Open Bible Data Home About News OET Key
OET OET-RV OET-LV ULT UST BSB MSB BLB AICNT OEB WEBBE WMBB NET LSV FBV TCNT T4T LEB BBE Moff JPS Wymth ASV DRA YLT Drby RV SLT Wbstr KJB-1769 KJB-1611 Bshps Gnva Cvdl TNT Wycl SR-GNT UHB BrLXX BrTr Related Topics Parallel Interlinear Reference Dictionary Search
ParallelVerse GEN EXO LEV NUM DEU JOB JOS JDG RUTH 1 SAM 2 SAM PSA AMOS HOS 1 KI 2 KI 1 CHR 2 CHR PROV ECC SNG JOEL MIC ISA ZEP HAB JER LAM YNA (JNA) NAH OBA DAN EZE EZRA EST NEH HAG ZEC MAL LAO GES LES ESG DNG 2 PS TOB JDT WIS SIR BAR LJE PAZ SUS BEL MAN 1 MAC 2 MAC 3 MAC 4 MAC YHN (JHN) MARK MAT LUKE ACTs YAC (JAM) GAL 1 TH 2 TH 1 COR 2 COR ROM COL PHM EPH PHP 1 TIM TIT 1 PET 2 PET 2 TIM HEB YUD (JUD) 1 YHN (1 JHN) 2 YHN (2 JHN) 3 YHN (3 JHN) REV
Gen Intro C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 C9 C10 C11 C12 C13 C14 C15 C16 C17 C18 C19 C20 C21 C22 C23 C24 C25 C26 C27 C28 C29 C30 C31 C32 C33 C34 C35 C36 C37 C38 C39 C40 C41 C42 C43 C44 C45 C46 C47 C48 C49 C50
Gen 34 V1 V2 V3 V4 V5 V6 V7 V8 V9 V10 V11 V12 V13 V14 V15 V17 V18 V19 V20 V21 V22 V23 V24 V25 V26 V27 V28 V29 V30 V31
Note: This view shows ‘verses’ which are not natural language units and hence sometimes only part of a sentence will be visible—click on any Bible version abbreviation down the left-hand side to see the verse in more of its context. Normally the OET discourages the reading of individual ‘verses’, but this view is only designed as a tool for doing comparisons of different translations—the older translations are further down the page (so you can read up from the bottom to trace the English translation history). The OET segments on this page are still very early looks into the unfinished texts of the Open English Translation of the Bible—please double-check these texts in advance before using in public.
Text critical issues=none Clarity of original=clear Importance to us=normal (All still tentative.)
OET (OET-RV) Then we’d give our daughters to you to marry, and we’d take your daughters for us to marry. And we’d settle among you, and we all would become one united people.![]()
OET-LV And_give DOM daughters_of_our to/for_you(pl) and_DOM daughters_of_your(pl) we_will_take to/for_us and_live with_you(pl) and_become as_people one.
![]()
UHB וְנָתַ֤נּוּ אֶת־בְּנֹתֵ֨ינוּ֙ לָכֶ֔ם וְאֶת־בְּנֹתֵיכֶ֖ם נִֽקַּֽח־לָ֑נוּ וְיָשַׁ֣בְנוּ אִתְּכֶ֔ם וְהָיִ֖ינוּ לְעַ֥ם אֶחָֽד׃ ‡
(vənātannū ʼet-bənotēynū lākem vəʼet-bənotēykem niqqaḩ-lānū vəyāshaⱱnū ʼittəkem vəhāyinū ləˊam ʼeḩād.)
Key: khaki:verbs.
Note: Automatic aligning of the OET-RV to the LV is done by some temporary software, hence the OET-RV alignments are incomplete (and may occasionally be wrong).
BrLXX Καὶ δώσομεν τὰς θυγατέρας ἡμῶν ὑμῖν, καὶ ἀπὸ τῶν θυγατέρων ὑμῶν ληψόμεθα ἡμῖν γυναῖκας, καὶ οἰκήσομεν παρʼ ὑμῖν, καὶ ἐσόμεθα ὡς γένος ἕν.
