources, although today there is an Arabian tribe named Hadad that are mostly Christians, and they are located throughout the Levant.
Tema was no doubt centered around the city by the same name, and it was located near the rival oasis of Dedan. King Nabonidus of Babylon made Tema his headquarters as he gained control over the other Arabian desert oases (see Jeremiah 49:28; also see “Oases of the Arabian Desert” map).
Jetur was likely located northeast of Gilead, because 1 Chronicles 5:18-22 records how the Reubenites, the Gadites, and the half-tribe of Manasseh attacked Jetur and the tribe of Naphish, captured many of them and their livestock, and occupied their territory until the time of the exile. By the time of Jesus, this tribe was known as the Itureans and had captured land just north of Israel.
Naphish was likely located just east of Gilead, because the Reubenites, the Gadites, and the half-tribe of Manasseh attacked them and the tribe of Jetur and occupied their territory until the time of the exile (1 Chronicles 5:18-22).
Kedemah may have been located near the Reubenite town of Kedemoth.
Though Scripture sometimes refers to various tribes of Ishmael as enemies of Israel (1 Chronicles 5:18-22; Psalm 83:5-8), Isaiah also prophesied to Israel of a glorious day coming when “all the flocks of Kedar shall be gathered to you, the rams of Nebaioth shall minister to you; they shall be acceptable on my altar, and I will glorify my glorious house” (Isaiah 60:7).
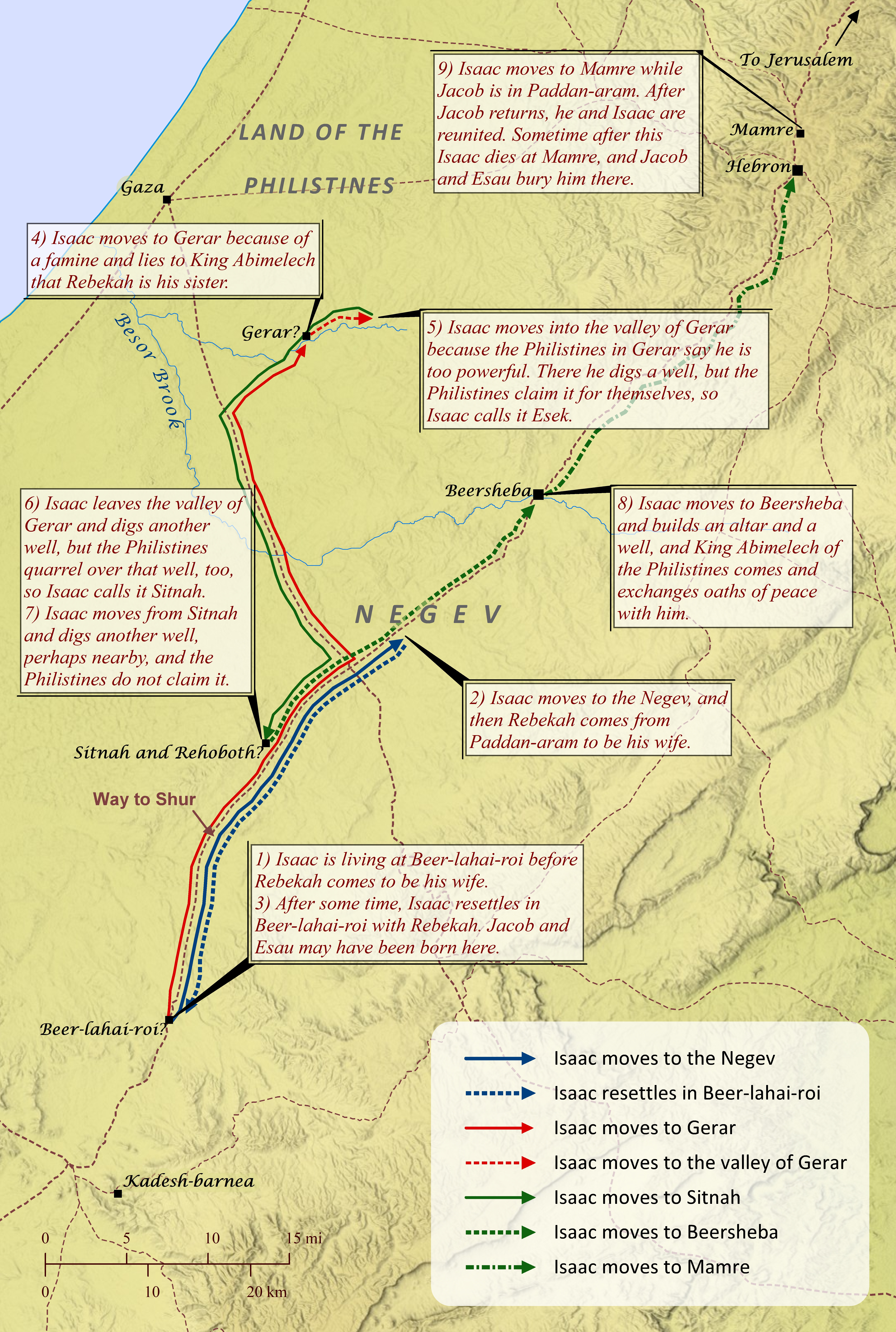
Genesis 21-35
Though the patriarch Isaac moved from place to place several times within southern Canaan, compared to his father Abraham and his son Jacob, Isaac appears to have been a bit of a homebody. In fact, unless Isaac resettled in places not recorded in Scripture, the farthest extent he ever traveled appears to have been only about 90 miles (113 km). Yet, as the child of God’s promise to Abraham to build a great nation from his descendants, Isaac’s relatively simple life served as a critical bridge from Abraham to the beginnings of the twelve tribes of Israel, who were descended from Isaac’s son Jacob. It is likely that Isaac was born at Beersheba (see Genesis 21:1-24), and later Abraham offered him as a sacrifice on Mount Moriah (located at Jerusalem; see 2 Chronicles 3:1). Then Abraham, Isaac, and those with them returned to Beersheba (Genesis 22:1-19). When Isaac reached adulthood, his father sent a servant to bring back a bride for him from Aram-naharaim, far north of Canaan. When his bride, Rebekah, arrived, Isaac had just come from Beer-lahai-roi and settled in the Negev (Genesis 24:62). Later Isaac resettled with Rebekah in Beer-lahai-roi, and this may have been where their twins son Esau and Jacob were born. A famine forced Isaac to go to Gerar (Genesis 26:1-6) in “the land of the Philistines.” The distinct people group known as the Philistines in later books of the Bible did not arrive until the time of the Judges, so the term here must have referred to another people group living in this region, and this is supported by the fact that King Abimelech’s name is Semitic, not Aegean (the likely origin of the later Philistines). While Isaac was there, he repeated his father’s error (Genesis 20) by lying to the king that his wife was only his sister. Isaac also became increasingly prosperous at Gerar, so the Philistines told him to leave their region. Isaac moved away from the town of Gerar and settled further away in the valley of Gerar. There he dug a well, but the Philistines claimed it for themselves, so he called it Esek, meaning “argument.” So Isaac’s men dug another well and called it Sitnah (meaning “hostility”), but it led to more quarreling, so he dug yet another well and called it Rehoboth (meaning “open space”). The locations of these two later wells are not certain, but they may have been located near Ruheibeh as shown on this map. Then Isaac moved to Beersheba and built an altar. He also dug a well there, and King Abimelech of the Philistines came and exchanged oaths of peace with him. It was likely at Beersheba that Isaac blessed his sons Esau and Jacob, and both sons eventually left Canaan (see “Jacob Goes to Paddan-Aram” map). When Jacob later returned, he traveled to Mamre near Hebron and reunited with Isaac. Sometime after this Isaac died, and Jacob and Esau buried him there.