(Kai dōsomen tas thugateras haʸmōn humin, kai apo tōn thugaterōn humōn laʸpsometha haʸmin gunaikas, kai oikaʸsomen parʼ humin, kai esometha hōs genos hen. )
BrTr And we will give our daughters to you, and we will take of your daughters for wives to us, and we will dwell with you, and we will be as one race.
ULT Then we will give our daughters to you, and we will take your daughters for us. And we will settle with you, and we will become one people.
UST If you do that, then we will allow your young men to marry our daughters, and we will allow your daughters to marry our young men. We will also live among you in this land, so that we become one people group.
BSB Then we will give you our daughters and take your daughters for ourselves. We will dwell among you and become one people.
MSB (Same as BSB above)
OEB Then will we give our daughters to you and take your daughters to us and will live with you and we will become one people.
WEBBE then will we give our daughters to you; and we will take your daughters to us, and we will dwell with you, and we will become one people.
WMBB (Same as above)
NET Then we will give you our daughters to marry, and we will take your daughters as wives for ourselves, and we will live among you and become one people.
LSV then we have given our daughters to you, and we take your daughters for ourselves, and we have dwelt with you, and have become one people;
FBV Then we will give you our daughters and take your daughters, and we will live among you and become one family.
T4T Then we will give our daughters to your young men to be your wives, and we will take your daughters to be the wives of our young men. We will live among you, and we will become one people-group.
LEB Then we will give our daughters to you, and we will take for ourselves your daughters, and we will live with you and become one family.
BBE Then we will give our daughters to you and take your daughters to us and go on living with you as one people.
Moff No Moff GEN book available
JPS then will we give our daughters unto you, and we will take your daughters to us, and we will dwell with you, and we will become one people.
ASV then will we give our daughters unto you, and we will take your daughters to us, and we will dwell with you, and we will become one people.
DRA Then will we mutually give and take your daughters, and ours: and we will dwell with you, and will be one people:
YLT then we have given our daughters to you, and your daughters we take to ourselves, and we have dwelt with you, and have become one people;
Drby then will we give our daughters to you, and take your daughters to us, and we will dwell with you, and be one people.
RV then will we give our daughters unto you, and we will take your daughters to us, and we will dwell with you, and we will become one people.
SLT And we will give our daughters to you, and we will take your daughters to us, and we will dwell with you and be one people.
Wbstr Then will we give our daughters to you, and we will take your daughters to us, and we will dwell with you, and we will become one people.
KJB-1769 Then will we give our daughters unto you, and we will take your daughters to us, and we will dwell with you, and we will become one people.
KJB-1611 Then wil we giue our daughters vnto you, and we wil take your daughters to vs, and we will dwell with you, and we will become one people.
(Modernised spelling is same as from KJB-1769 above)
Bshps Then wyll we geue our daughters vnto you, and take your daughters to vs, and will dwell with you, and be one people.
(Then will we give our daughters unto you, and take your daughters to us, and will dwell with you, and be one people.)
Gnva Then will we giue our daughters to you, and we will take your daughters to vs, and will dwell with you, and be one people.
(Then will we give our daughters to you, and we will take your daughters to us, and will dwell with you, and be one people. )
Cvdl then will we geue you oure doughters, and take youre doughters vnto vs, and dwell with you, and be one people.
(then will we give you our daughters, and take your(pl) daughters unto us, and dwell with you, and be one people.)
Wycl thanne we schulen yyue and take togidre oure douytris and youre; and we schulen dwelle with you, and we schulen be o puple.
(then we should give and take together our daughters and youre; and we should dwell with you, and we should be o people.)
Luth Dann wollen wir unsere Töchter euch geben und eure Töchter uns nehmen und bei euch wohnen und ein Volk sein.
(Then want we/us our daughters you give and your(pl) daughters us/to_us/ourselves take and at/in you live/reside and a people be.)
ClVg tunc dabimus et accipiemus mutuo filias vestras ac nostras: et habitabimus vobiscum, erimusque unus populus.
(then we_will_give and be_acceptedemus mutually daughters your and ours: and habitbimus with_you(pl), we_will_beque one the_people. )
34:1-31 Once Jacob and his family settled in the land, the Canaanite presence became a threat. This account is a stern warning to the Israelites about the possibility of their being defiled by the Canaanites. The nation of Israel was later commanded not to intermarry or make treaties with them, for they were a corrupt and corrupting people. This chapter implicitly warns against becoming familiar with the way they lived (34:1-2). It also taught Israel that in dealing with the Canaanites, they were to keep their integrity and not use the holy things of the covenant for deception and slaughter (34:13); Israel’s reputation was at stake in the land (34:30). For their ruthless violence, Simeon and Levi were passed over in the birthright blessing (49:5-7).
Note 1 topic: figures-of-speech / exclusive
וְנָתַ֤נּוּ אֶת־בְּנֹתֵ֨ינוּ֙ לָכֶ֔ם וְאֶת־בְּנֹתֵיכֶ֖ם נִֽקַּֽח־לָ֑נוּ
and,give DOM daughters_of,our to/for=you(pl) and=DOM daughters_of,your(pl) take to/for=us
The pronouns “we,” “our,” and us are exclusive in verses 14-17 except for the last we in verse 16. Also see how you translated “give … daughters … take … daughters …” in verse 9. Alternate translation: [Then we will let our daughters marry your young men, and our young men will marry your daughters] or [After you do that, then we will allow your young men to marry our daughters, and we will allow your daughters to marry our young men]
וְיָשַׁ֣בְנוּ אִתְּכֶ֔ם
and,live with,you(pl)
See how you translated settle with in verse 10. Alternate translation: [We will also settle among you in this land]
Note 2 topic: figures-of-speech / exclusive
וְהָיִ֖ינוּ לְעַ֥ם אֶחָֽד
and,become as,people one(ms)
Here the we is inclusive because Jacob’s sons are including Shechem and Hamor’s people. If you have an inclusive form of this pronoun in your language, you could use it here. Alternate translation: [and as a result we will all be one ethnic group]
Genesis 21-35
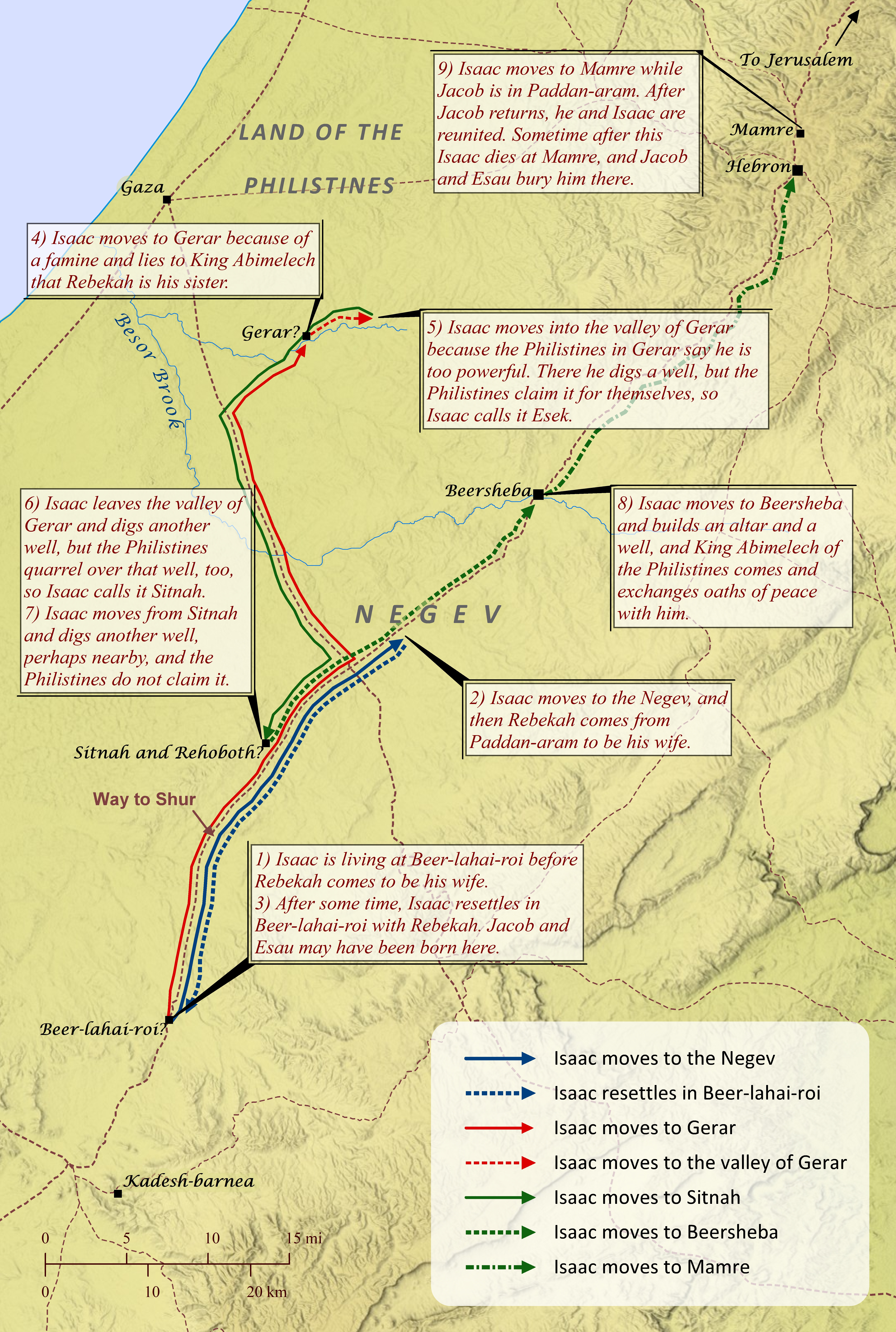
Though the patriarch Isaac moved from place to place several times within southern Canaan, compared to his father Abraham and his son Jacob, Isaac appears to have been a bit of a homebody. In fact, unless Isaac resettled in places not recorded in Scripture, the farthest extent he ever traveled appears to have been only about 90 miles (113 km). Yet, as the child of God’s promise to Abraham to build a great nation from his descendants, Isaac’s relatively simple life served as a critical bridge from Abraham to the beginnings of the twelve tribes of Israel, who were descended from Isaac’s son Jacob. It is likely that Isaac was born at Beersheba (see Genesis 21:1-24), and later Abraham offered him as a sacrifice on Mount Moriah (located at Jerusalem; see 2 Chronicles 3:1). Then Abraham, Isaac, and those with them returned to Beersheba (Genesis 22:1-19). When Isaac reached adulthood, his father sent a servant to bring back a bride for him from Aram-naharaim, far north of Canaan. When his bride, Rebekah, arrived, Isaac had just come from Beer-lahai-roi and settled in the Negev (Genesis 24:62). Later Isaac resettled with Rebekah in Beer-lahai-roi, and this may have been where their twins son Esau and Jacob were born. A famine forced Isaac to go to Gerar (Genesis 26:1-6) in “the land of the Philistines.” The distinct people group known as the Philistines in later books of the Bible did not arrive until the time of the Judges, so the term here must have referred to another people group living in this region, and this is supported by the fact that King Abimelech’s name is Semitic, not Aegean (the likely origin of the later Philistines). While Isaac was there, he repeated his father’s error (Genesis 20) by lying to the king that his wife was only his sister. Isaac also became increasingly prosperous at Gerar, so the Philistines told him to leave their region. Isaac moved away from the town of Gerar and settled further away in the valley of Gerar. There he dug a well, but the Philistines claimed it for themselves, so he called it Esek, meaning “argument.” So Isaac’s men dug another well and called it Sitnah (meaning “hostility”), but it led to more quarreling, so he dug yet another well and called it Rehoboth (meaning “open space”). The locations of these two later wells are not certain, but they may have been located near Ruheibeh as shown on this map. Then Isaac moved to Beersheba and built an altar. He also dug a well there, and King Abimelech of the Philistines came and exchanged oaths of peace with him. It was likely at Beersheba that Isaac blessed his sons Esau and Jacob, and both sons eventually left Canaan (see “Jacob Goes to Paddan-Aram” map). When Jacob later returned, he traveled to Mamre near Hebron and reunited with Isaac. Sometime after this Isaac died, and Jacob and Esau buried him there.
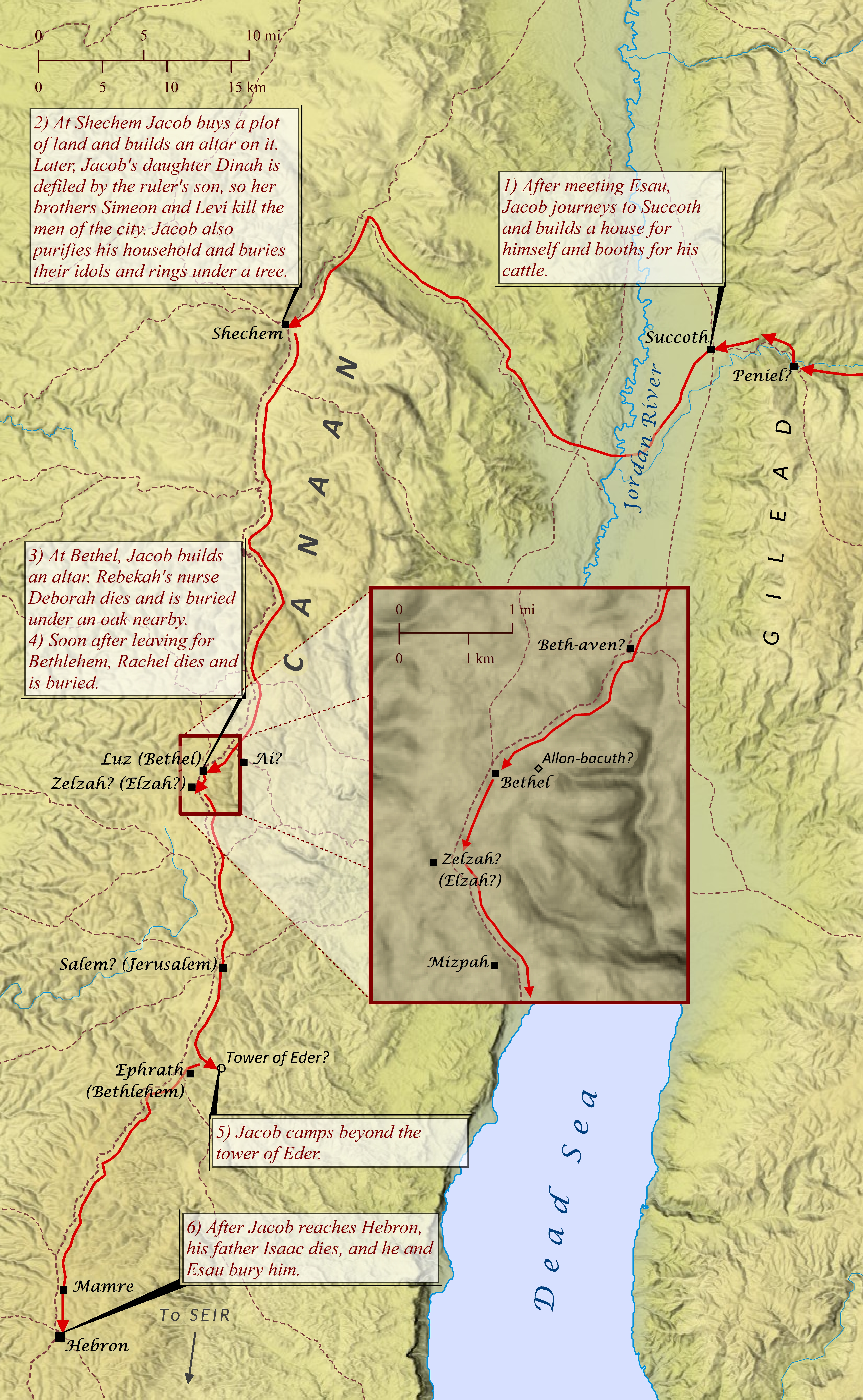
Genesis 32-36
As with many of the stories of the Bible, the events of Jacob’s life are often misunderstood by readers as disjointed pericopes arranged primarily for theological and cultural purposes. Because of this, readers often fail to see that these stories follow a clear geographical progression of the patriarch throughout the land of Canaan. This realistic and coherent geographical framework behind the stories gives strong support to the belief that these stories are authentic, historical accounts of the experiences of Jacob and his ancestors. The overall framework for virtually all of Jacob’s stories is very simple: Jacob is born and raised in southern Canaan but comes into conflict with his twin brother Esau, so he flees to Paddan-aram in Mesopotamia (Genesis 25-28; see “Jacob Goes to Paddan-Aram” map). There he builds a large family and great wealth (Genesis 29-30) and eventually returns to southern Canaan, likely retracing the exact steps he followed when he fled (Genesis 31-35; see also “Jacob Returns to Canaan” map). During this time, Esau moves to the hill country of Seir, likely just south of southern Canaan (“Edom and the Land of Seir” map), and establishes his own family there, giving rise to the nation of Edom (Genesis 36). Though the primary intent of Jacob’s return was no doubt to resettle in Canaan, comments made during his reunion with Esau near Peniel may reveal that he also intended to travel even further to Seir to visit his brother there (Genesis 33:12-14). After crossing from Mahanaim to Peniel in Gilead, Jacob reunites with Esau and settles in Succoth for a time and builds a house for himself and booths for his cattle. He eventually crosses the Jordan River and enters Canaan, stopping first at the ancient city of Shechem. There Jacob’s daughter Dinah is defiled by the son of the region’s leader, and her brothers take revenge by killing all the men of the city. Thus, Jacob is forced to leave, but first he calls upon all his household to purify themselves. He collects their idols and rings and buries them beneath a tree in Shechem. Upon reaching Bethel, Jacob builds an altar and calls it El-bethel. The nurse of Jacob’s mother Rebekah also dies at Bethel and is buried under an oak below the town, leading them to call the place Allon-bacuth (“oak of weeping”). Jacob and his family leave for Bethlehem, but very soon after they start the journey Rachel gives birth to Benjamin and then dies. Jacob buries her along the way, apparently near a place called Zelzah (or perhaps Elzah; see 1 Samuel 10 and “Saul Search for His Donkeys” map). Jacob continues on and camps beyond the tower of Eder, perhaps near Bethlehem, since that seems to have been his original destination. Finally Jacob reaches Mamre and Hebron. Soon after this Isaac dies, and Esau and Jacob bury him. The story of Jacob’s journey ends at Genesis 35, and we are not explicitly told if Jacob traveled even further to Seir. Genesis 36, however, catalogs the descendants of Esau, the Edomites, perhaps indicating that Jacob did indeed fulfill the intentions he stated in Genesis 33:12-14.